Henk-Jan Boele
Privacy-Preserving Object Detection & Localization Using Distributed Machine Learning: A Case Study of Infant Eyeblink Conditioning
Oct 14, 2020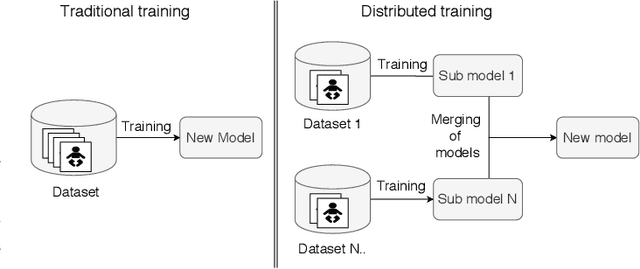
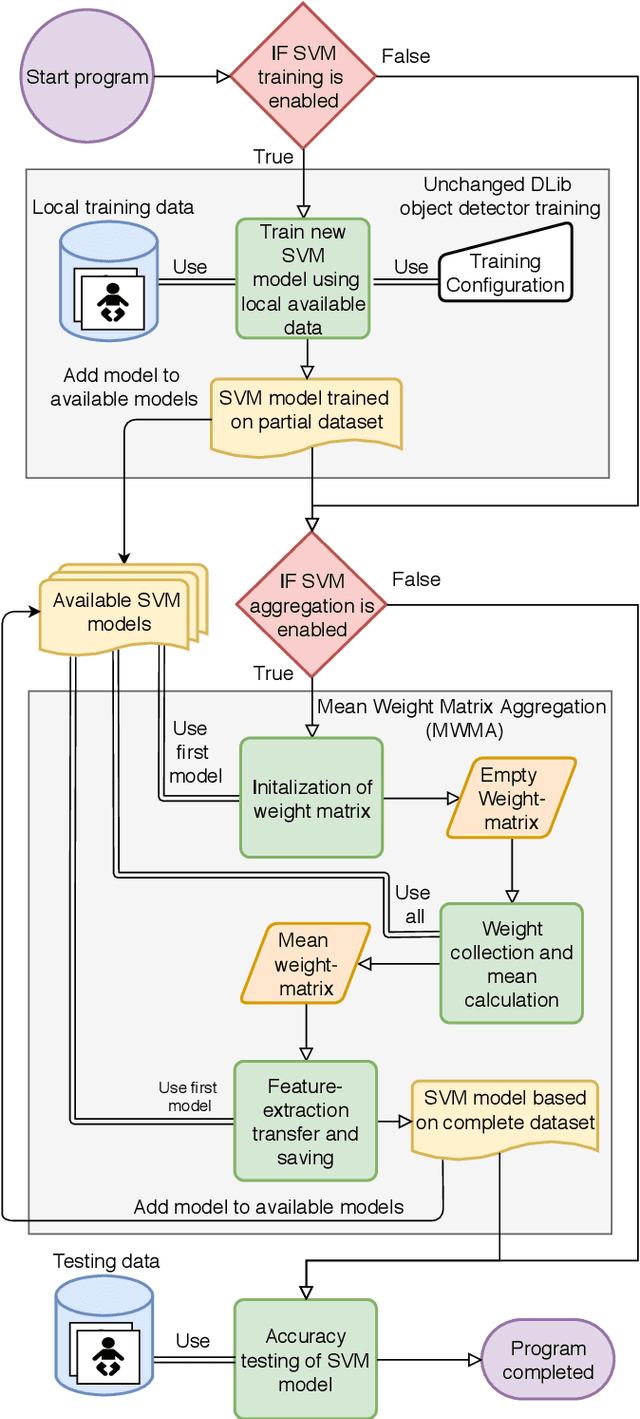
Abstract:Distributed machine learning is becoming a popular model-training method due to privacy, computational scalability, and bandwidth capacities. In this work, we explore scalable distributed-training versions of two algorithms commonly used in object detection. A novel distributed training algorithm using Mean Weight Matrix Aggregation (MWMA) is proposed for Linear Support Vector Machine (L-SVM) object detection based in Histogram of Orientated Gradients (HOG). In addition, a novel Weighted Bin Aggregation (WBA) algorithm is proposed for distributed training of Ensemble of Regression Trees (ERT) landmark localization. Both algorithms do not restrict the location of model aggregation and allow custom architectures for model distribution. For this work, a Pool-Based Local Training and Aggregation (PBLTA) architecture for both algorithms is explored. The application of both algorithms in the medical field is examined using a paradigm from the fields of psychology and neuroscience - eyeblink conditioning with infants - where models need to be trained on facial images while protecting participant privacy. Using distributed learning, models can be trained without sending image data to other nodes. The custom software has been made available for public use on GitHub: https://github.com/SLWZwaard/DMT. Results show that the aggregation of models for the HOG algorithm using MWMA not only preserves the accuracy of the model but also allows for distributed learning with an accuracy increase of 0.9% compared with traditional learning. Furthermore, WBA allows for ERT model aggregation with an accuracy increase of 8% when compared to single-node models.
Real-Time Face and Landmark Localization for Eyeblink Detection
Jun 01, 2020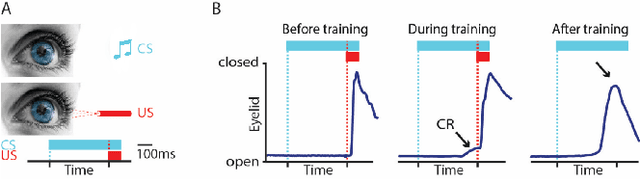
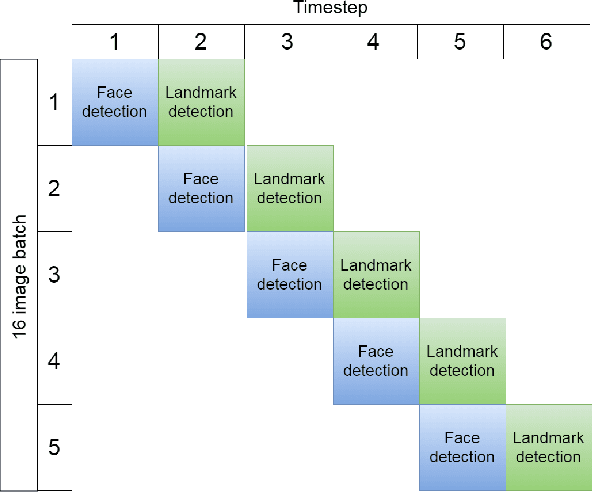
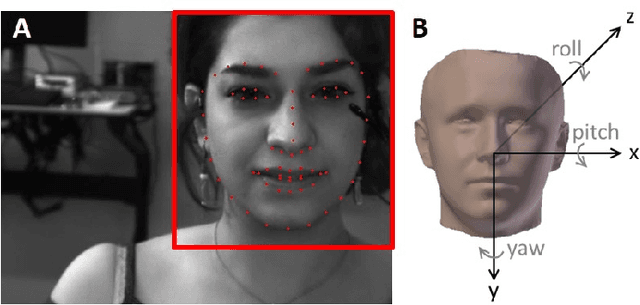
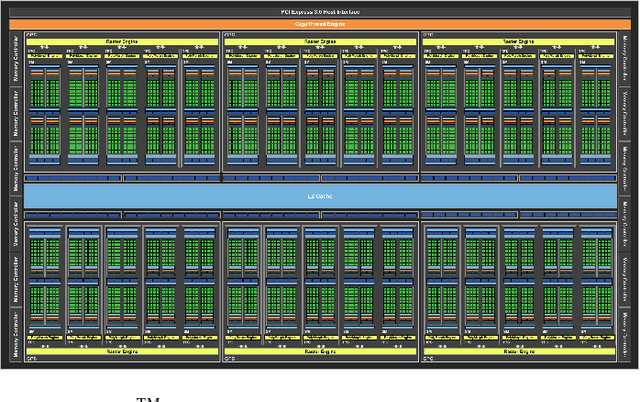
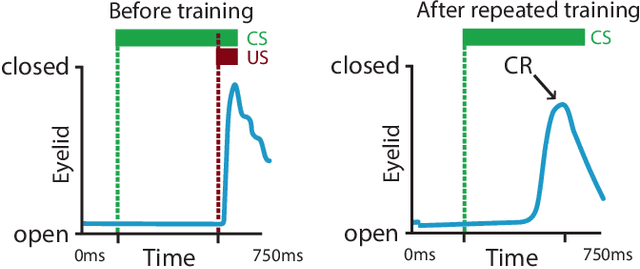
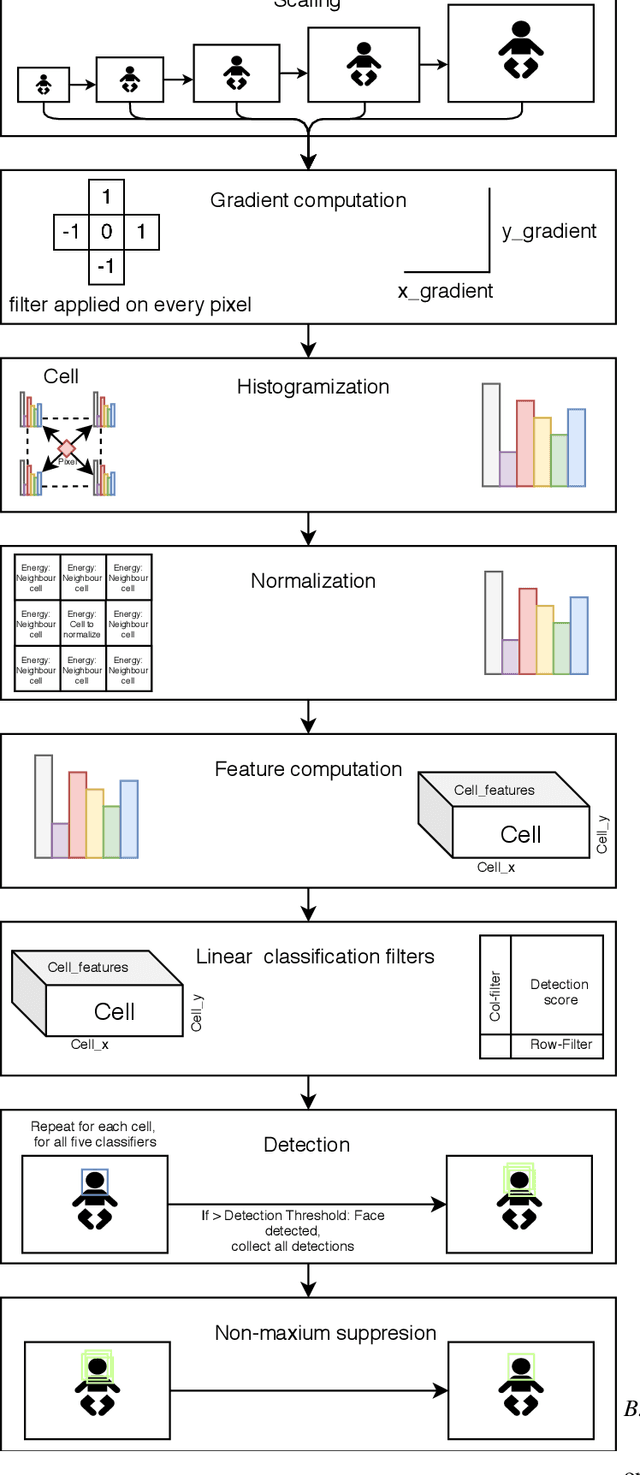
Abstract:Pavlovian eyeblink conditioning is a powerful experiment used in the field of neuroscience to measure multiple aspects of how we learn in our daily life. To track the movement of the eyelid during an experiment, researchers have traditionally made use of potentiometers or electromyography. More recently, the use of computer vision and image processing alleviated the need for these techniques but currently employed methods require human intervention and are not fast enough to enable real-time processing. In this work, a face- and landmark-detection algorithm have been carefully combined in order to provide fully automated eyelid tracking, and have further been accelerated to make the first crucial step towards online, closed-loop experiments. Such experiments have not been achieved so far and are expected to offer significant insights in the workings of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Based on an extensive literature search, various different algorithms for face detection and landmark detection have been analyzed and evaluated. Two algorithms were identified as most suitable for eyelid detection: the Histogram-of-Oriented-Gradients (HOG) algorithm for face detection and the Ensemble-of-Regression-Trees (ERT) algorithm for landmark detection. These two algorithms have been accelerated on GPU and CPU, achieving speedups of 1,753$\times$ and 11$\times$, respectively. To demonstrate the usefulness of our eyelid-detection algorithm, a research hypothesis was formed and a well-established neuroscientific experiment was employed: eyeblink detection. Our experimental evaluation reveals an overall application runtime of 0.533 ms per frame, which is 1,101$\times$ faster than the sequential implementation and well within the real-time requirements of eyeblink conditioning in humans, i.e. faster than 500 frames per second.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge