Harindra S. Mavikumbure
Spintronic Physical Reservoir for Autonomous Prediction and Long-Term Household Energy Load Forecasting
Apr 06, 2023Abstract:In this study, we have shown autonomous long-term prediction with a spintronic physical reservoir. Due to the short-term memory property of the magnetization dynamics, non-linearity arises in the reservoir states which could be used for long-term prediction tasks using simple linear regression for online training. During the prediction stage, the output is directly fed to the input of the reservoir for autonomous prediction. We employ our proposed reservoir for the modeling of the chaotic time series such as Mackey-Glass and dynamic time-series data, such as household building energy loads. Since only the last layer of a RC needs to be trained with linear regression, it is well suited for learning in real time on edge devices. Here we show that a skyrmion based magnetic tunnel junction can potentially be used as a prototypical RC but any nanomagnetic magnetic tunnel junction with nonlinear magnetization behavior can implement such a RC. By comparing our spintronic physical RC approach with state-of-the-art energy load forecasting algorithms, such as LSTMs and RNNs, we conclude that the proposed framework presents good performance in achieving high predictions accuracy, while also requiring low memory and energy both of which are at a premium in hardware resource and power constrained edge applications. Further, the proposed approach is shown to require very small training datasets and at the same time being at least 16X energy efficient compared to the state-of-the-art sequence to sequence LSTM for accurate household load predictions.
RX-ADS: Interpretable Anomaly Detection using Adversarial ML for Electric Vehicle CAN data
Sep 05, 2022
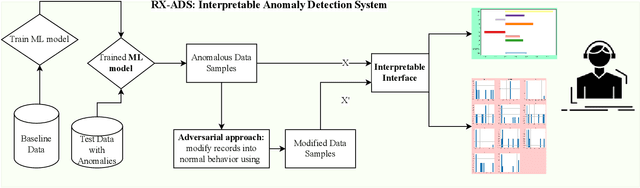
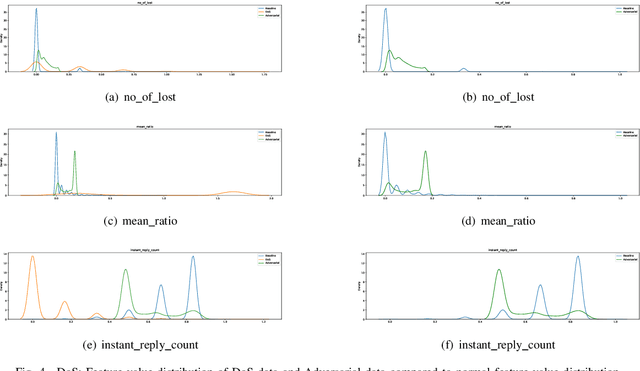
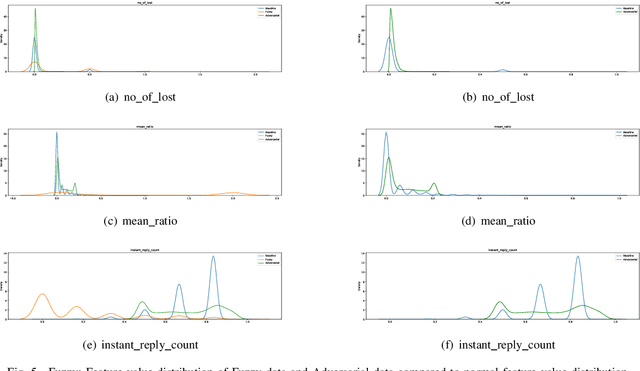
Abstract:Recent year has brought considerable advancements in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and associated infrastructures/communications. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are widely deployed for anomaly detection in such critical infrastructures. This paper presents an Interpretable Anomaly Detection System (RX-ADS) for intrusion detection in CAN protocol communication in EVs. Contributions include: 1) window based feature extraction method; 2) deep Autoencoder based anomaly detection method; and 3) adversarial machine learning based explanation generation methodology. The presented approach was tested on two benchmark CAN datasets: OTIDS and Car Hacking. The anomaly detection performance of RX-ADS was compared against the state-of-the-art approaches on these datasets: HIDS and GIDS. The RX-ADS approach presented performance comparable to the HIDS approach (OTIDS dataset) and has outperformed HIDS and GIDS approaches (Car Hacking dataset). Further, the proposed approach was able to generate explanations for detected abnormal behaviors arising from various intrusions. These explanations were later validated by information used by domain experts to detect anomalies. Other advantages of RX-ADS include: 1) the method can be trained on unlabeled data; 2) explanations help experts in understanding anomalies and root course analysis, and also help with AI model debugging and diagnostics, ultimately improving user trust in AI systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge