Henrique Ferreira
Using Meta-Knowledge Mined from Identifiers to Improve Intent Recognition in Neuro-Symbolic Algorithms
Dec 16, 2020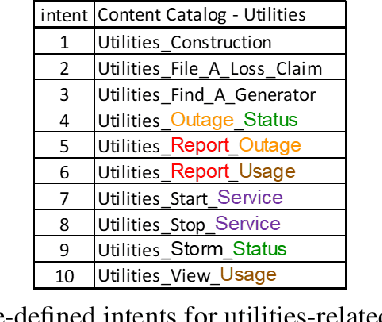
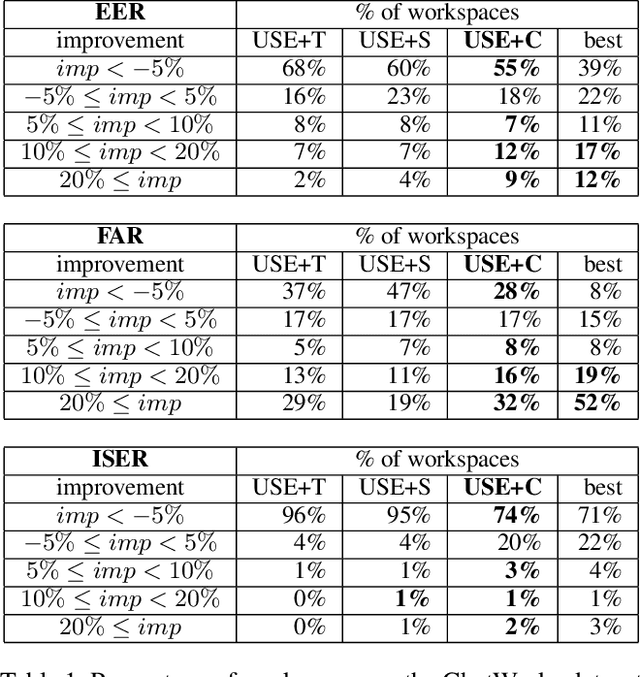
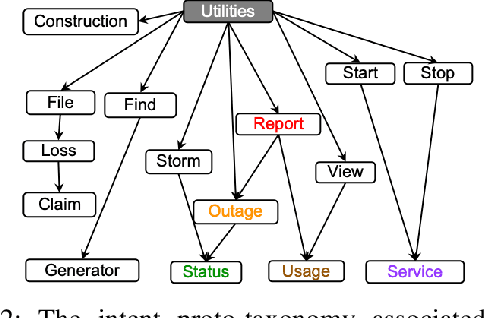
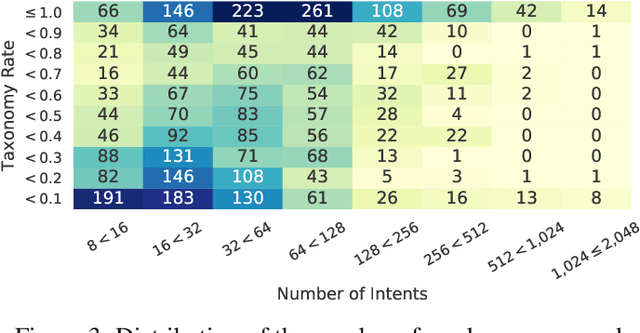
Abstract:In this paper we explore the use of meta-knowledge embedded in intent identifiers to improve intent recognition in conversational systems. As evidenced by the analysis of thousands of real-world chatbots and in interviews with professional chatbot curators, developers and domain experts tend to organize the set of chatbot intents by identifying them using proto-taxonomies, i.e., meta-knowledge connecting high-level, symbolic concepts shared across different intents. By using neuro-symbolic algorithms able to incorporate such proto-taxonomies to expand intent representation, we show that such mined meta-knowledge can improve accuracy in intent recognition. In a dataset with intents and example utterances from hundreds of professional chatbots, we saw improvements of more than 10% in the equal error rate (EER) in almost a third of the chatbots when we apply those algorithms in comparison to a baseline of the same algorithms without the meta-knowledge. The meta-knowledge proved to be even more relevant in detecting out-of-scope utterances, decreasing the false acceptance rate (FAR) in more than 20\% in about half of the chatbots. The experiments demonstrate that such symbolic meta-knowledge structures can be effectively mined and used by neuro-symbolic algorithms, apparently by incorporating into the learning process higher-level structures of the problem being solved. Based on these results, we also discuss how the use of mined meta-knowledge can be an answer for the challenge of knowledge acquisition in neuro-symbolic algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge