Hangjin Jiang
Split-and-Conquer: Distributed Factor Modeling for High-Dimensional Matrix-Variate Time Series
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we propose a distributed framework for reducing the dimensionality of high-dimensional, large-scale, heterogeneous matrix-variate time series data using a factor model. The data are first partitioned column-wise (or row-wise) and allocated to node servers, where each node estimates the row (or column) loading matrix via two-dimensional tensor PCA. These local estimates are then transmitted to a central server and aggregated, followed by a final PCA step to obtain the global row (or column) loading matrix estimator. Given the estimated loading matrices, the corresponding factor matrices are subsequently computed. Unlike existing distributed approaches, our framework preserves the latent matrix structure, thereby improving computational efficiency and enhancing information utilization. We also discuss row- and column-wise clustering procedures for settings in which the group memberships are unknown. Furthermore, we extend the analysis to unit-root nonstationary matrix-variate time series. Asymptotic properties of the proposed method are derived for the diverging dimension of the data in each computing unit and the sample size $T$. Simulation results assess the computational efficiency and estimation accuracy of the proposed framework, and real data applications further validate its predictive performance.
Equitability of Dependence Measure
Jul 11, 2018


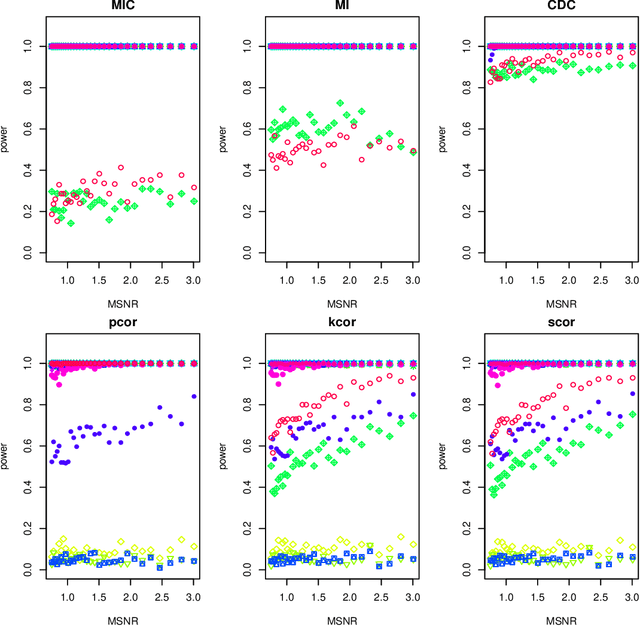
Abstract:Measuring dependence between two random variables is very important, and critical in many applied areas such as variable selection, brain network analysis. However, we do not know what kind of functional relationship is between two covariates, which requires the dependence measure to be equitable. That is, it gives similar scores to equally noisy relationship of different types. In fact, the dependence score is a continuous random variable taking values in $[0,1]$, thus it is theoretically impossible to give similar scores. In this paper, we introduce a new definition of equitability of a dependence measure, i.e, power-equitable (weak-equitable) and show by simulation that HHG and Copula Dependence Coefficient (CDC) are weak-equitable.
Dependence Measure for non-additive model
Mar 25, 2018

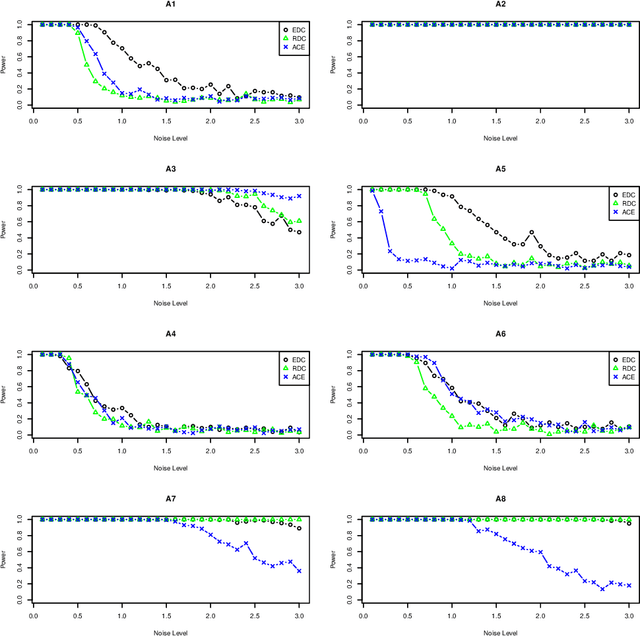
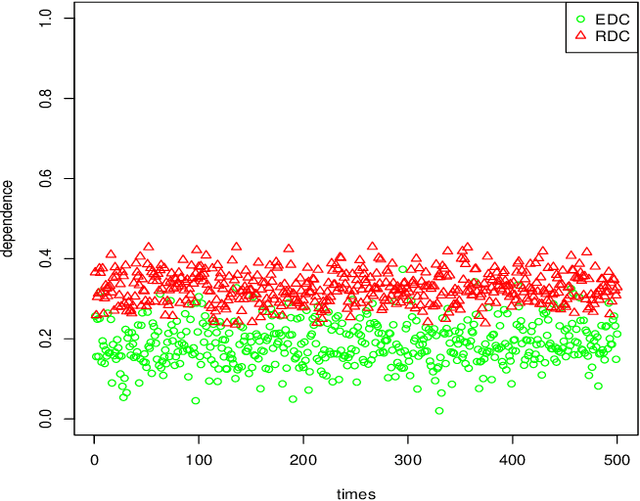
Abstract:We proposed a new statistical dependency measure called Copula Dependency Coefficient(CDC) for two sets of variables based on copula. It is robust to outliers, easy to implement, powerful and appropriate to high-dimensional variables. These properties are important in many applications. Experimental results show that CDC can detect the dependence between variables in both additive and non-additive models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge