Haobo Song
Increasing Model Capacity for Free: A Simple Strategy for Parameter Efficient Fine-tuning
Jul 01, 2024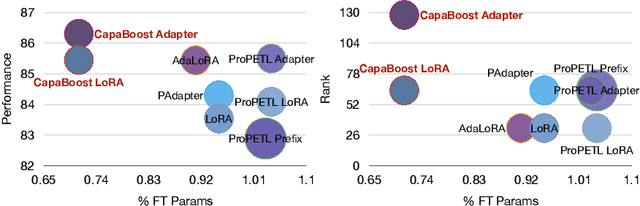
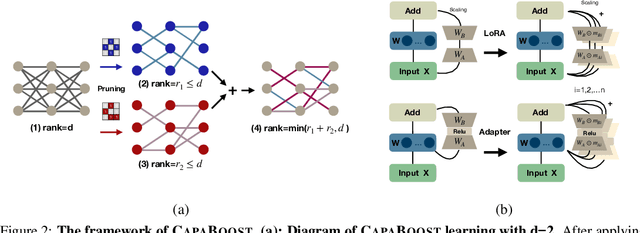
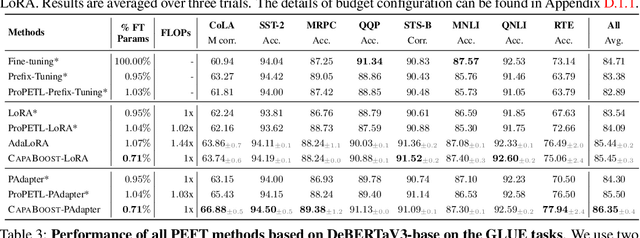
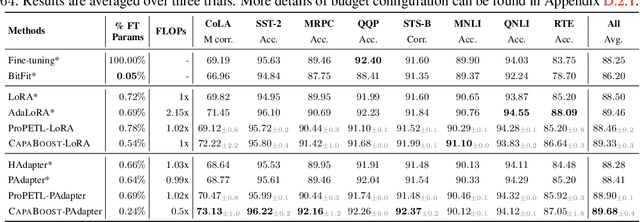
Abstract:Fine-tuning large pre-trained foundation models, such as the 175B GPT-3, has attracted more attention for downstream tasks recently. While parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods have been proposed and proven effective without retraining all model parameters, their performance is limited by the capacity of incremental modules, especially under constrained parameter budgets. \\ To overcome this challenge, we propose CapaBoost, a simple yet effective strategy that enhances model capacity by leveraging low-rank updates through parallel weight modules in target layers. By applying static random masks to the shared weight matrix, CapaBoost constructs a diverse set of weight matrices, effectively increasing the rank of incremental weights without adding parameters. Notably, our approach can be seamlessly integrated into various existing parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods. We extensively validate the efficacy of CapaBoost through experiments on diverse downstream tasks, including natural language understanding, question answering, and image classification. Our results demonstrate significant improvements over baselines, without incurring additional computation or storage costs. Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/LINs-lab/CapaBoost}.
Revisiting Implicit Models: Sparsity Trade-offs Capability in Weight-tied Model for Vision Tasks
Jul 16, 2023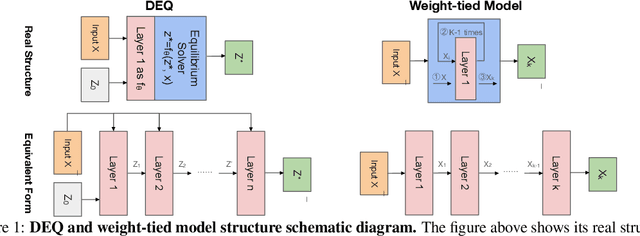
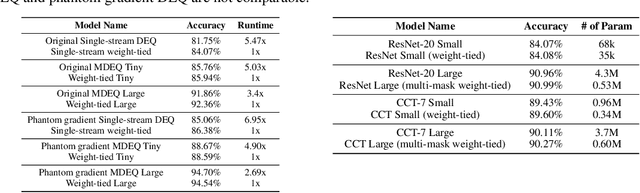
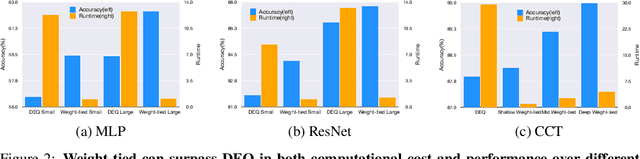
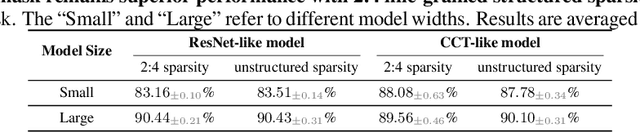
Abstract:Implicit models such as Deep Equilibrium Models (DEQs) have garnered significant attention in the community for their ability to train infinite layer models with elegant solution-finding procedures and constant memory footprint. However, despite several attempts, these methods are heavily constrained by model inefficiency and optimization instability. Furthermore, fair benchmarking across relevant methods for vision tasks is missing. In this work, we revisit the line of implicit models and trace them back to the original weight-tied models. Surprisingly, we observe that weight-tied models are more effective, stable, as well as efficient on vision tasks, compared to the DEQ variants. Through the lens of these simple-yet-clean weight-tied models, we further study the fundamental limits in the model capacity of such models and propose the use of distinct sparse masks to improve the model capacity. Finally, for practitioners, we offer design guidelines regarding the depth, width, and sparsity selection for weight-tied models, and demonstrate the generalizability of our insights to other learning paradigms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge