Hamed Kebriaei
OptiGradTrust: Byzantine-Robust Federated Learning with Multi-Feature Gradient Analysis and Reinforcement Learning-Based Trust Weighting
Jul 31, 2025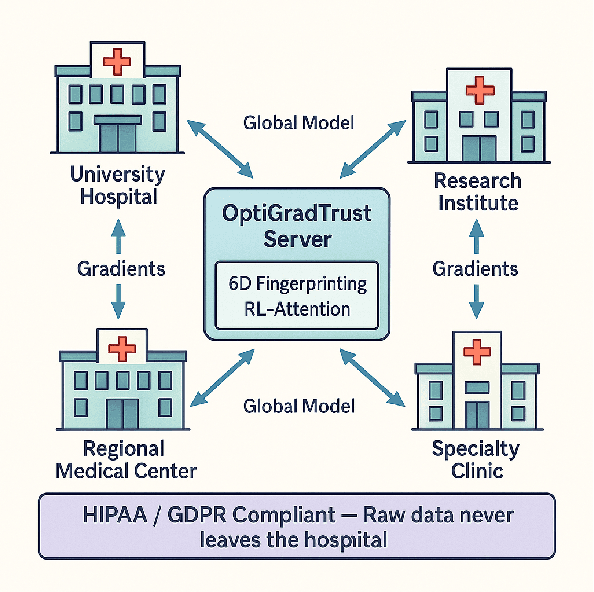
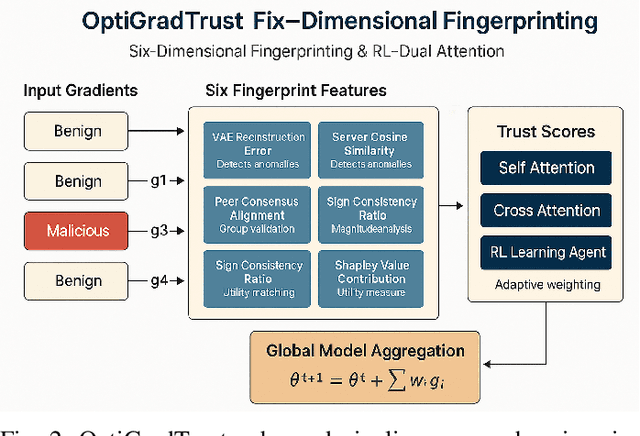
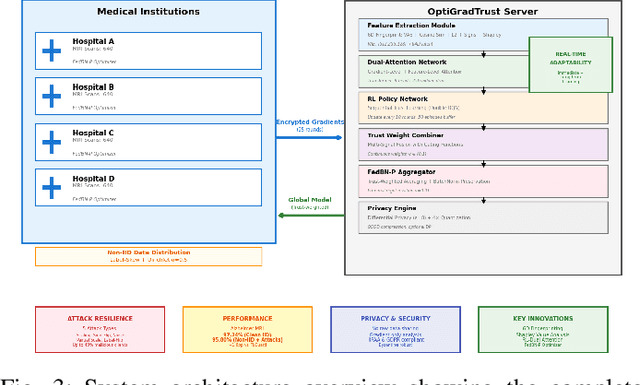
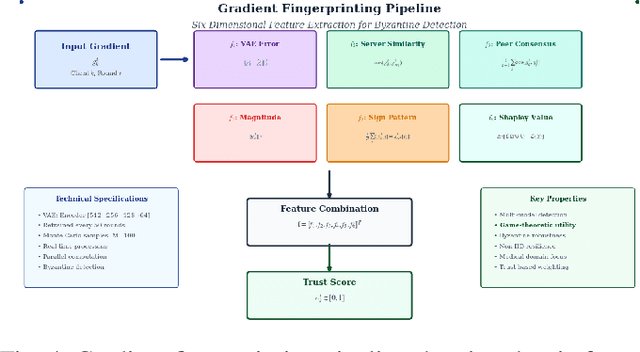
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative model training across distributed medical institutions while preserving patient privacy, but remains vulnerable to Byzantine attacks and statistical heterogeneity. We present OptiGradTrust, a comprehensive defense framework that evaluates gradient updates through a novel six-dimensional fingerprint including VAE reconstruction error, cosine similarity metrics, $L_2$ norm, sign-consistency ratio, and Monte Carlo Shapley value, which drive a hybrid RL-attention module for adaptive trust scoring. To address convergence challenges under data heterogeneity, we develop FedBN-Prox (FedBN-P), combining Federated Batch Normalization with proximal regularization for optimal accuracy-convergence trade-offs. Extensive evaluation across MNIST, CIFAR-10, and Alzheimer's MRI datasets under various Byzantine attack scenarios demonstrates significant improvements over state-of-the-art defenses, achieving up to +1.6 percentage points over FLGuard under non-IID conditions while maintaining robust performance against diverse attack patterns through our adaptive learning approach.
Towards Opinion Shaping: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach in Bot-User Interactions
Sep 12, 2024Abstract:This paper aims to investigate the impact of interference in social network algorithms via user-bot interactions, focusing on the Stochastic Bounded Confidence Model (SBCM). This paper explores two approaches: positioning bots controlled by agents into the network and targeted advertising under various circumstances, operating with an advertising budget. This study integrates the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) algorithm and its variants to experiment with different Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). Finally, experimental results demonstrate that this approach can result in efficient opinion shaping, indicating its potential in deploying advertising resources on social platforms.
Risk Sensitivity in Markov Games and Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning: A Systematic Review
Jun 10, 2024

Abstract:Markov games (MGs) and multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) are studied to model decision making in multi-agent systems. Traditionally, the objective in MG and MARL has been risk-neutral, i.e., agents are assumed to optimize a performance metric such as expected return, without taking into account subjective or cognitive preferences of themselves or of other agents. However, ignoring such preferences leads to inaccurate models of decision making in many real-world scenarios in finance, operations research, and behavioral economics. Therefore, when these preferences are present, it is necessary to incorporate a suitable measure of risk into the optimization objective of agents, which opens the door to risk-sensitive MG and MARL. In this paper, we systemically review the literature on risk sensitivity in MG and MARL that has been growing in recent years alongside other areas of reinforcement learning and game theory. We define and mathematically describe different risk measures used in MG and MARL and individually for each measure, discuss articles that incorporate it. Finally, we identify recent trends in theoretical and applied works in the field and discuss possible directions of future research.
Risk-Sensitive Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning in Network Aggregative Markov Games
Feb 08, 2024Abstract:Classical multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) assumes risk neutrality and complete objectivity for agents. However, in settings where agents need to consider or model human economic or social preferences, a notion of risk must be incorporated into the RL optimization problem. This will be of greater importance in MARL where other human or non-human agents are involved, possibly with their own risk-sensitive policies. In this work, we consider risk-sensitive and non-cooperative MARL with cumulative prospect theory (CPT), a non-convex risk measure and a generalization of coherent measures of risk. CPT is capable of explaining loss aversion in humans and their tendency to overestimate/underestimate small/large probabilities. We propose a distributed sampling-based actor-critic (AC) algorithm with CPT risk for network aggregative Markov games (NAMGs), which we call Distributed Nested CPT-AC. Under a set of assumptions, we prove the convergence of the algorithm to a subjective notion of Markov perfect Nash equilibrium in NAMGs. The experimental results show that subjective CPT policies obtained by our algorithm can be different from the risk-neutral ones, and agents with a higher loss aversion are more inclined to socially isolate themselves in an NAMG.
Continuous Reinforcement Learning-based Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment in a Visual Working Memory Game
Aug 24, 2023



Abstract:Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment (DDA) is a viable approach to enhance a player's experience in video games. Recently, Reinforcement Learning (RL) methods have been employed for DDA in non-competitive games; nevertheless, they rely solely on discrete state-action space with a small search space. In this paper, we propose a continuous RL-based DDA methodology for a visual working memory (VWM) game to handle the complex search space for the difficulty of memorization. The proposed RL-based DDA tailors game difficulty based on the player's score and game difficulty in the last trial. We defined a continuous metric for the difficulty of memorization. Then, we consider the task difficulty and the vector of difficulty-score as the RL's action and state, respectively. We evaluated the proposed method through a within-subject experiment involving 52 subjects. The proposed approach was compared with two rule-based difficulty adjustment methods in terms of player's score and game experience measured by a questionnaire. The proposed RL-based approach resulted in a significantly better game experience in terms of competence, tension, and negative and positive affect. Players also achieved higher scores and win rates. Furthermore, the proposed RL-based DDA led to a significantly less decline in the score in a 20-trial session.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge