Inbal Yahav
HeBERT & HebEMO: a Hebrew BERT Model and a Tool for Polarity Analysis and Emotion Recognition
Feb 25, 2021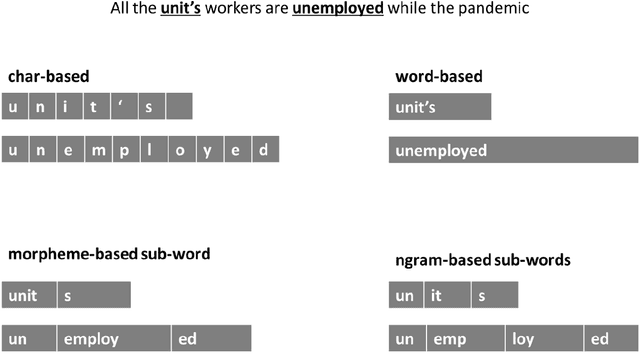
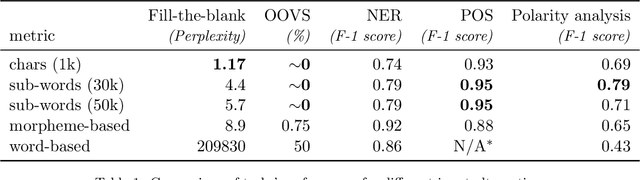
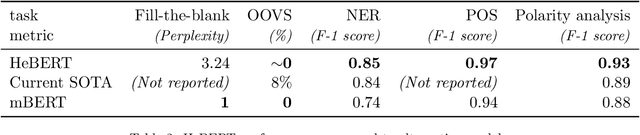
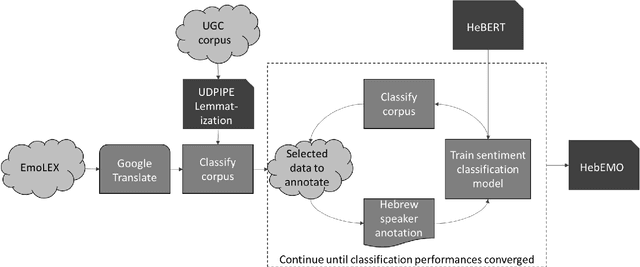
Abstract:This paper introduces HeBERT and HebEMO. HeBERT is a Transformer-based model for modern Hebrew text, which relies on a BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations for Transformers) architecture. BERT has been shown to outperform alternative architectures in sentiment analysis, and is suggested to be particularly appropriate for MRLs. Analyzing multiple BERT specifications, we find that while model complexity correlates with high performance on language tasks that aim to understand terms in a sentence, a more-parsimonious model better captures the sentiment of entire sentence. Either way, out BERT-based language model outperforms all existing Hebrew alternatives on all common language tasks. HebEMO is a tool that uses HeBERT to detect polarity and extract emotions from Hebrew UGC. HebEMO is trained on a unique Covid-19-related UGC dataset that we collected and annotated for this study. Data collection and annotation followed an active learning procedure that aimed to maximize predictability. We show that HebEMO yields a high F1-score of 0.96 for polarity classification. Emotion detection reaches F1-scores of 0.78-0.97 for various target emotions, with the exception of surprise, which the model failed to capture (F1 = 0.41). These results are better than the best-reported performance, even among English-language models of emotion detection.
Whom to Test? Active Sampling Strategies for Managing COVID-19
Dec 25, 2020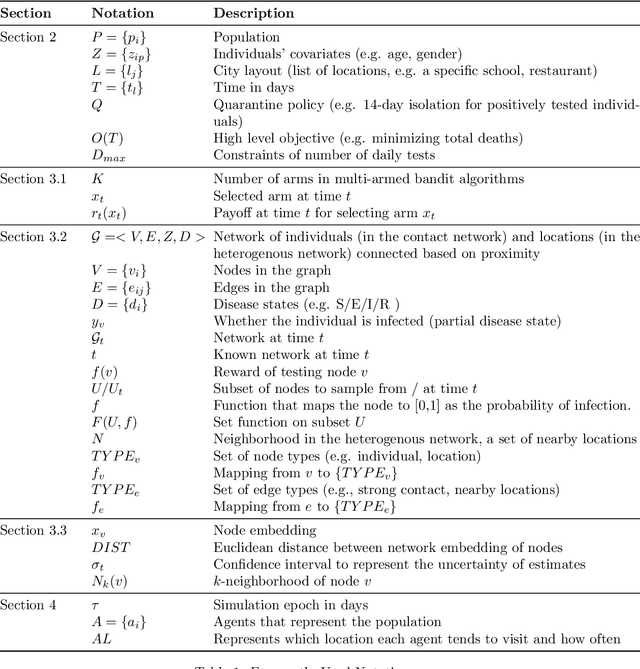
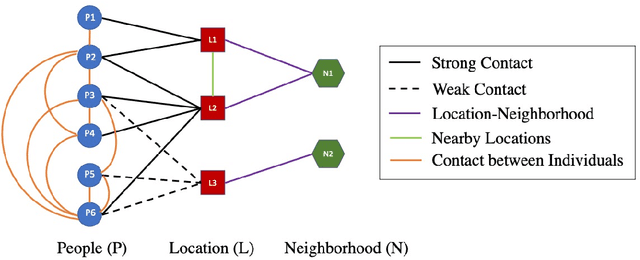

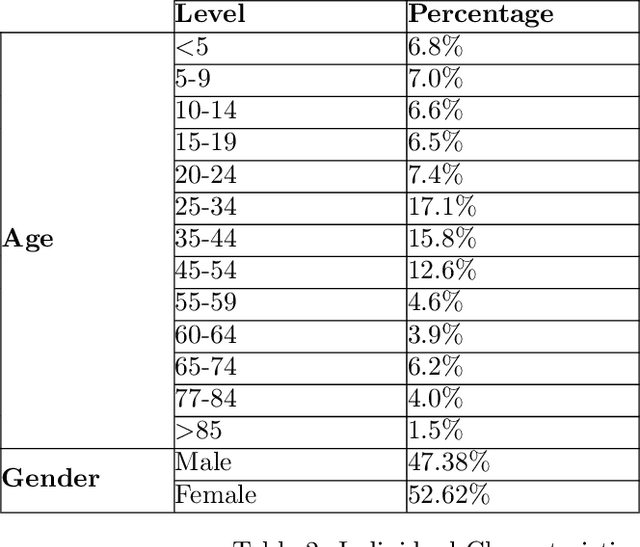
Abstract:This paper presents methods to choose individuals to test for infection during a pandemic such as COVID-19, characterized by high contagion and presence of asymptomatic carriers. The smart-testing ideas presented here are motivated by active learning and multi-armed bandit techniques in machine learning. Our active sampling method works in conjunction with quarantine policies, can handle different objectives, is dynamic and adaptive in the sense that it continually adapts to changes in real-time data. The bandit algorithm uses contact tracing, location-based sampling and random sampling in order to select specific individuals to test. Using a data-driven agent-based model simulating New York City we show that the algorithm samples individuals to test in a manner that rapidly traces infected individuals. Experiments also suggest that smart-testing can significantly reduce the death rates as compared to current methods such as testing symptomatic individuals with or without contact tracing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge