Ismael Benito-Altamirano
Image color consistency in datasets: the Smooth-TPS3D method
Sep 08, 2024



Abstract:Image color consistency is the key problem in digital imaging consistency when creating datasets. Here, we propose an improved 3D Thin-Plate Splines (TPS3D) color correction method to be used, in conjunction with color charts (i.e. Macbeth ColorChecker) or other machine-readable patterns, to achieve image consistency by post-processing. Also, we benchmark our method against its former implementation and the alternative methods reported to date with an augmented dataset based on the Gehler's ColorChecker dataset. Benchmark includes how corrected images resemble the ground-truth images and how fast these implementations are. Results demonstrate that the TPS3D is the best candidate to achieve image consistency. Furthermore, our Smooth-TPS3D method shows equivalent results compared to the original method and reduced the 11-15% of ill-conditioned scenarios which the previous method failed to less than 1%. Moreover, we demonstrate that the Smooth-TPS method is 20% faster than the original method. Finally, we discuss how different methods offer different compromises between quality, correction accuracy and computational load.
Better Spanish Emotion Recognition In-the-wild: Bringing Attention to Deep Spectrum Voice Analysis
Sep 08, 2024

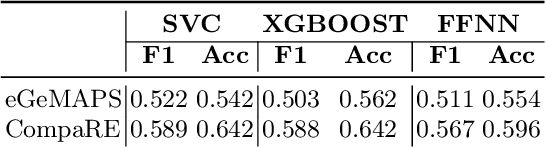

Abstract:Within the context of creating new Socially Assistive Robots, emotion recognition has become a key development factor, as it allows the robot to adapt to the user's emotional state in the wild. In this work, we focused on the analysis of two voice recording Spanish datasets: ELRA-S0329 and EmoMatchSpanishDB. Specifically, we centered our work in the paralanguage, e.~g. the vocal characteristics that go along with the message and clarifies the meaning. We proposed the use of the DeepSpectrum method, which consists of extracting a visual representation of the audio tracks and feeding them to a pretrained CNN model. For the classification task, DeepSpectrum is often paired with a Support Vector Classifier --DS-SVC--, or a Fully-Connected deep-learning classifier --DS-FC--. We compared the results of the DS-SVC and DS-FC architectures with the state-of-the-art (SOTA) for ELRA-S0329 and EmoMatchSpanishDB. Moreover, we proposed our own classifier based upon Attention Mechanisms, namely DS-AM. We trained all models against both datasets, and we found that our DS-AM model outperforms the SOTA models for the datasets and the SOTA DeepSpectrum architectures. Finally, we trained our DS-AM model in one dataset and tested it in the other, to simulate real-world conditions on how biased is the model to the dataset.
Enhancing Facial Expression Recognition through Dual-Direction Attention Mixed Feature Networks: Application to 7th ABAW Challenge
Jul 19, 2024Abstract:We present our contribution to the 7th ABAW challenge at ECCV 2024, by utilizing a Dual-Direction Attention Mixed Feature Network for multitask facial expression recognition we achieve results far beyond the proposed baseline for the Multi-Task ABAW challenge. Our proposal uses the well-known DDAMFN architecture as base to effectively predict valence-arousal, emotion recognition, and action units. We demonstrate the architecture ability to handle these tasks simultaneously, providing insights into its architecture and the rationale behind its design. Additionally, we compare our results for a multitask solution with independent single-task performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge