Hagit Messer
AWaRe-SAC: Proactive Slice Admission Control under Weather-Induced Capacity Uncertainty
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:As emerging applications demand higher throughput and lower latencies, operators are increasingly deploying millimeter-wave (mmWave) links within x-haul transport networks, spanning fronthaul, midhaul, and backhaul segments. However, the inherent susceptibility of mmWave frequencies to weather-related attenuation, particularly rain fading, complicates the maintenance of stringent Quality of Service (QoS) requirements. This creates a critical challenge: making admission decisions under uncertainty regarding future network capacity. To address this, we develop a proactive slice admission control framework for mmWave x-haul networks subject to rain-induced fluctuations. Our objective is to improve network performance, ensure QoS, and optimize revenue, thereby surpassing the limitations of standard reactive approaches. The proposed framework integrates a deep learning predictor of future network conditions with a proactive Q-learning-based slice admission control mechanism. We validate our solution using real-world data from a mmWave x-haul deployment in a dense urban area, incorporating realistic models of link capacity attenuation and dynamic slice demands. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that our proactive solution achieves 2-3x higher long-term average revenue under dynamic link conditions, providing a scalable and resilient framework for adaptive admission control.
Learned Bayesian Cramér-Rao Bound for Unknown Measurement Models Using Score Neural Networks
Feb 02, 2025Abstract:The Bayesian Cram\'er-Rao bound (BCRB) is a crucial tool in signal processing for assessing the fundamental limitations of any estimation problem as well as benchmarking within a Bayesian frameworks. However, the BCRB cannot be computed without full knowledge of the prior and the measurement distributions. In this work, we propose a fully learned Bayesian Cram\'er-Rao bound (LBCRB) that learns both the prior and the measurement distributions. Specifically, we suggest two approaches to obtain the LBCRB: the Posterior Approach and the Measurement-Prior Approach. The Posterior Approach provides a simple method to obtain the LBCRB, whereas the Measurement-Prior Approach enables us to incorporate domain knowledge to improve the sample complexity and {interpretability}. To achieve this, we introduce a Physics-encoded score neural network which enables us to easily incorporate such domain knowledge into a neural network. We {study the learning} errors of the two suggested approaches theoretically, and validate them numerically. We demonstrate the two approaches on several signal processing examples, including a linear measurement problem with unknown mixing and Gaussian noise covariance matrices, frequency estimation, and quantized measurement. In addition, we test our approach on a nonlinear signal processing problem of frequency estimation with real-world underwater ambient noise.
Learning to Bound: A Generative Cramér-Rao Bound
Mar 07, 2022
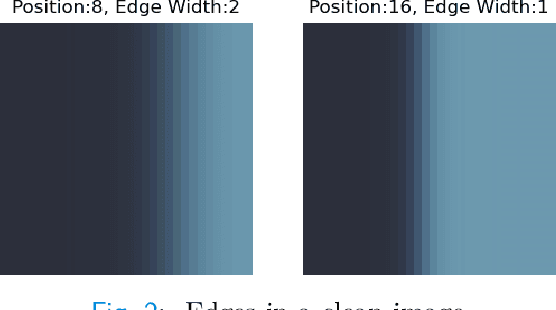


Abstract:The Cram\'er-Rao bound (CRB), a well-known lower bound on the performance of any unbiased parameter estimator, has been used to study a wide variety of problems. However, to obtain the CRB, requires an analytical expression for the likelihood of the measurements given the parameters, or equivalently a precise and explicit statistical model for the data. In many applications, such a model is not available. Instead, this work introduces a novel approach to approximate the CRB using data-driven methods, which removes the requirement for an analytical statistical model. This approach is based on the recent success of deep generative models in modeling complex, high-dimensional distributions. Using a learned normalizing flow model, we model the distribution of the measurements and obtain an approximation of the CRB, which we call Generative Cram\'er-Rao Bound (GCRB). Numerical experiments on simple problems validate this approach, and experiments on two image processing tasks of image denoising and edge detection with a learned camera noise model demonstrate its power and benefits.
Switching in the Rain: Predictive Wireless x-haul Network Reconfiguration
Mar 07, 2022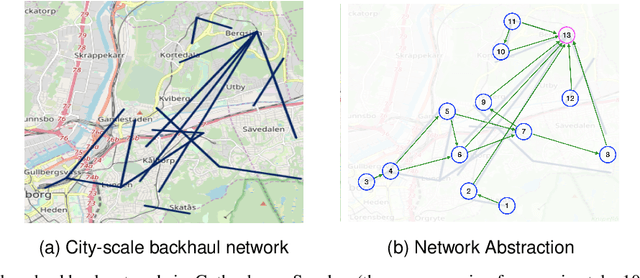
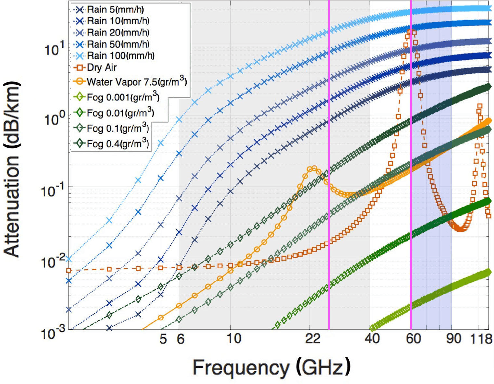
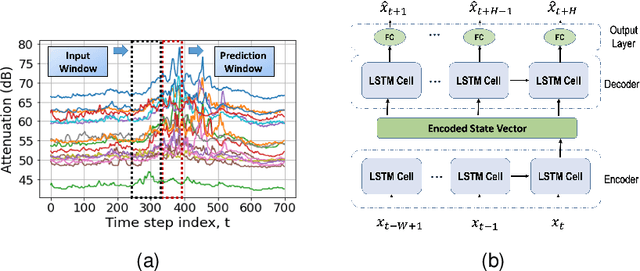
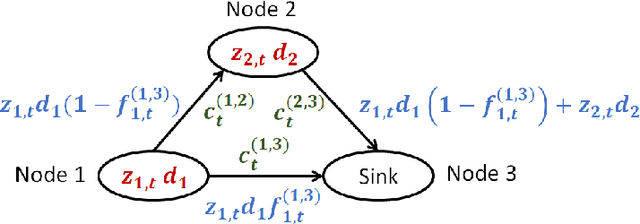
Abstract:Wireless x-haul networks rely on microwave and millimeter-wave links between 4G and/or 5G base-stations to support ultra-high data rate and ultra-low latency. A major challenge associated with these high frequency links is their susceptibility to weather conditions. In particular, precipitation may cause severe signal attenuation, which significantly degrades the network performance. In this paper, we develop a Predictive Network Reconfiguration (PNR) framework that uses historical data to predict the future condition of each link and then prepares the network ahead of time for imminent disturbances. The PNR framework has two components: (i) an Attenuation Prediction (AP) mechanism; and (ii) a Multi-Step Network Reconfiguration (MSNR) algorithm. The AP mechanism employs an encoder-decoder Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model to predict the sequence of future attenuation levels of each link. The MSNR algorithm leverages these predictions to dynamically optimize routing and admission control decisions aiming to maximize network utilization, while preserving max-min fairness among the base-stations sharing the network and preventing transient congestion that may be caused by re-routing. We train, validate, and evaluate the PNR framework using a dataset containing over 2 million measurements collected from a real-world city-scale backhaul network. The results show that the framework: (i) predicts attenuation with high accuracy, with an RMSE of less than 0.4 dB for a prediction horizon of 50 seconds; and (ii) can improve the instantaneous network utilization by more than 200% when compared to reactive network reconfiguration algorithms that cannot leverage information about future disturbances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge