Ivan Bogatyy
SyntaxNet Models for the CoNLL 2017 Shared Task
Mar 15, 2017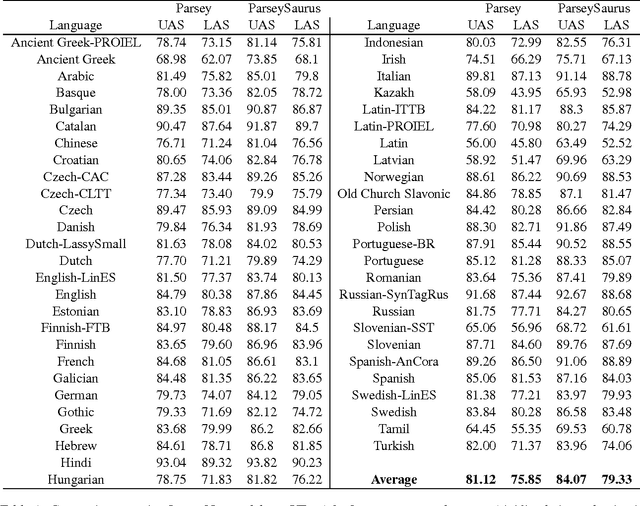
Abstract:We describe a baseline dependency parsing system for the CoNLL2017 Shared Task. This system, which we call "ParseySaurus," uses the DRAGNN framework [Kong et al, 2017] to combine transition-based recurrent parsing and tagging with character-based word representations. On the v1.3 Universal Dependencies Treebanks, the new system outpeforms the publicly available, state-of-the-art "Parsey's Cousins" models by 3.47% absolute Labeled Accuracy Score (LAS) across 52 treebanks.
DRAGNN: A Transition-based Framework for Dynamically Connected Neural Networks
Mar 13, 2017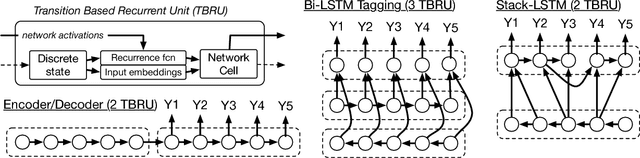
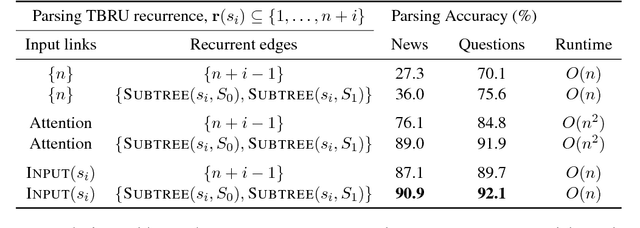
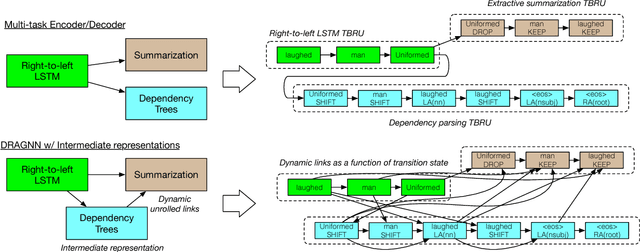

Abstract:In this work, we present a compact, modular framework for constructing novel recurrent neural architectures. Our basic module is a new generic unit, the Transition Based Recurrent Unit (TBRU). In addition to hidden layer activations, TBRUs have discrete state dynamics that allow network connections to be built dynamically as a function of intermediate activations. By connecting multiple TBRUs, we can extend and combine commonly used architectures such as sequence-to-sequence, attention mechanisms, and re-cursive tree-structured models. A TBRU can also serve as both an encoder for downstream tasks and as a decoder for its own task simultaneously, resulting in more accurate multi-task learning. We call our approach Dynamic Recurrent Acyclic Graphical Neural Networks, or DRAGNN. We show that DRAGNN is significantly more accurate and efficient than seq2seq with attention for syntactic dependency parsing and yields more accurate multi-task learning for extractive summarization tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge