J. He
Automated segmenta-on of pediatric neuroblastoma on multi-modal MRI: Results of the SPPIN challenge at MICCAI 2023
May 01, 2025Abstract:Surgery plays an important role within the treatment for neuroblastoma, a common pediatric cancer. This requires careful planning, often via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based anatomical 3D models. However, creating these models is often time-consuming and user dependent. We organized the Surgical Planning in Pediatric Neuroblastoma (SPPIN) challenge, to stimulate developments on this topic, and set a benchmark for fully automatic segmentation of neuroblastoma on multi-model MRI. The challenge started with a training phase, where teams received 78 sets of MRI scans from 34 patients, consisting of both diagnostic and post-chemotherapy MRI scans. The final test phase, consisting of 18 MRI sets from 9 patients, determined the ranking of the teams. Ranking was based on the Dice similarity coefficient (Dice score), the 95th percentile of the Hausdorff distance (HD95) and the volumetric similarity (VS). The SPPIN challenge was hosted at MICCAI 2023. The final leaderboard consisted of 9 teams. The highest-ranking team achieved a median Dice score 0.82, a median HD95 of 7.69 mm and a VS of 0.91, utilizing a large, pretrained network called STU-Net. A significant difference for the segmentation results between diagnostic and post-chemotherapy MRI scans was observed (Dice = 0.89 vs Dice = 0.59, P = 0.01) for the highest-ranking team. SPPIN is the first medical segmentation challenge in extracranial pediatric oncology. The highest-ranking team used a large pre-trained network, suggesting that pretraining can be of use in small, heterogenous datasets. Although the results of the highest-ranking team were high for most patients, segmentation especially in small, pre-treated tumors were insufficient. Therefore, more reliable segmentation methods are needed to create clinically applicable models to aid surgical planning in pediatric neuroblastoma.
Discriminative Feature Representation with Spatio-temporal Cues for Vehicle Re-identification
Nov 13, 2020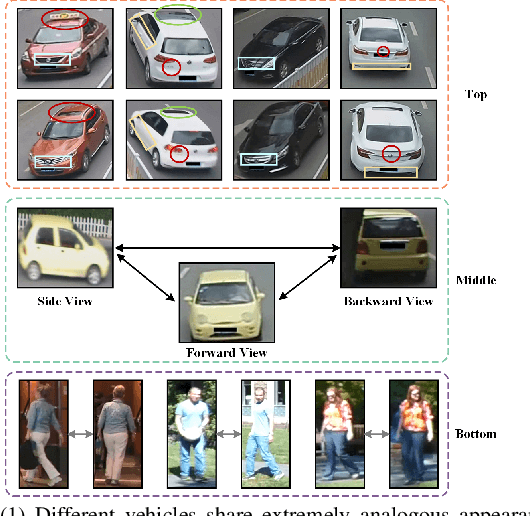
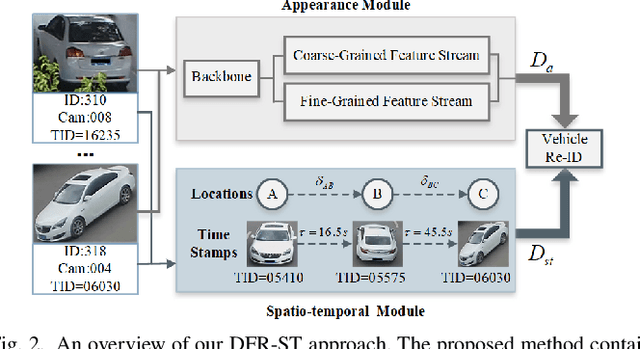
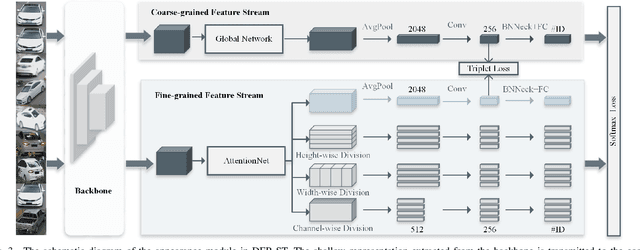
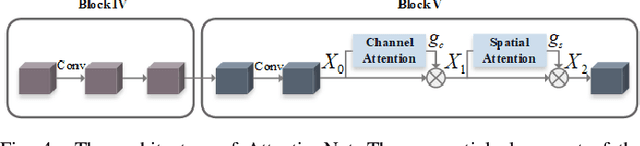
Abstract:Vehicle re-identification (re-ID) aims to discover and match the target vehicles from a gallery image set taken by different cameras on a wide range of road networks. It is crucial for lots of applications such as security surveillance and traffic management. The remarkably similar appearances of distinct vehicles and the significant changes of viewpoints and illumination conditions take grand challenges to vehicle re-ID. Conventional solutions focus on designing global visual appearances without sufficient consideration of vehicles' spatiotamporal relationships in different images. In this paper, we propose a novel discriminative feature representation with spatiotemporal clues (DFR-ST) for vehicle re-ID. It is capable of building robust features in the embedding space by involving appearance and spatio-temporal information. Based on this multi-modal information, the proposed DFR-ST constructs an appearance model for a multi-grained visual representation by a two-stream architecture and a spatio-temporal metric to provide complementary information. Experimental results on two public datasets demonstrate DFR-ST outperforms the state-of-the-art methods, which validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge