Ilias Dimitriadis
FAIRTOPIA: Envisioning Multi-Agent Guardianship for Disrupting Unfair AI Pipelines
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:AI models have become active decision makers, often acting without human supervision. The rapid advancement of AI technology has already caused harmful incidents that have hurt individuals and societies and AI unfairness in heavily criticized. It is urgent to disrupt AI pipelines which largely neglect human principles and focus on computational biases exploration at the data (pre), model(in), and deployment (post) processing stages. We claim that by exploiting the advances of agents technology, we will introduce cautious, prompt, and ongoing fairness watch schemes, under realistic, systematic, and human-centric fairness expectations. We envision agents as fairness guardians, since agents learn from their environment, adapt to new information, and solve complex problems by interacting with external tools and other systems. To set the proper fairness guardrails in the overall AI pipeline, we introduce a fairness-by-design approach which embeds multi-role agents in an end-to-end (human to AI) synergetic scheme. Our position is that we may design adaptive and realistic AI fairness frameworks, and we introduce a generalized algorithm which can be customized to the requirements and goals of each AI decision making scenario. Our proposed, so called FAIRTOPIA framework, is structured over a three-layered architecture, which encapsulates the AI pipeline inside an agentic guardian and a knowledge-based, self-refining layered scheme. Based on our proposition, we enact fairness watch in all of the AI pipeline stages, under robust multi-agent workflows, which will inspire new fairness research hypothesis, heuristics, and methods grounded in human-centric, systematic, interdisciplinary, socio-technical principles.
AgoraSpeech: A multi-annotated comprehensive dataset of political discourse through the lens of humans and AI
Jan 09, 2025Abstract:Political discourse datasets are important for gaining political insights, analyzing communication strategies or social science phenomena. Although numerous political discourse corpora exist, comprehensive, high-quality, annotated datasets are scarce. This is largely due to the substantial manual effort, multidisciplinarity, and expertise required for the nuanced annotation of rhetorical strategies and ideological contexts. In this paper, we present AgoraSpeech, a meticulously curated, high-quality dataset of 171 political speeches from six parties during the Greek national elections in 2023. The dataset includes annotations (per paragraph) for six natural language processing (NLP) tasks: text classification, topic identification, sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, polarization and populism detection. A two-step annotation was employed, starting with ChatGPT-generated annotations and followed by exhaustive human-in-the-loop validation. The dataset was initially used in a case study to provide insights during the pre-election period. However, it has general applicability by serving as a rich source of information for political and social scientists, journalists, or data scientists, while it can be used for benchmarking and fine-tuning NLP and large language models (LLMs).
Towards Hybrid Intelligence in Journalism: Findings and Lessons Learnt from a Collaborative Analysis of Greek Political Rhetoric by ChatGPT and Humans
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:This chapter introduces a research project titled "Analyzing the Political Discourse: A Collaboration Between Humans and Artificial Intelligence", which was initiated in preparation for Greece's 2023 general elections. The project focused on the analysis of political leaders' campaign speeches, employing Artificial Intelligence (AI), in conjunction with an interdisciplinary team comprising journalists, a political scientist, and data scientists. The chapter delves into various aspects of political discourse analysis, including sentiment analysis, polarization, populism, topic detection, and Named Entities Recognition (NER). This experimental study investigates the capabilities of large language model (LLMs), and in particular OpenAI's ChatGPT, for analyzing political speech, evaluates its strengths and weaknesses, and highlights the essential role of human oversight in using AI in journalism projects and potentially other societal sectors. The project stands as an innovative example of human-AI collaboration (known also as "hybrid intelligence") within the realm of digital humanities, offering valuable insights for future initiatives.
My tweets bring all the traits to the yard: Predicting personality and relational traits in Online Social Networks
Sep 22, 2020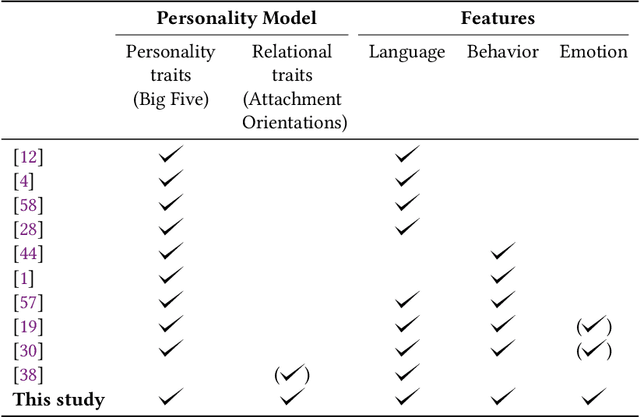
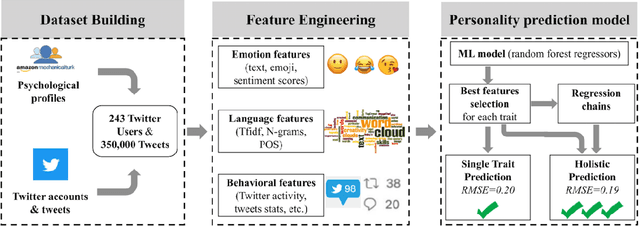
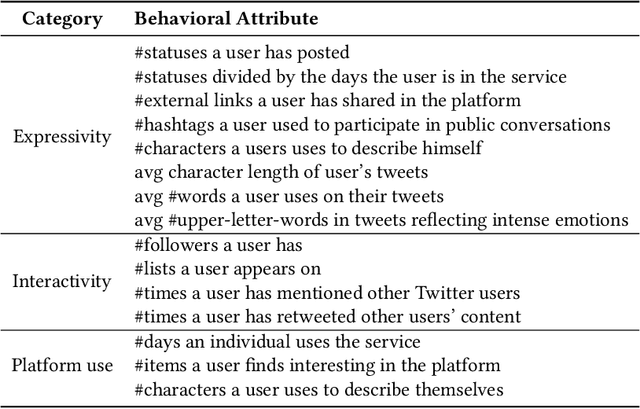

Abstract:Users in Online Social Networks (OSN) leaves traces that reflect their personality characteristics. The study of these traces is important for a number of fields, such as a social science, psychology, OSN, marketing, and others. Despite a marked increase on research in personality prediction on based on online behavior the focus has been heavily on individual personality traits largely neglecting relational facets of personality. This study aims to address this gap by providing a prediction model for a holistic personality profiling in OSNs that included socio-relational traits (attachment orientations) in combination with standard personality traits. Specifically, we first designed a feature engineering methodology that extracts a wide range of features (accounting for behavior, language, and emotions) from OSN accounts of users. Then, we designed a machine learning model that predicts scores for the psychological traits of the users based on the extracted features. The proposed model architecture is inspired by characteristics embedded in psychological theory, i.e, utilizing interrelations among personality facets, and leads to increased accuracy in comparison with the state of the art approaches. To demonstrate the usefulness of this approach, we applied our model to two datasets, one of random OSN users and one of organizational leaders, and compared their psychological profiles. Our findings demonstrate that the two groups can be clearly separated by only using their psychological profiles, which opens a promising direction for future research on OSN user characterization and classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge