Haiming Chen
Heterogeneous Attributed Graph Learning via Neighborhood-Aware Star Kernels
Nov 14, 2025



Abstract:Attributed graphs, typically characterized by irregular topologies and a mix of numerical and categorical attributes, are ubiquitous in diverse domains such as social networks, bioinformatics, and cheminformatics. While graph kernels provide a principled framework for measuring graph similarity, existing kernel methods often struggle to simultaneously capture heterogeneous attribute semantics and neighborhood information in attributed graphs. In this work, we propose the Neighborhood-Aware Star Kernel (NASK), a novel graph kernel designed for attributed graph learning. NASK leverages an exponential transformation of the Gower similarity coefficient to jointly model numerical and categorical features efficiently, and employs star substructures enhanced by Weisfeiler-Lehman iterations to integrate multi-scale neighborhood structural information. We theoretically prove that NASK is positive definite, ensuring compatibility with kernel-based learning frameworks such as SVMs. Extensive experiments are conducted on eleven attributed and four large-scale real-world graph benchmarks. The results demonstrate that NASK consistently achieves superior performance over sixteen state-of-the-art baselines, including nine graph kernels and seven Graph Neural Networks.
Grammar construction methods for extended deterministic expressions
Jan 24, 2023Abstract:Extended regular expressions with counting and interleaving are widely used in practice. However the related theoretical studies for this kind of expressions currently cannot meet the need of practical work. This paper develops syntax definitions for extended deterministic expressions and their subclasses, hope to completely solve the long-standing problem that there are no syntax definitions for this kind of expressions, which has become an important reason for restricting the use of extended expressions.
An Effective Algorithm for Learning Single Occurrence Regular Expressions with Interleaving
Jun 05, 2019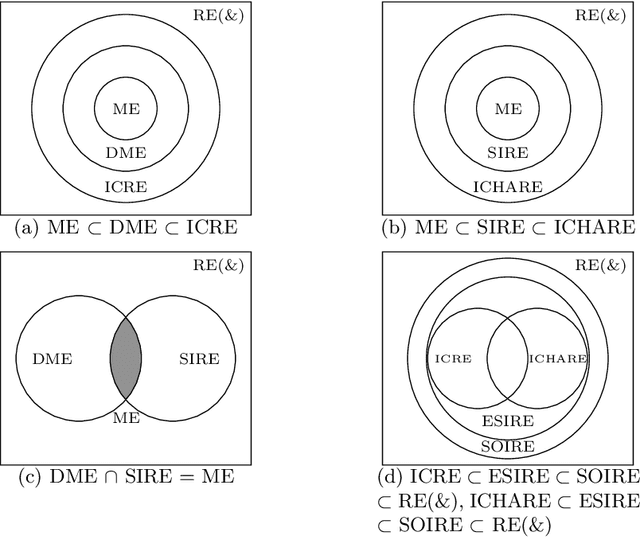
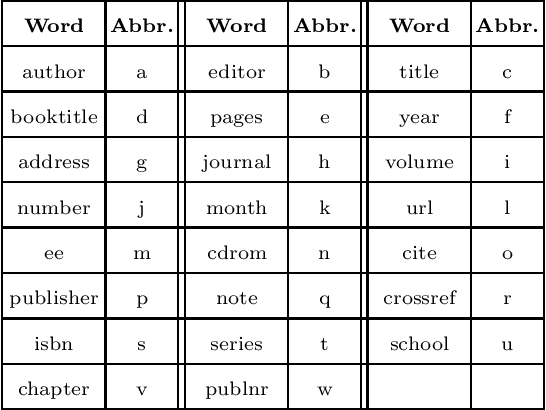
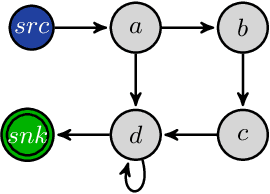
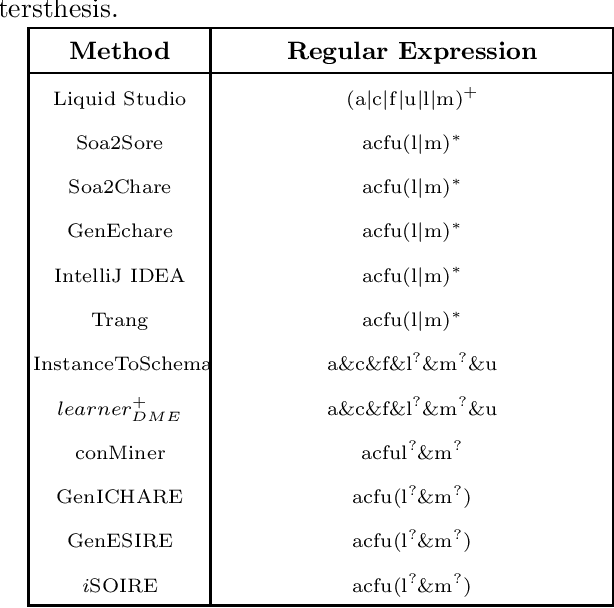
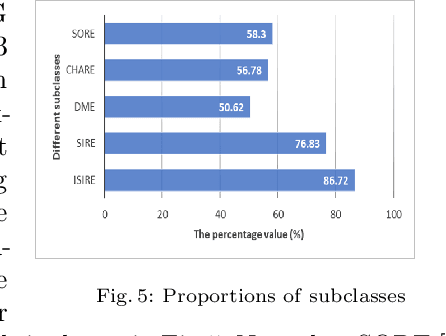
Abstract:The advantages offered by the presence of a schema are numerous. However, many XML documents in practice are not accompanied by a (valid) schema, making schema inference an attractive research problem. The fundamental task in XML schema learning is inferring restricted subclasses of regular expressions. Most previous work either lacks support for interleaving or only has limited support for interleaving. In this paper, we first propose a new subclass Single Occurrence Regular Expressions with Interleaving (SOIRE), which has unrestricted support for interleaving. Then, based on single occurrence automaton and maximum independent set, we propose an algorithm iSOIRE to infer SOIREs. Finally, we further conduct a series of experiments on real datasets to evaluate the effectiveness of our work, comparing with both ongoing learning algorithms in academia and industrial tools in real-world. The results reveal the practicability of SOIRE and the effectiveness of iSOIRE, showing the high preciseness and conciseness of our work.
Learning Restricted Regular Expressions with Interleaving
Apr 30, 2019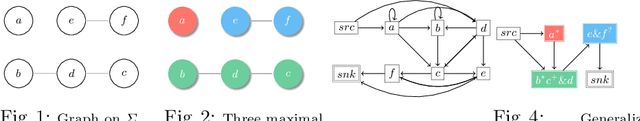
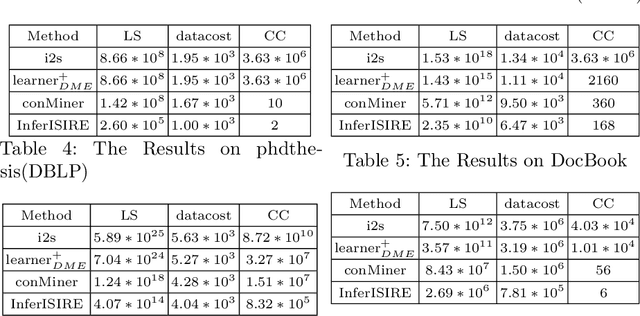
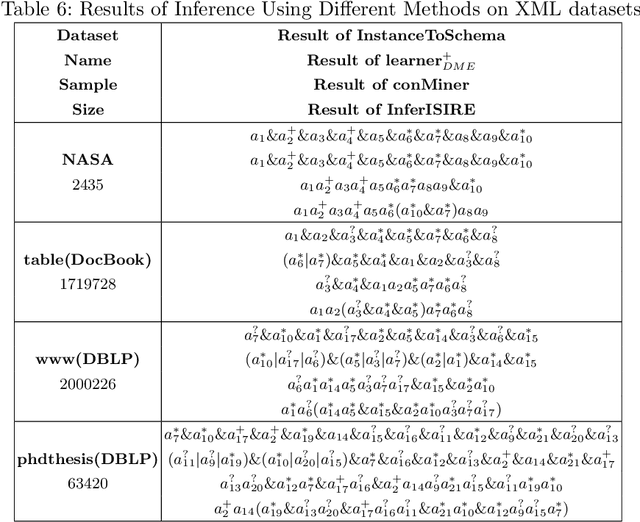
Abstract:The advantages for the presence of an XML schema for XML documents are numerous. However, many XML documents in practice are not accompanied by a schema or by a valid schema. Relax NG is a popular and powerful schema language, which supports the unconstrained interleaving operator. Focusing on the inference of Relax NG, we propose a new subclass of regular expressions with interleaving and design a polynomial inference algorithm. Then we conducted a series of experiments based on large-scale real data and on three XML data corpora, and experimental results show that our subclass has a better practicality than previous ones, and the regular expressions inferred by our algorithm are more precise.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge