Igor Garcia Ballhausen Sampaio
Combining Two Adversarial Attacks Against Person Re-Identification Systems
Sep 24, 2023
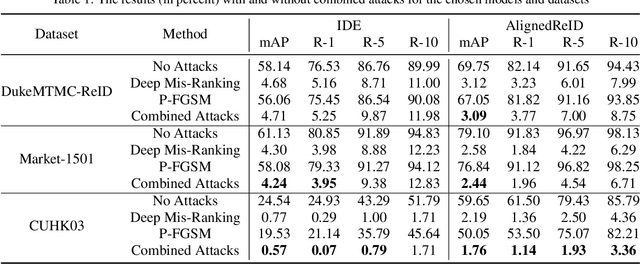


Abstract:The field of Person Re-Identification (Re-ID) has received much attention recently, driven by the progress of deep neural networks, especially for image classification. The problem of Re-ID consists in identifying individuals through images captured by surveillance cameras in different scenarios. Governments and companies are investing a lot of time and money in Re-ID systems for use in public safety and identifying missing persons. However, several challenges remain for successfully implementing Re-ID, such as occlusions and light reflections in people's images. In this work, we focus on adversarial attacks on Re-ID systems, which can be a critical threat to the performance of these systems. In particular, we explore the combination of adversarial attacks against Re-ID models, trying to strengthen the decrease in the classification results. We conduct our experiments on three datasets: DukeMTMC-ReID, Market-1501, and CUHK03. We combine the use of two types of adversarial attacks, P-FGSM and Deep Mis-Ranking, applied to two popular Re-ID models: IDE (ResNet-50) and AlignedReID. The best result demonstrates a decrease of 3.36% in the Rank-10 metric for AlignedReID applied to CUHK03. We also try to use Dropout during the inference as a defense method.
A novel method for object detection using deep learning and CAD models
Feb 12, 2021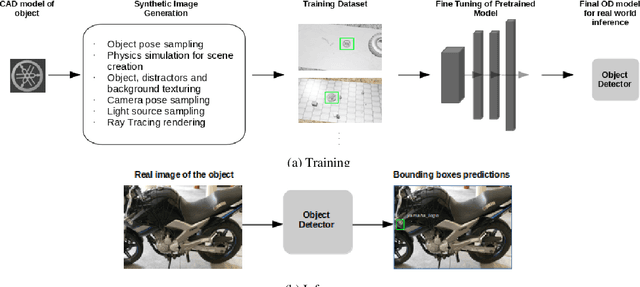
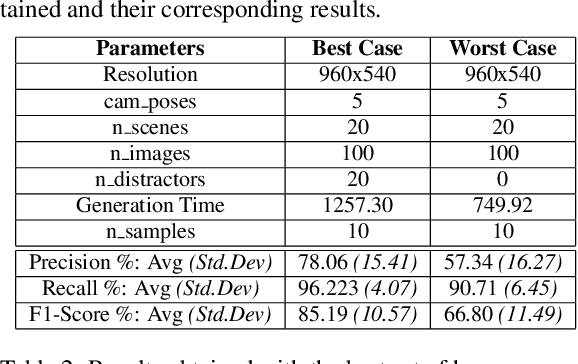
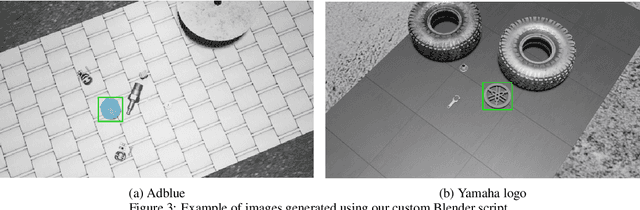
Abstract:Object Detection (OD) is an important computer vision problem for industry, which can be used for quality control in the production lines, among other applications. Recently, Deep Learning (DL) methods have enabled practitioners to train OD models performing well on complex real world images. However, the adoption of these models in industry is still limited by the difficulty and the significant cost of collecting high quality training datasets. On the other hand, when applying OD to the context of production lines, CAD models of the objects to be detected are often available. In this paper, we introduce a fully automated method that uses a CAD model of an object and returns a fully trained OD model for detecting this object. To do this, we created a Blender script that generates realistic labeled datasets of images containing the object, which are then used for training the OD model. The method is validated experimentally on two practical examples, showing that this approach can generate OD models performing well on real images, while being trained only on synthetic images. The proposed method has potential to facilitate the adoption of object detection models in industry as it is easy to adapt for new objects and highly flexible. Hence, it can result in significant costs reduction, gains in productivity and improved products quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge