Hrvoje Leventić
Evaluation Framework for Computer Vision-Based Guidance of the Visually Impaired
Sep 20, 2022
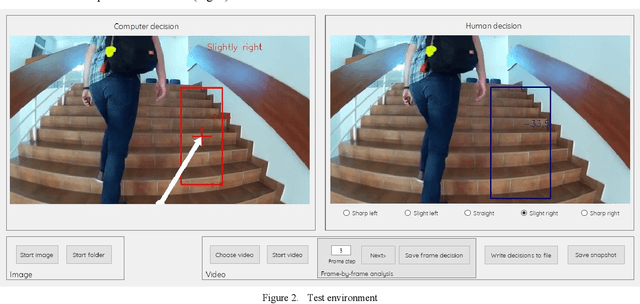
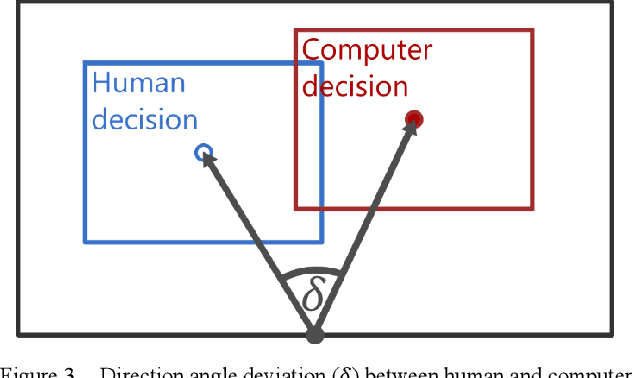
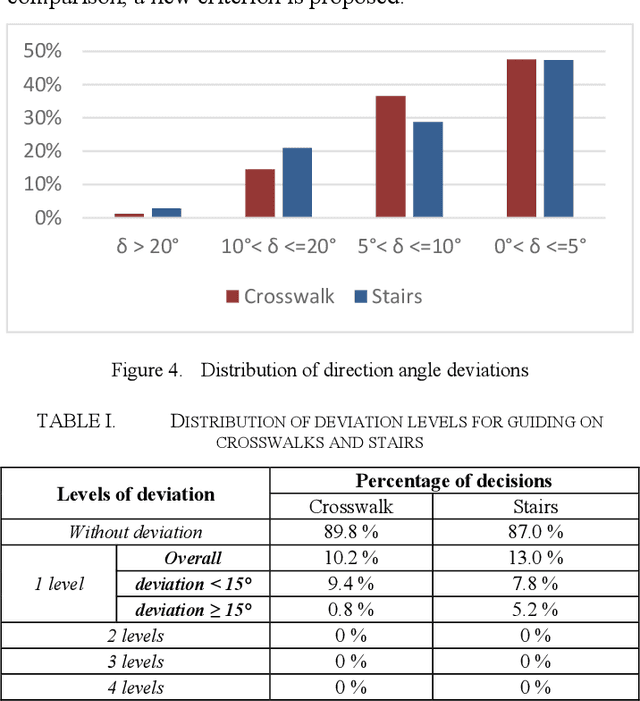
Abstract:Visually impaired persons have significant problems in their everyday movement. Therefore, some of our previous work involves computer vision in developing assistance systems for guiding the visually impaired in critical situations. Some of those situations includes crosswalks on road crossings and stairs in indoor and outdoor environment. This paper presents an evaluation framework for computer vision-based guiding of the visually impaired persons in such critical situations. Presented framework includes the interface for labeling and storing referent human decisions for guiding directions and compares them to computer vision-based decisions. Since strict evaluation methodology in this research field is not clearly defined and due to the specifics of the transfer of information to visually impaired persons, evaluation criterion for specific simplified guiding instructions is proposed.
A Survey of Left Atrial Appendage Segmentation and Analysis in 3D and 4D Medical Images
May 13, 2022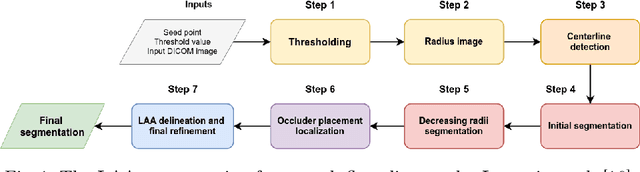
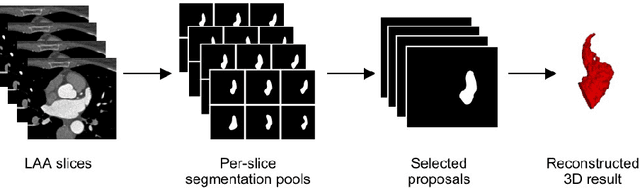
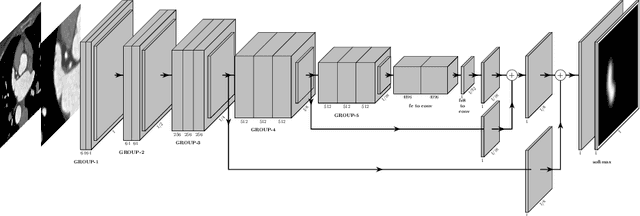
Abstract:Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a cardiovascular disease identified as one of the main risk factors for stroke. The majority of strokes due to AF are caused by clots originating in the left atrial appendage (LAA). LAA occlusion is an effective procedure for reducing stroke risk. Planning the procedure using pre-procedural imaging and analysis has shown benefits. The analysis is commonly done by manually segmenting the appendage on 2D slices. Automatic LAA segmentation methods could save an expert's time and provide insightful 3D visualizations and accurate automatic measurements to aid in medical procedures. Several semi- and fully-automatic methods for segmenting the appendage have been proposed. This paper provides a review of automatic LAA segmentation methods on 3D and 4D medical images, including CT, MRI, and echocardiogram images. We classify methods into heuristic and model-based methods, as well as into semi- and fully-automatic methods. We summarize and compare the proposed methods, evaluate their effectiveness, and present current challenges in the field and approaches to overcome them.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge