Hiroki Azuma
ZoDi: Zero-Shot Domain Adaptation with Diffusion-Based Image Transfer
Mar 20, 2024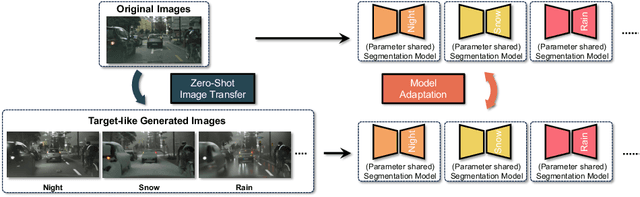
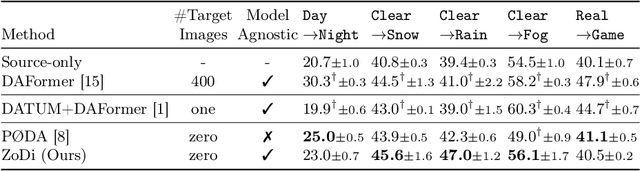
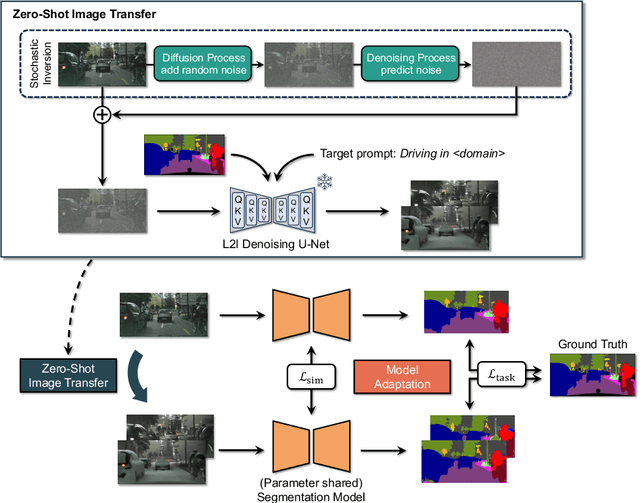
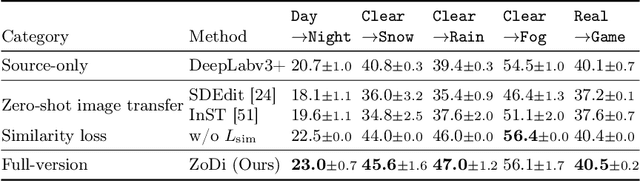
Abstract:Deep learning models achieve high accuracy in segmentation tasks among others, yet domain shift often degrades the models' performance, which can be critical in real-world scenarios where no target images are available. This paper proposes a zero-shot domain adaptation method based on diffusion models, called ZoDi, which is two-fold by the design: zero-shot image transfer and model adaptation. First, we utilize an off-the-shelf diffusion model to synthesize target-like images by transferring the domain of source images to the target domain. In this we specifically try to maintain the layout and content by utilising layout-to-image diffusion models with stochastic inversion. Secondly, we train the model using both source images and synthesized images with the original segmentation maps while maximizing the feature similarity of images from the two domains to learn domain-robust representations. Through experiments we show benefits of ZoDi in the task of image segmentation over state-of-the-art methods. It is also more applicable than existing CLIP-based methods because it assumes no specific backbone or models, and it enables to estimate the model's performance without target images by inspecting generated images. Our implementation will be publicly available.
Defense-Prefix for Preventing Typographic Attacks on CLIP
Apr 10, 2023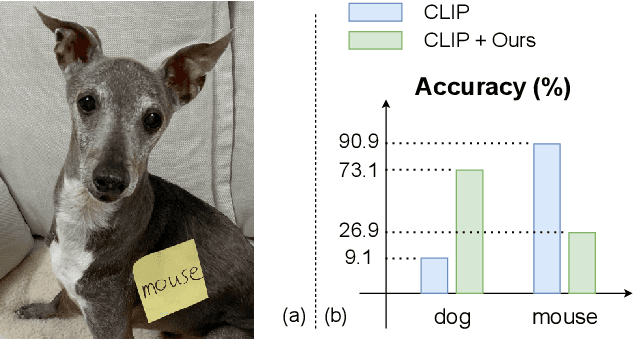
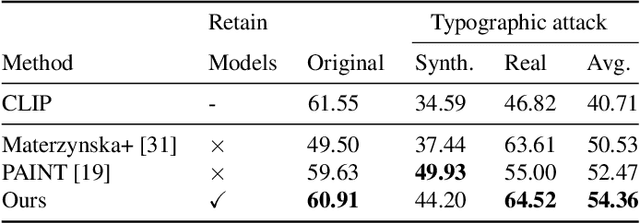
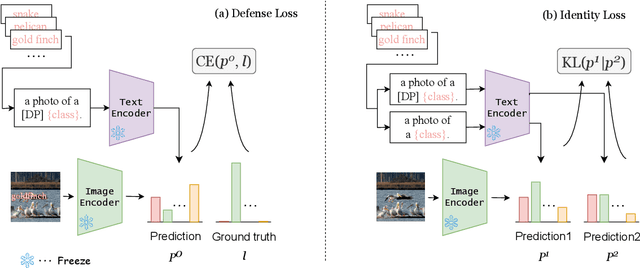
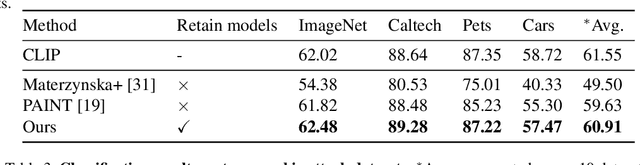
Abstract:Vision-language pre-training models (VLPs) have exhibited revolutionary improvements in various vision-language tasks. In VLP, some adversarial attacks fool a model into false or absurd classifications. Previous studies addressed these attacks by fine-tuning the model or changing its architecture. However, these methods risk losing the original model's performance and are difficult to apply to downstream tasks. In particular, their applicability to other tasks has not been considered. In this study, we addressed the reduction of the impact of typographic attacks on CLIP without changing the model parameters. To achieve this, we expand the idea of ``prefix learning'' and introduce our simple yet effective method: Defense-Prefix (DP), which inserts the DP token before a class name to make words ``robust'' against typographic attacks. Our method can be easily applied to downstream tasks, such as object detection, because the proposed method is independent of the model parameters. Our method significantly improves the accuracy of classification tasks for typographic attack datasets, while maintaining the zero-shot capabilities of the model. In addition, we leverage our proposed method for object detection, demonstrating its high applicability and effectiveness. The codes and datasets will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge