Hiroshi Yamashita
Spatial-photonic Boltzmann machines: low-rank combinatorial optimization and statistical learning by spatial light modulation
Mar 27, 2023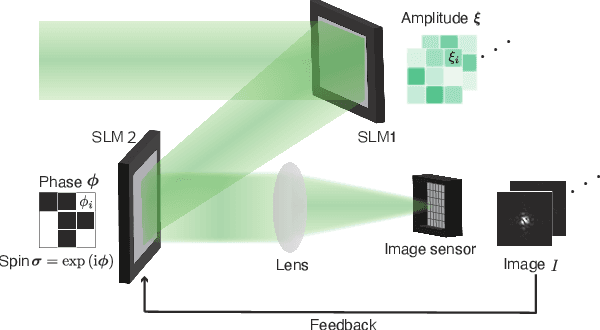
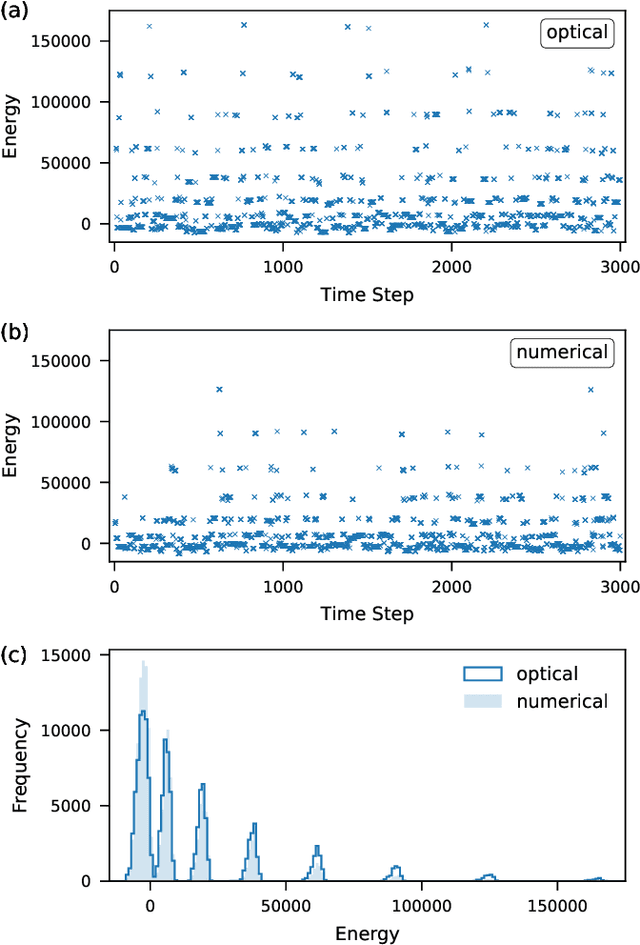
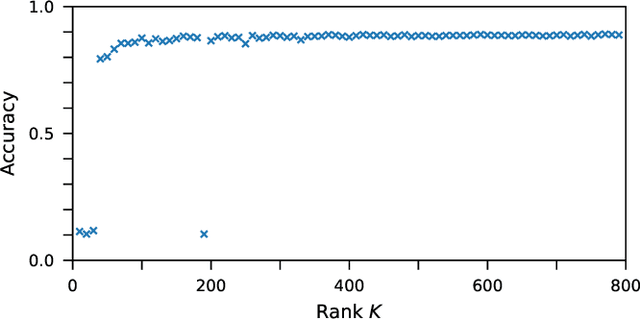

Abstract:The spatial-photonic Ising machine (SPIM) [D. Pierangeli et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 213902 (2019)] is a promising optical architecture utilizing spatial light modulation for solving large-scale combinatorial optimization problems efficiently. However, the SPIM can accommodate Ising problems with only rank-one interaction matrices, which limits its applicability to various real-world problems. In this Letter, we propose a new computing model for the SPIM that can accommodate any Ising problem without changing its optical implementation. The proposed model is particularly efficient for Ising problems with low-rank interaction matrices, such as knapsack problems. Moreover, the model acquires learning ability and can thus be termed a spatial-photonic Boltzmann machine (SPBM). We demonstrate that learning, classification, and sampling of the MNIST handwritten digit images are achieved efficiently using SPBMs with low-rank interactions. Thus, the proposed SPBM model exhibits higher practical applicability to various problems of combinatorial optimization and statistical learning, without losing the scalability inherent in the SPIM architecture.
Entropic Herding
Dec 22, 2021



Abstract:Herding is a deterministic algorithm used to generate data points that can be regarded as random samples satisfying input moment conditions. The algorithm is based on the complex behavior of a high-dimensional dynamical system and is inspired by the maximum entropy principle of statistical inference. In this paper, we propose an extension of the herding algorithm, called entropic herding, which generates a sequence of distributions instead of points. Entropic herding is derived as the optimization of the target function obtained from the maximum entropy principle. Using the proposed entropic herding algorithm as a framework, we discuss a closer connection between herding and the maximum entropy principle. Specifically, we interpret the original herding algorithm as a tractable version of entropic herding, the ideal output distribution of which is mathematically represented. We further discuss how the complex behavior of the herding algorithm contributes to optimization. We argue that the proposed entropic herding algorithm extends the application of herding to probabilistic modeling. In contrast to original herding, entropic herding can generate a smooth distribution such that both efficient probability density calculation and sample generation become possible. To demonstrate the viability of these arguments in this study, numerical experiments were conducted, including a comparison with other conventional methods, on both synthetic and real data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge