Hamzeh Beyranvand
High-Speed Trains Access Connectivity Through RIS-Assisted FSO Communications
Oct 25, 2021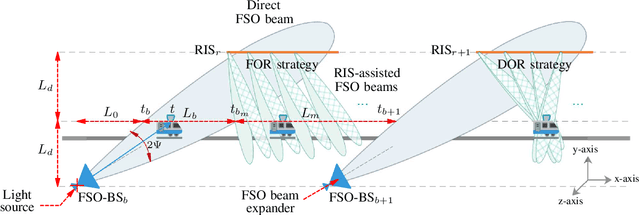
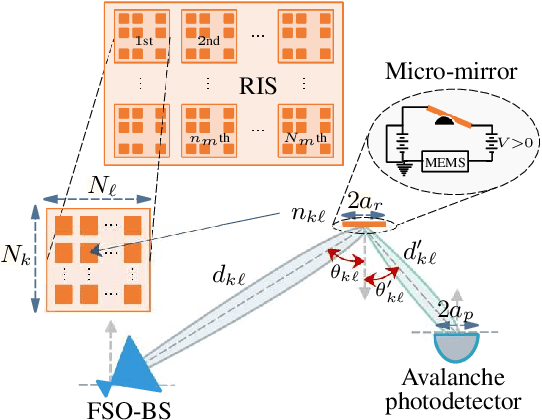

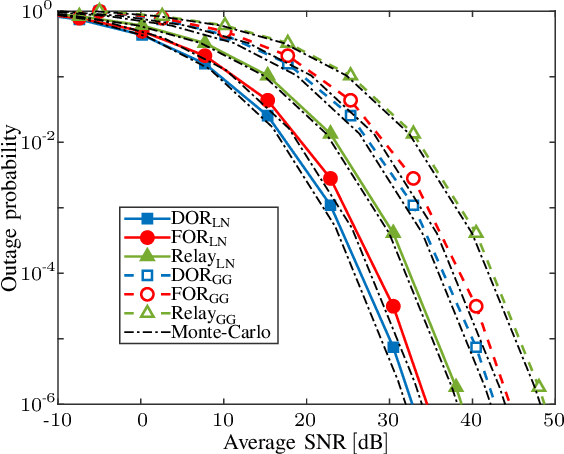
Abstract:Free-space optic (FSO) is a promising solution to provide broadband Internet access for high-speed trains (HSTs). Besides, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) are considered as hardware technology to improve performance of optical wireless communication systems. In this paper, we propose a RIS-assisted FSO system to provide access connectivity for HTSs, as an upgrade for the existing direct and relay-assisted FSO access setups. Our motivation is mainly based on well-proven results indicating that a RIS-assisted optical wireless system, with a large enough number of RIS elements, outperforms a relay-assisted one thanks to its programmable structure. We firstly compute the statistical expressions of the considered RIS-assisted FSO channels under weak and moderate-to-strong fading conditions. Then, the network's average signal-to-noise ratio and outage probability are formulated based on the assumed fading conditions, and for two fixed- and dynamic-oriented RIS coverage scenarios. Our results reveal that the proposed access network offers up to around 44% higher data rates and 240% wider coverage area for each FSO base station (FSO-BS) compared to those of the relay-assisted one. The increase of coverage area, on average, reduces 67% the number of required FSO-BSs for a given distance, which results in fewer handover processes compared to the alternative setups. Finally, the results are verified through Monte-Carlo simulations.
UAV-Assisted Underwater Sensor Networks using RF and Optical Wireless Links
Apr 27, 2021



Abstract:Underwater sensor networks (UWSNs) are of interest to gather data from underwater sensor nodes (SNs) and deliver information to a terrestrial access point (AP) in the uplink transmission, and transfer data from the AP to the SNs in the downlink transmission. In this paper, we investigate a triple-hop UWSN in which autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) relays enable end-to-end communications between the SNs and the AP. It is assumed that the SN--AUV, AUV--UAV, and UAV--AP links are deployed by underwater optical communication (UWOC), free-space optic (FSO), and radio frequency (RF) technologies, respectively. Two scenarios are proposed for the FSO uplink and downlink transmissions between the AUV and the UAV, subject to water-to-air and air-to-water interface impacts; direct transmission scenario (DTS) and retro-reflection scenario (RRS). After providing the channel models and their statistics, the UWSN's outage probability and average bit error rate (BER) are computed. Besides, a tracking procedure is proposed to set up reliable and stable AUV--UAV FSO communications. Through numerical results, it is concluded that the RSS scheme outperforms the DTS one with about 200% (32%) and 80% (17%) better outage probability (average BER) in the uplink and downlink, respectively. It is also shown that the tracking procedure provides on average 480% and 170% improvements in the network's outage probability and average BER, respectively, compared to poorly aligned FSO conditions. The results are verified by applying Monte-Carlo simulations.
Energy Efficiency Maximization in the Uplink Delta-OMA Networks
Mar 15, 2021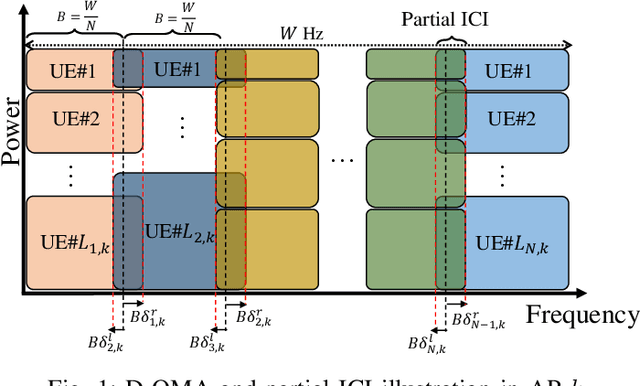

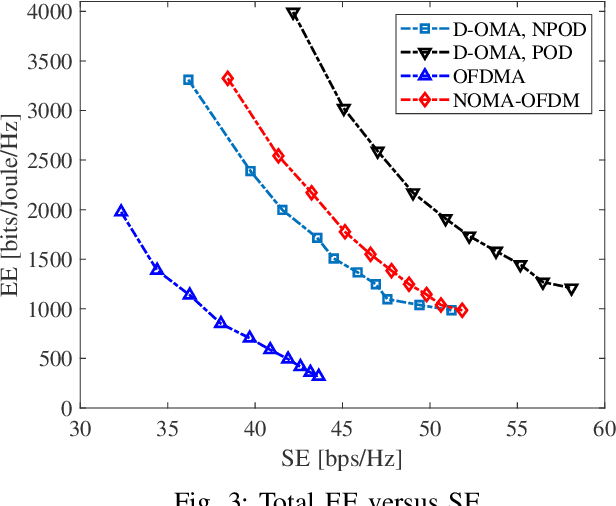

Abstract:Delta-orthogonal multiple access (D-OMA) has been recently investigated as a potential technique to enhance the spectral efficiency in 6G networks. D-OMA enables partial overlapping of the adjacent sub-channels that are assigned to different clusters of users served by non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA), at the expense of additional interference. In this paper, we analyze the performance of D-OMA in the uplink and develop a multi-objective optimization framework to maximize the uplink energy efficiency in a multi-cell network enabled by D-OMA. Specifically, we optimize the subchannel and transmit power allocations of the users as well as the overlapping percentage of the spectrum between the adjacent sub-channels. The formulated problem is a mixed binary non-linear programming problem; therefore, we first transform the problem into a single-objective problem using Tchebyshev method. Then, we apply the monotonic optimization (MO) to explore the hidden monotonicity of the objective function and constraints, and reformulate the problem into a standard MO in canonical form. The re-formulated problem is then solved by applying the outer polyblock approximation method. Our numerical results show that D-OMA outperforms the conventional non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) when the adjacent sub-channel overlap and scheduling is optimized jointly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge