Haley M. So
Neural Ganglion Sensors: Learning Task-specific Event Cameras Inspired by the Neural Circuit of the Human Retina
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Inspired by the data-efficient spiking mechanism of neurons in the human eye, event cameras were created to achieve high temporal resolution with minimal power and bandwidth requirements by emitting asynchronous, per-pixel intensity changes rather than conventional fixed-frame rate images. Unlike retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) in the human eye, however, which integrate signals from multiple photoreceptors within a receptive field to extract spatio-temporal features, conventional event cameras do not leverage local spatial context when deciding which events to fire. Moreover, the eye contains around 20 different kinds of RGCs operating in parallel, each attuned to different features or conditions. Inspired by this biological design, we introduce Neural Ganglion Sensors, an extension of traditional event cameras that learns task-specific spatio-temporal retinal kernels (i.e., RGC "events"). We evaluate our design on two challenging tasks: video interpolation and optical flow. Our results demonstrate that our biologically inspired sensing improves performance relative to conventional event cameras while reducing overall event bandwidth. These findings highlight the promise of RGC-inspired event sensors for edge devices and other low-power, real-time applications requiring efficient, high-resolution visual streams.
PixelRNN: In-pixel Recurrent Neural Networks for End-to-end-optimized Perception with Neural Sensors
Apr 11, 2023



Abstract:Conventional image sensors digitize high-resolution images at fast frame rates, producing a large amount of data that needs to be transmitted off the sensor for further processing. This is challenging for perception systems operating on edge devices, because communication is power inefficient and induces latency. Fueled by innovations in stacked image sensor fabrication, emerging sensor-processors offer programmability and minimal processing capabilities directly on the sensor. We exploit these capabilities by developing an efficient recurrent neural network architecture, PixelRNN, that encodes spatio-temporal features on the sensor using purely binary operations. PixelRNN reduces the amount of data to be transmitted off the sensor by a factor of 64x compared to conventional systems while offering competitive accuracy for hand gesture recognition and lip reading tasks. We experimentally validate PixelRNN using a prototype implementation on the SCAMP-5 sensor-processor platform.
MantissaCam: Learning Snapshot High-dynamic-range Imaging with Perceptually-based In-pixel Irradiance Encoding
Dec 09, 2021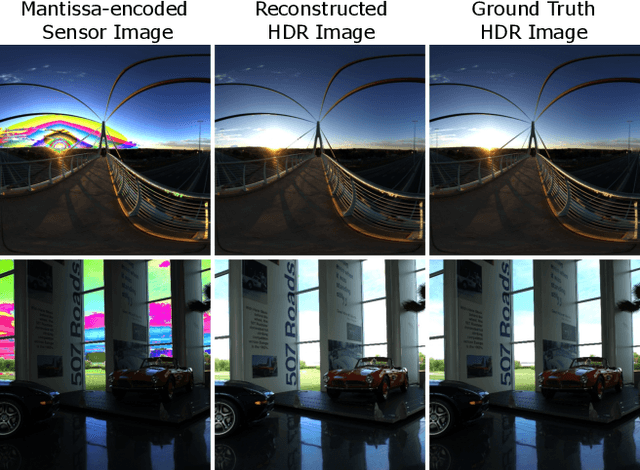
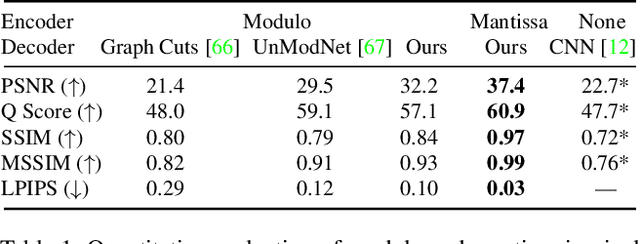
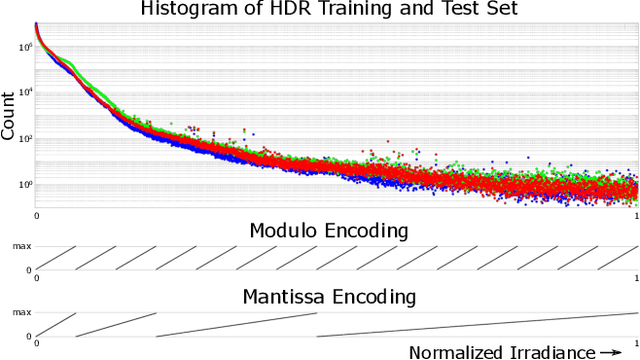
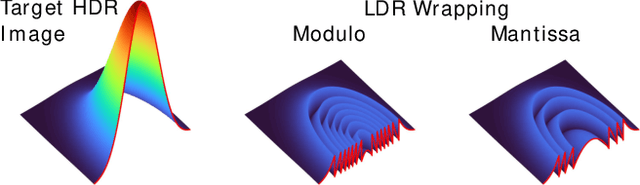
Abstract:The ability to image high-dynamic-range (HDR) scenes is crucial in many computer vision applications. The dynamic range of conventional sensors, however, is fundamentally limited by their well capacity, resulting in saturation of bright scene parts. To overcome this limitation, emerging sensors offer in-pixel processing capabilities to encode the incident irradiance. Among the most promising encoding schemes is modulo wrapping, which results in a computational photography problem where the HDR scene is computed by an irradiance unwrapping algorithm from the wrapped low-dynamic-range (LDR) sensor image. Here, we design a neural network--based algorithm that outperforms previous irradiance unwrapping methods and, more importantly, we design a perceptually inspired "mantissa" encoding scheme that more efficiently wraps an HDR scene into an LDR sensor. Combined with our reconstruction framework, MantissaCam achieves state-of-the-art results among modulo-type snapshot HDR imaging approaches. We demonstrate the efficacy of our method in simulation and show preliminary results of a prototype MantissaCam implemented with a programmable sensor.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge