Ivan Letteri
DISIM, University of L'Aquila, Italy
A Stock Trading System for a Medium Volatile Asset using Multi Layer Perceptron
Jan 17, 2022
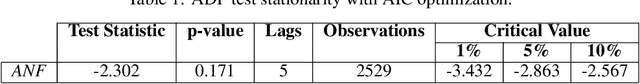
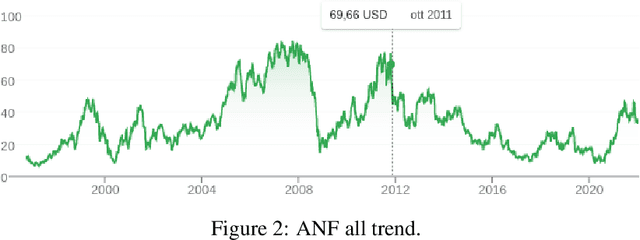
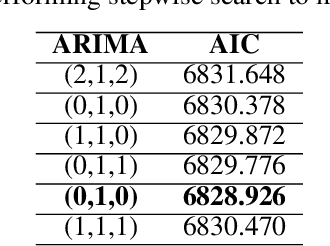
Abstract:Stock market forecasting is a lucrative field of interest with promising profits but not without its difficulties and for some people could be even causes of failure. Financial markets by their nature are complex, non-linear and chaotic, which implies that accurately predicting the prices of assets that are part of it becomes very complicated. In this paper we propose a stock trading system having as main core the feed-forward deep neural networks (DNN) to predict the price for the next 30 days of open market, of the shares issued by Abercrombie & Fitch Co. (ANF) in the stock market of the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). The system we have elaborated calculates the most effective technical indicator, applying it to the predictions computed by the DNNs, for generating trades. The results showed an increase in values such as Expectancy Ratio of 2.112% of profitable trades with Sharpe, Sortino, and Calmar Ratios of 2.194, 3.340, and 12.403 respectively. As a verification, we adopted a backtracking simulation module in our system, which maps trades to actual test data consisting of the last 30 days of open market on the ANF asset. Overall, the results were promising bringing a total profit factor of 3.2% in just one month from a very modest budget of $100. This was possible because the system reduced the number of trades by choosing the most effective and efficient trades, saving on commissions and slippage costs.
A Logic-based Multi-agent System for Ethical Monitoring and Evaluation of Dialogues
Sep 17, 2021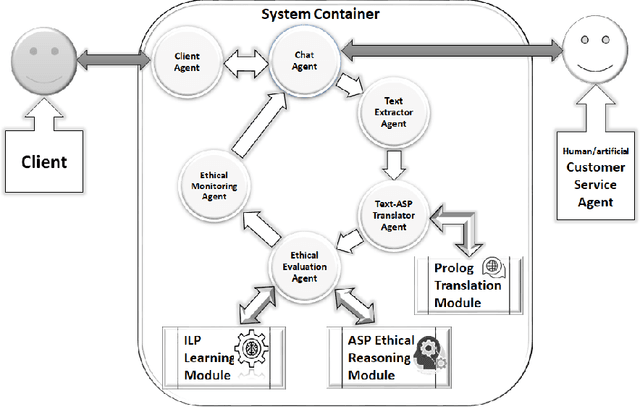
Abstract:Dialogue Systems are tools designed for various practical purposes concerning human-machine interaction. These systems should be built on ethical foundations because their behavior may heavily influence a user (think especially about children). The primary objective of this paper is to present the architecture and prototype implementation of a Multi Agent System (MAS) designed for ethical monitoring and evaluation of a dialogue system. A prototype application, for monitoring and evaluation of chatting agents' (human/artificial) ethical behavior in an online customer service chat point w.r.t their institution/company's codes of ethics and conduct, is developed and presented. Future work and open issues with this research are discussed.
* In Proceedings ICLP 2021, arXiv:2109.07914
A Novel Resampling Technique for Imbalanced Dataset Optimization
Dec 30, 2020


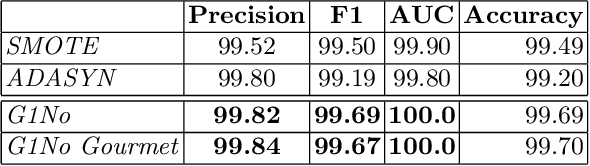
Abstract:Despite the enormous amount of data, particular events of interest can still be quite rare. Classification of rare events is a common problem in many domains, such as fraudulent transactions, malware traffic analysis and network intrusion detection. Many studies have been developed for malware detection using machine learning approaches on various datasets, but as far as we know only the MTA-KDD'19 dataset has the peculiarity of updating the representative set of malicious traffic on a daily basis. This daily updating is the added value of the dataset, but it translates into a potential due to the class imbalance problem that the RRw-Optimized MTA-KDD'19 will occur. We capture difficulties of class distribution in real datasets by considering four types of minority class examples: safe, borderline, rare and outliers. In this work, we developed two versions of Generative Silhouette Resampling 1-Nearest Neighbour (G1Nos) oversampling algorithms for dealing with class imbalance problem. The first module of G1Nos algorithms performs a coefficient-based instance selection silhouette identifying the critical threshold of Imbalance Degree. (ID), the second module generates synthetic samples using a SMOTE-like oversampling algorithm. The balancing of the classes is done by our G1Nos algorithms to re-establish the proportions between the two classes of the used dataset. The experimental results show that our oversampling algorithm work better than the other two SOTA methodologies in all the metrics considered.
Dataset Optimization Strategies for MalwareTraffic Detection
Sep 23, 2020
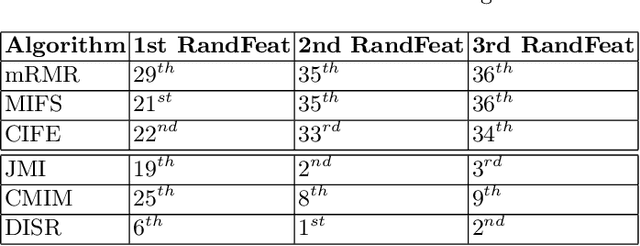
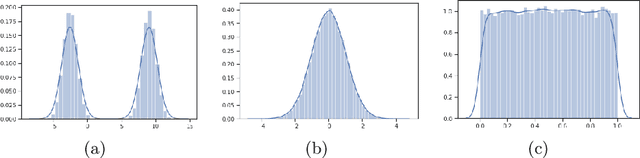
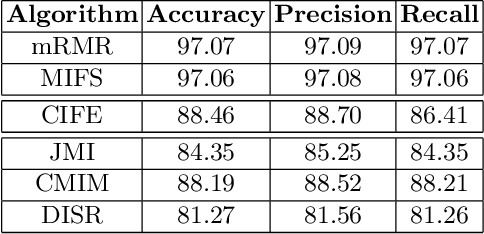
Abstract:Machine learning is rapidly becoming one of the most important technology for malware traffic detection, since the continuous evolution of malware requires a constant adaptation and the ability to generalize. However, network traffic datasets are usually oversized and contain redundant and irrelevant information, and this may dramatically increase the computational cost and decrease the accuracy of most classifiers, with the risk to introduce further noise. We propose two novel dataset optimization strategies which exploit and combine several state-of-the-art approaches in order to achieve an effective optimization of the network traffic datasets used to train malware detectors. The first approach is a feature selection technique based on mutual information measures and sensibility enhancement. The second is a dimensional reduction technique based autoencoders. Both these approaches have been experimentally applied on the MTA-KDD'19 dataset, and the optimized results evaluated and compared using a Multi Layer Perceptron as machine learning model for malware detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge