Hideaki Imaizumi
Assessing Robustness of Deep learning Methods in Dermatological Workflow
Jan 15, 2020



Abstract:This paper aims to evaluate the suitability of current deep learning methods for clinical workflow especially by focusing on dermatology. Although deep learning methods have been attempted to get dermatologist level accuracy in several individual conditions, it has not been rigorously tested for common clinical complaints. Most projects involve data acquired in well-controlled laboratory conditions. This may not reflect regular clinical evaluation where corresponding image quality is not always ideal. We test the robustness of deep learning methods by simulating non-ideal characteristics on user submitted images of ten classes of diseases. Assessing via imitated conditions, we have found the overall accuracy to drop and individual predictions change significantly in many cases despite of robust training.
Improving image classifiers for small datasets by learning rate adaptations
Mar 27, 2019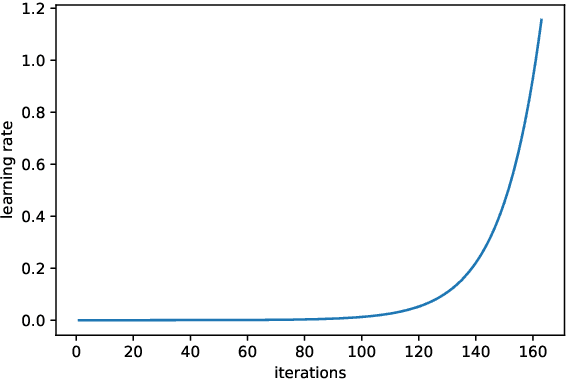
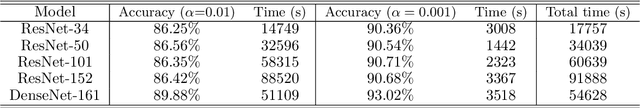
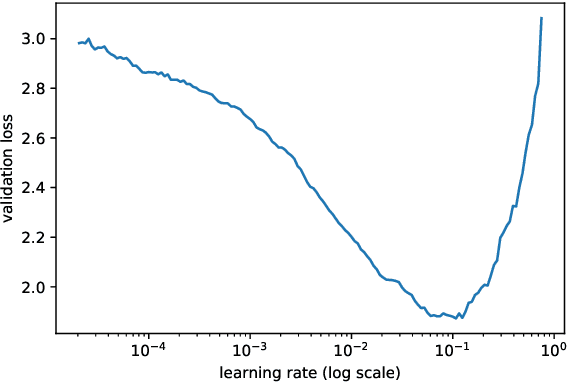
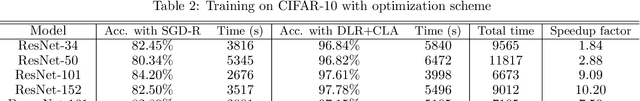
Abstract:Our paper introduces an efficient combination of established techniques to improve classifier performance, in terms of accuracy and training time. We achieve two-fold to ten-fold speedup in nearing state of the art accuracy, over different model architectures, by dynamically tuning the learning rate. We find it especially beneficial in the case of a small dataset, where reliability of machine reasoning is lower. We validate our approach by comparing our method versus vanilla training on CIFAR-10. We also demonstrate its practical viability by implementing on an unbalanced corpus of diagnostic images.
Supervised classification of Dermatological diseases by Deep learning
Jul 31, 2018



Abstract:This paper introduces a deep-learning based efficient classifier for common dermatological conditions, aimed at people without easy access to skin specialists. We report approximately 80% accuracy, in a situation where primary care doctors have attained 57% success rate, according to recent literature. The rationale of its design is centered on deploying and updating it on handheld devices in near future. Dermatological diseases are common in every population and have a wide spectrum in severity. With a shortage of dermatological expertise being observed in several countries, machine learning solutions can augment medical services and advise regarding existence of common diseases. The paper implements supervised classification of nine distinct conditions which have high occurrence in East Asian countries. Our current attempt establishes that deep learning based techniques are viable avenues for preliminary information to aid patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge