J. Cho
Prairie View A&M University
FOSSIL: Regret-minimizing weighting for robust learning under imbalance and small data
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Imbalanced and small data regimes are pervasive in domains such as rare disease imaging, genomics, and disaster response, where labeled samples are scarce and naive augmentation often introduces artifacts. Existing solutions such as oversampling, focal loss, or meta-weighting address isolated aspects of this challenge but remain fragile or complex. We introduce FOSSIL (Flexible Optimization via Sample Sensitive Importance Learning), a unified weighting framework that seamlessly integrates class imbalance correction, difficulty-aware curricula, augmentation penalties, and warmup dynamics into a single interpretable formula. Unlike prior heuristics, the proposed framework provides regret-based theoretical guarantees and achieves consistent empirical gains over ERM, curriculum, and meta-weighting baselines on synthetic and real-world datasets, while requiring no architectural changes.
Deep Neural Network for Water/Fat Separation: Supervised Training, Unsupervised Training, and No Training
Apr 16, 2020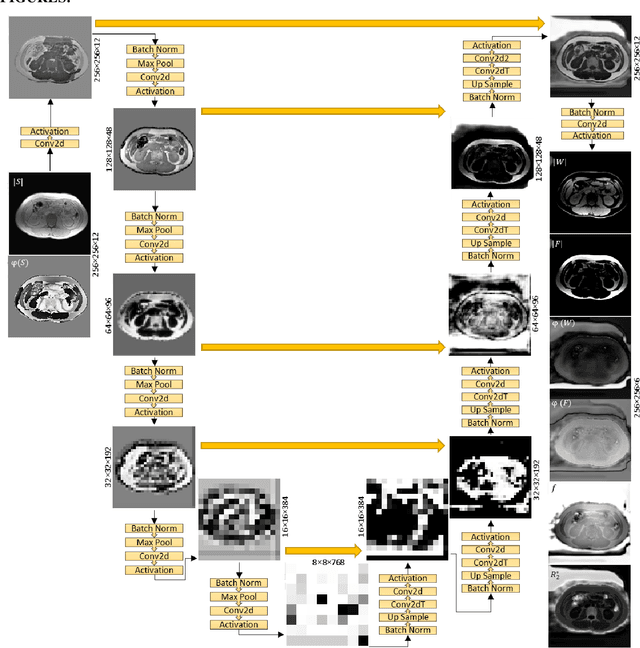
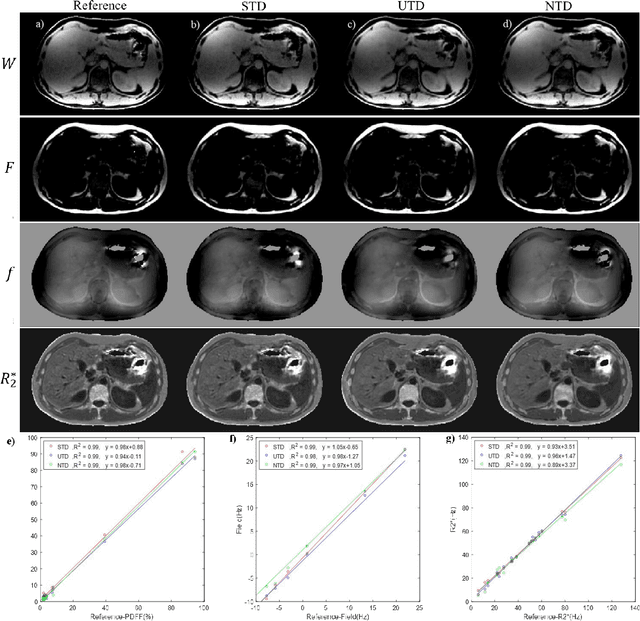
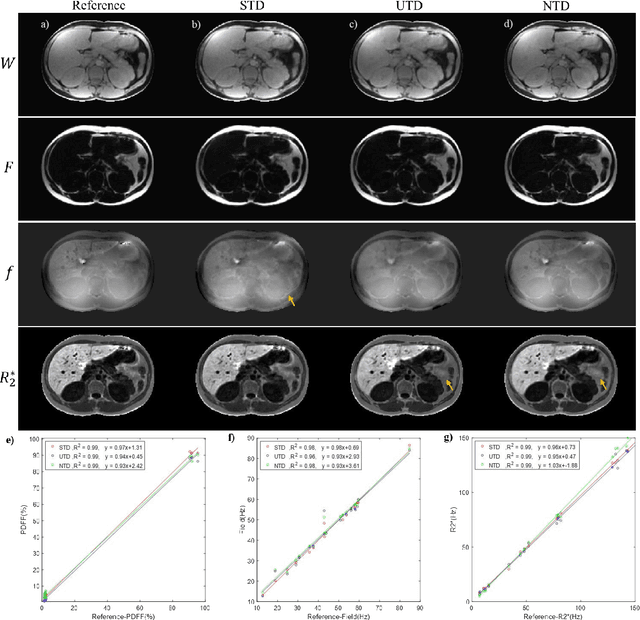
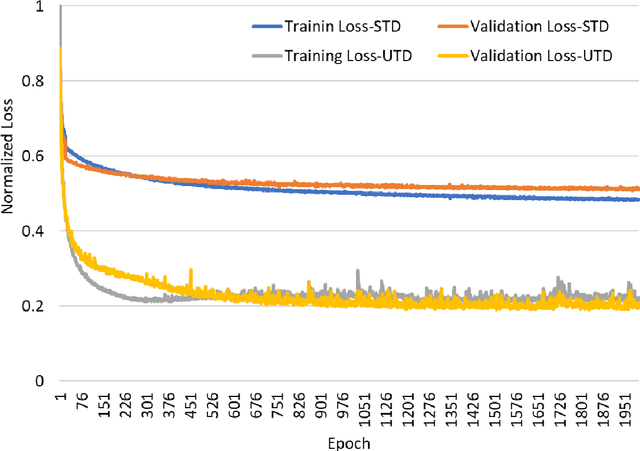
Abstract:Purpose: To use a deep neural network (DNN) for solving the optimization problem of water/fat separation and to compare supervised and unsupervised training. Methods: The current T2*-IDEAL algorithm for solving fat/water separation is dependent on initialization. Recently, deep neural networks (DNN) have been proposed to solve fat/water separation without the need for suitable initialization. However, this approach requires supervised training of DNN (STD) using the reference fat/water separation images. Here we propose two novel DNN water/fat separation methods 1) unsupervised training of DNN (UTD) using the physical forward problem as the cost function during training, and 2) no-training of DNN (NTD) using physical cost and backpropagation to directly reconstruct a single dataset. The STD, UTD and NTD methods were compared with the reference T2*-IDEAL. Results: All DNN methods generated consistent water/fat separation results that agreed well with T2*-IDEAL under proper initialization. Conclusion: The water/fat separation problem can be solved using unsupervised deep neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge