Hajar Sadeghi Sokeh
Summarizing Videos with Attention
Dec 05, 2018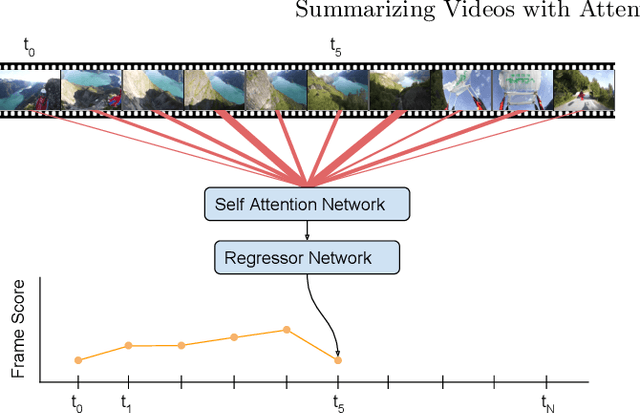
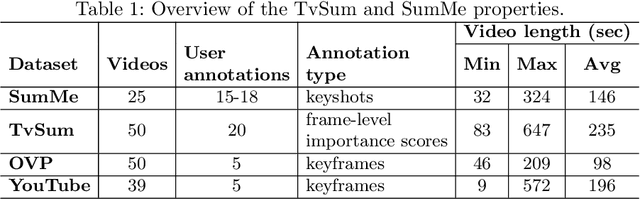
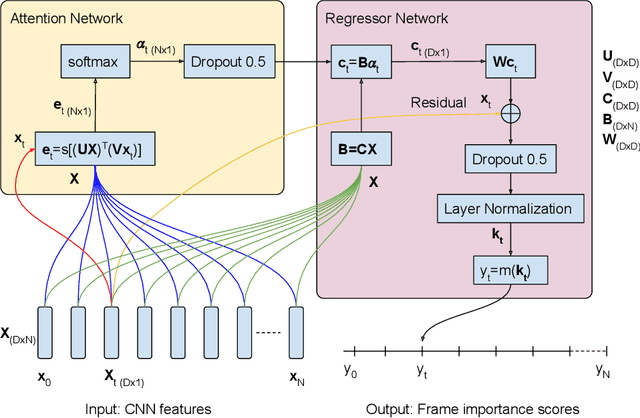
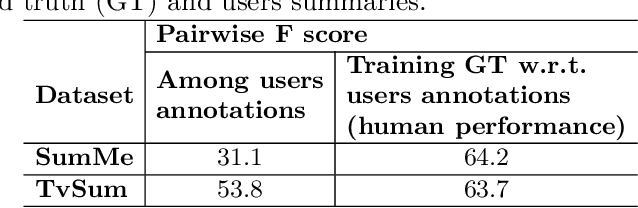
Abstract:In this work we propose a novel method for supervised, keyshots based video summarization by applying a conceptually simple and computationally efficient soft, self-attention mechanism. Current state of the art methods leverage bi-directional recurrent networks such as BiLSTM combined with attention. These networks are complex to implement and computationally demanding compared to fully connected networks. To that end we propose a simple, self-attention based network for video summarization which performs the entire sequence to sequence transformation in a single feed forward pass and single backward pass during training. Our method sets a new state of the art results on two benchmarks TvSum and SumMe, commonly used in this domain.
Superframes, A Temporal Video Segmentation
Apr 18, 2018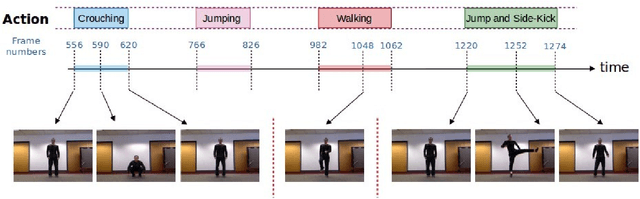
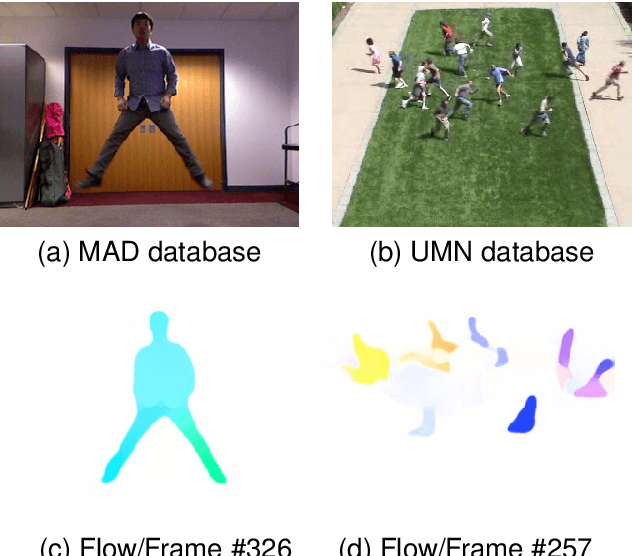
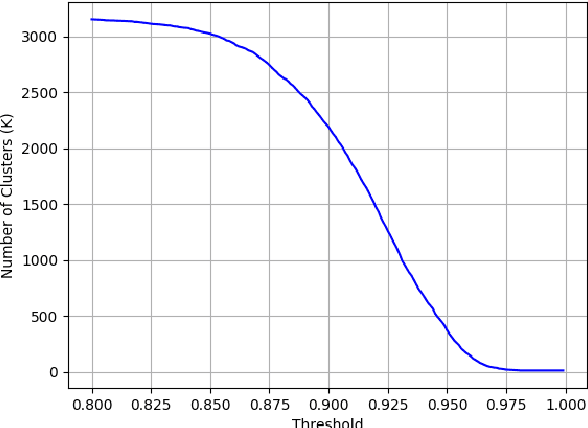
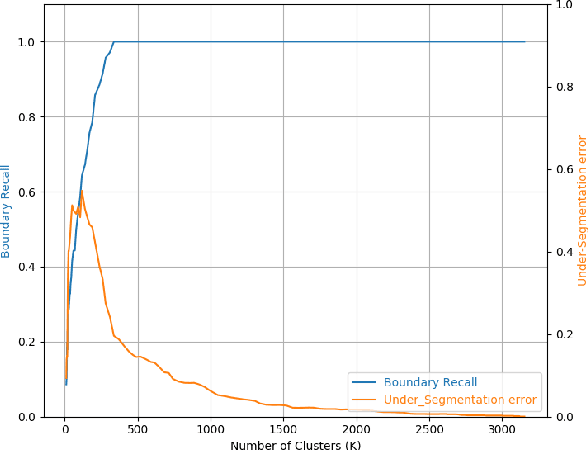
Abstract:The goal of video segmentation is to turn video data into a set of concrete motion clusters that can be easily interpreted as building blocks of the video. There are some works on similar topics like detecting scene cuts in a video, but there is few specific research on clustering video data into the desired number of compact segments. It would be more intuitive, and more efficient, to work with perceptually meaningful entity obtained from a low-level grouping process which we call it superframe. This paper presents a new simple and efficient technique to detect superframes of similar content patterns in videos. We calculate the similarity of content-motion to obtain the strength of change between consecutive frames. With the help of existing optical flow technique using deep models, the proposed method is able to perform more accurate motion estimation efficiently. We also propose two criteria for measuring and comparing the performance of different algorithms on various databases. Experimental results on the videos from benchmark databases have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge