Hyewon Kim
Inscanner: Dual-Phase Detection and Classification of Auxiliary Insulation Using YOLOv8 Models
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:This study proposes a two-phase methodology for detecting and classifying auxiliary insulation in structural components. In the detection phase, a YOLOv8x model is trained on a dataset of complete structural blueprints, each annotated with bounding boxes indicating areas that should contain insulation. In the classification phase, these detected insulation patches are cropped and categorized into two classes: present or missing. These are then used to train a YOLOv8x-CLS model that determines the presence or absence of auxiliary insulation. Preprocessing steps for both datasets included annotation, augmentation, and appropriate cropping of the insulation regions. The detection model achieved a mean average precision (mAP) score of 82%, while the classification model attained an accuracy of 98%. These findings demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in automating insulation detection and classification, providing a foundation for further advancements in this domain.
Applications of Machine Learning in Pharmacogenomics: Clustering Plasma Concentration-Time Curves
Oct 24, 2022Abstract:Pharmaceutical researchers are continually searching for techniques to improve both drug development processes and patient outcomes. An area of recent interest is the potential for machine learning applications within pharmacology. One such application not yet given close study is the unsupervised clustering of plasma concentration-time curves, hereafter, pharmacokinetic (PK) curves. This can be done by treating a PK curve as a time series object and subsequently utilizing the extensive body of research related to the clustering of time series data objects. In this paper, we introduce hierarchical clustering within the context of clustering PK curves and find it to be effective at identifying similar-shaped PK curves and informative for understanding patterns of PK curves via its dendrogram data visualization. We also examine many dissimilarity measures between time series objects to identify Euclidean distance as generally most appropriate for clustering PK curves. We further show that dynamic time warping, Fr\'echet, and structure-based measures of dissimilarity like correlation may produce unexpected results. Finally, we apply these methods to a dataset of 250 PK curves as an illustrative case study to demonstrate how the clustering of PK curves can be used as a descriptive tool for summarizing and visualizing complex PK data, which may enhance the study of pharmacogenomics in the context of precision medicine.
CareCall: a Call-Based Active Monitoring Dialog Agent for Managing COVID-19 Pandemic
Jul 06, 2020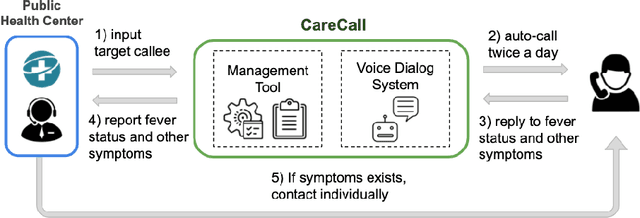
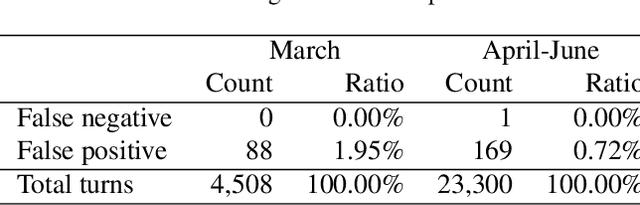
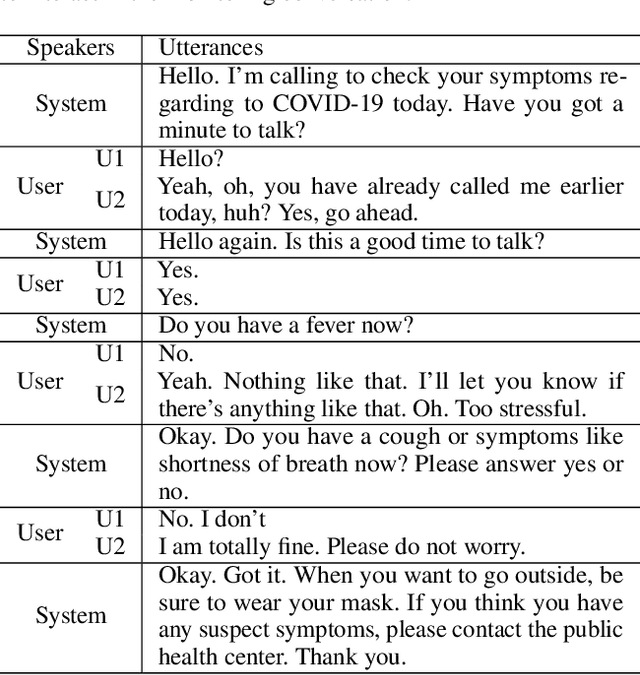
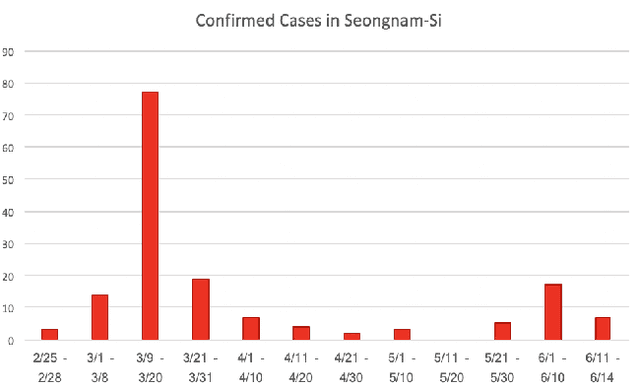
Abstract:Tracking suspected cases of COVID-19 is crucial to suppressing the spread of COVID-19 pandemic. Active monitoring and proactive inspection are indispensable to mitigate COVID-19 spread, though these require considerable social and economic expense. To address this issue, we introduce CareCall, a call-based dialog agent which is deployed for active monitoring in Korea and Japan. We describe our system with a case study with statistics to show how the system works. Finally, we discuss a simple idea which uses CareCall to support proactive inspection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge