Ismael Peruga Nasarre
On the Potential of Using Sub-THz Frequencies for Beyond 5G
Apr 12, 2022



Abstract:This paper studies the potential of using above 71GHz frequencies for 5G-Advanced or later in 6G. More specifically, the focus is to analyze what could be needed in terms of waveform and numerologies. The results suggest that higher baseline subcarrier spacings (SCSs) may be needed when moving above 71GHz, to fulfill the need for higher required bandwidths and phase noise robustness. The required SCS depends on carrier frequency and modulation order. It is also illustrated that single-carrier waveforms, especially Known Tail Discrete Fourier Transform Spread Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (KT-DFT-s-OFDM) waveform is a potential candidate to be used in 5G-Advanced or 6G for sub-THz frequencies due to its robustness to phase noise, lower output power back-off and flexible adaptation of head and tail lengths.
Phase Noise Resilient Three-Level Continuous-Phase Modulation for DFT-Spread OFDM
Oct 12, 2021
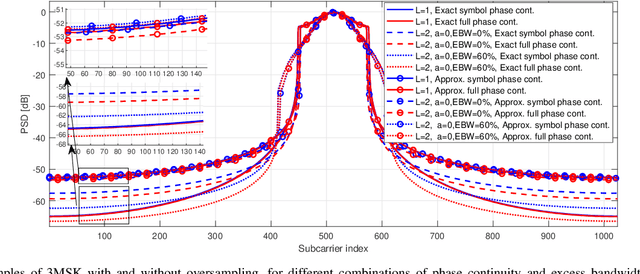
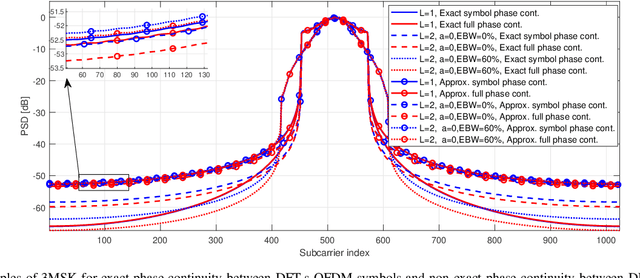

Abstract:A novel OFDM-based waveform with low peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) and high robustness against phase noise (PN) is presented. It follows the discrete Fourier transform spread orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (DFT-s-OFDM) signal model. 3MSK, is inspired by continuous-phase frequency shift keying (FSK), but it uses three frequencies in the baseband model -- specifically, 0 and $\pm f_{symbol}/4$, where $f_{symbol}$ is the symbol rate -- which effectively constrains the phase transitions between consecutive symbols to 0 and $\pm \pi/2$ rad. Motivated by the phase controlled model of modulation, different degrees of phase continuity can be achieved, while supporting receiver processing with low complexity. The signal characteristics are improved by generating an initial time-domain nearly constant envelope signal at higher than the symbol rate. This helps to reach smooth phase transitions between 3MSK symbols. Also the possibility of using excess bandwidth is investigated by transmitting additional non-zero subcarriers outside active subcarriers of the basic DFT-s-OFDM model, which provides the capability to greatly reduce the PAPR. Due to the fact that the information is encoded in the phase transitions, a receiver model that tracks the phase variations without needing reference signals is developed. To this end, it is shown that this new modulation is well-suited for non-coherent receivers, even under strong phase noise (PN) conditions, thus allowing to reduce the overhead of reference signals. Evaluations of this physical-layer modulation and waveform scheme are performed in terms of transmitter metrics such as PAPR, OOB emissions and achievable output power after the power amplifier (PA). Finally, coded radio link evaluations are also shown and provided, demonstrating that 3MSK has a similar BER performance as that of traditional QPSK.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge