Iker De la Iglesia
Medical Argument Mining: Exploitation of Scarce Data Using NLI Systems
Jun 15, 2025
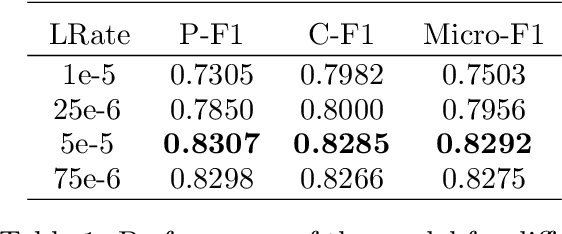
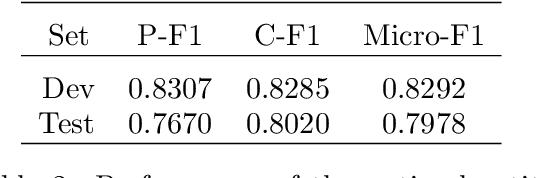
Abstract:This work presents an Argument Mining process that extracts argumentative entities from clinical texts and identifies their relationships using token classification and Natural Language Inference techniques. Compared to straightforward methods like text classification, this methodology demonstrates superior performance in data-scarce settings. By assessing the effectiveness of these methods in identifying argumentative structures that support or refute possible diagnoses, this research lays the groundwork for future tools that can provide evidence-based justifications for machine-generated clinical conclusions.
ArgHiTZ at ArchEHR-QA 2025: A Two-Step Divide and Conquer Approach to Patient Question Answering for Top Factuality
Jun 15, 2025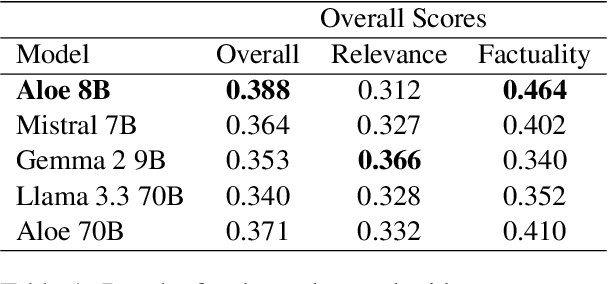
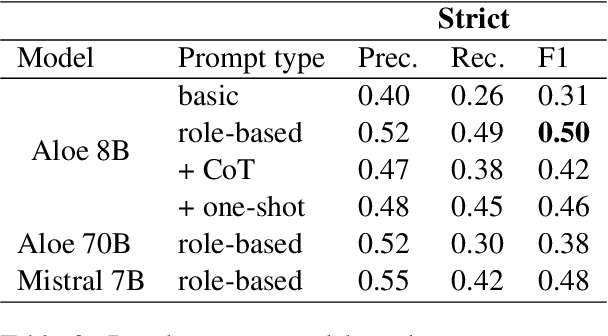
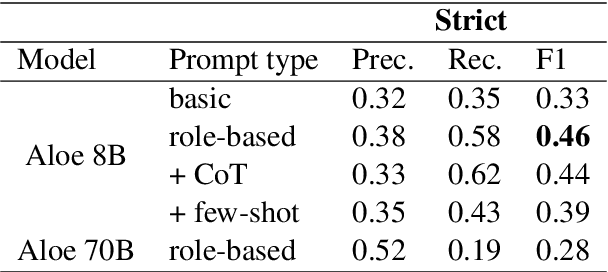
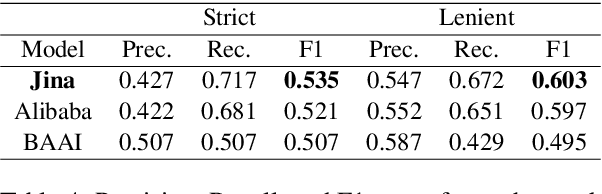
Abstract:This work presents three different approaches to address the ArchEHR-QA 2025 Shared Task on automated patient question answering. We introduce an end-to-end prompt-based baseline and two two-step methods to divide the task, without utilizing any external knowledge. Both two step approaches first extract essential sentences from the clinical text, by prompt or similarity ranking, and then generate the final answer from these notes. Results indicate that the re-ranker based two-step system performs best, highlighting the importance of selecting the right approach for each subtask. Our best run achieved an overall score of 0.44, ranking 8th out of 30 on the leaderboard, securing the top position in overall factuality.
Ranking Over Scoring: Towards Reliable and Robust Automated Evaluation of LLM-Generated Medical Explanatory Arguments
Sep 30, 2024Abstract:Evaluating LLM-generated text has become a key challenge, especially in domain-specific contexts like the medical field. This work introduces a novel evaluation methodology for LLM-generated medical explanatory arguments, relying on Proxy Tasks and rankings to closely align results with human evaluation criteria, overcoming the biases typically seen in LLMs used as judges. We demonstrate that the proposed evaluators are robust against adversarial attacks, including the assessment of non-argumentative text. Additionally, the human-crafted arguments needed to train the evaluators are minimized to just one example per Proxy Task. By examining multiple LLM-generated arguments, we establish a methodology for determining whether a Proxy Task is suitable for evaluating LLM-generated medical explanatory arguments, requiring only five examples and two human experts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge