Hongfa Xue
Twin-Finder: Integrated Reasoning Engine for Pointer-related Code Clone Detection
Nov 05, 2019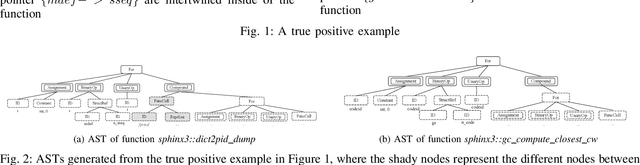

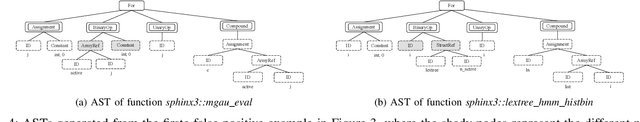
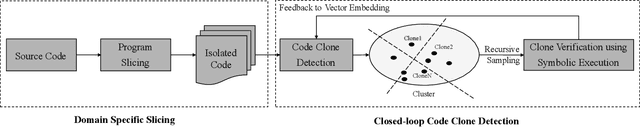
Abstract:Detecting code clones is crucial in various software engineering tasks. In particular, code clone detection can have significant uses in the context of analyzing and fixing bugs in large scale applications. However, prior works, such as machine learning based clone detection, may cause a considerable amount of false positives. In this paper, we propose Twin-Finder, a novel, closed-loop approach for pointer-related code clone detection that integrates machine learning and symbolic execution techniques to achieve precision. Twin-Finder introduces a clone verification mechanism to formally verify if two clone samples are indeed clones and a feedback loop to automatically generated formal rules to tune machine learning algorithm and further reduce the false positives. Our experimental results show Twin-Finder that can swiftly identify up 9X more code clones comparing to conventional code clone detection approaches. We conduct security analysis for memory safety using real-world applications Links version 2.14 and libreOffice-6.0.0.1. Twin-Finder is able to find 6 unreported bugs in Links version 2.14 and one public patched bug in libreOffice-6.0.0.1.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge