Ioannis E. Livieris
An evaluation framework for synthetic data generation models
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:Nowadays, the use of synthetic data has gained popularity as a cost-efficient strategy for enhancing data augmentation for improving machine learning models performance as well as addressing concerns related to sensitive data privacy. Therefore, the necessity of ensuring quality of generated synthetic data, in terms of accurate representation of real data, consists of primary importance. In this work, we present a new framework for evaluating synthetic data generation models' ability for developing high-quality synthetic data. The proposed approach is able to provide strong statistical and theoretical information about the evaluation framework and the compared models' ranking. Two use case scenarios demonstrate the applicability of the proposed framework for evaluating the ability of synthetic data generation models to generated high quality data. The implementation code can be found in https://github.com/novelcore/synthetic_data_evaluation_framework.
C-XGBoost: A tree boosting model for causal effect estimation
Mar 31, 2024Abstract:Causal effect estimation aims at estimating the Average Treatment Effect as well as the Conditional Average Treatment Effect of a treatment to an outcome from the available data. This knowledge is important in many safety-critical domains, where it often needs to be extracted from observational data. In this work, we propose a new causal inference model, named C-XGBoost, for the prediction of potential outcomes. The motivation of our approach is to exploit the superiority of tree-based models for handling tabular data together with the notable property of causal inference neural network-based models to learn representations that are useful for estimating the outcome for both the treatment and non-treatment cases. The proposed model also inherits the considerable advantages of XGBoost model such as efficiently handling features with missing values requiring minimum preprocessing effort, as well as it is equipped with regularization techniques to avoid overfitting/bias. Furthermore, we propose a new loss function for efficiently training the proposed causal inference model. The experimental analysis, which is based on the performance profiles of Dolan and Mor{\'e} as well as on post-hoc and non-parametric statistical tests, provide strong evidence about the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Explainable Image Similarity: Integrating Siamese Networks and Grad-CAM
Oct 14, 2023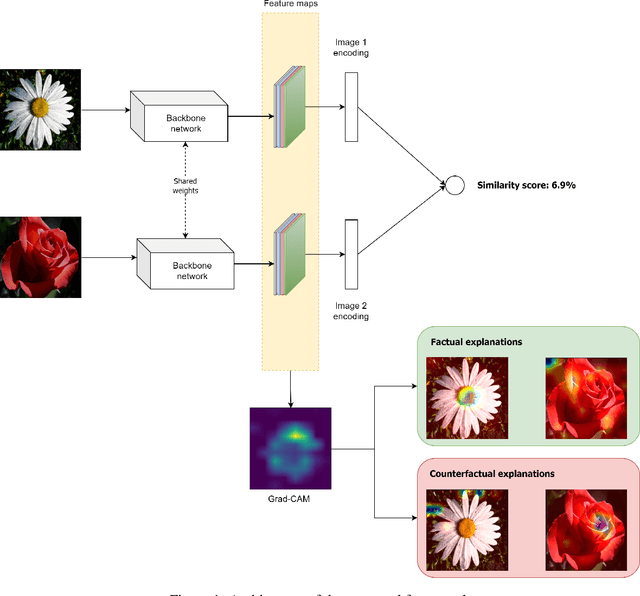
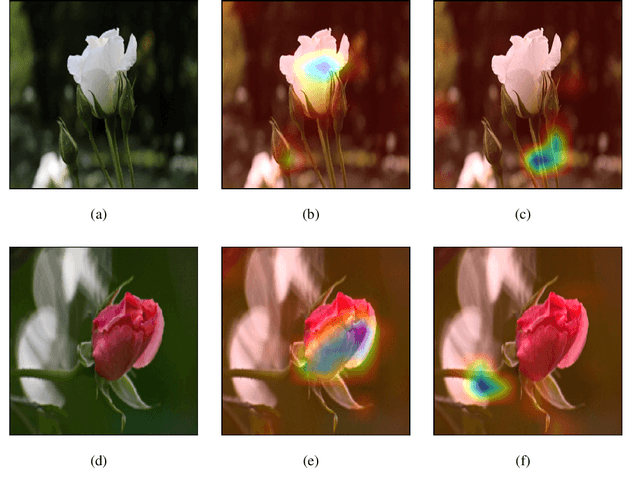

Abstract:With the proliferation of image-based applications in various domains, the need for accurate and interpretable image similarity measures has become increasingly critical. Existing image similarity models often lack transparency, making it challenging to understand the reasons why two images are considered similar. In this paper, we propose the concept of explainable image similarity, where the goal is the development of an approach, which is capable of providing similarity scores along with visual factual and counterfactual explanations. Along this line, we present a new framework, which integrates Siamese Networks and Grad-CAM for providing explainable image similarity and discuss the potential benefits and challenges of adopting this approach. In addition, we provide a comprehensive discussion about factual and counterfactual explanations provided by the proposed framework for assisting decision making. The proposed approach has the potential to enhance the interpretability, trustworthiness and user acceptance of image-based systems in real-world image similarity applications. The implementation code can be found in https://github.com/ioannislivieris/Grad_CAM_Siamese.git.
* The manuscript has been accepted for publication in "Journal of Imaging"
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge