H. Ritter
Training set cleansing of backdoor poisoning by self-supervised representation learning
Oct 19, 2022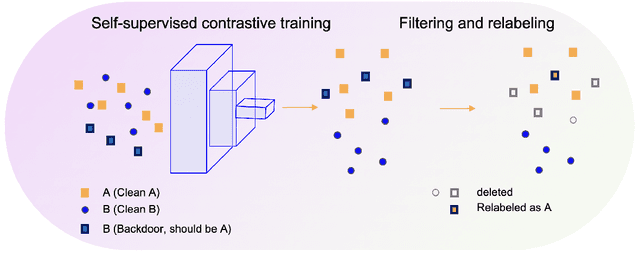
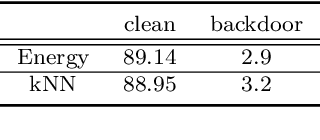
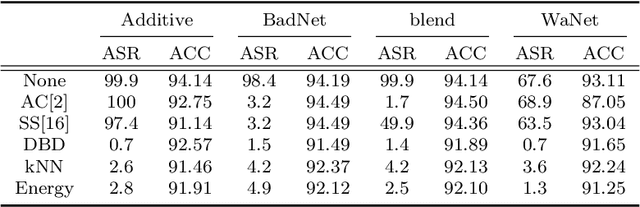
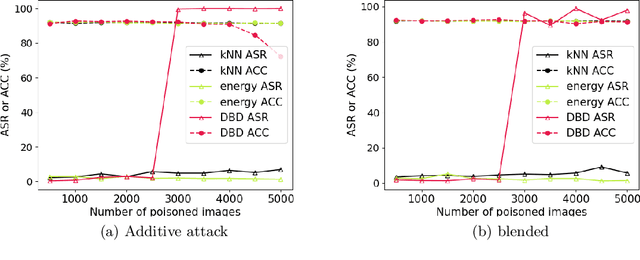
Abstract:A backdoor or Trojan attack is an important type of data poisoning attack against deep neural network (DNN) classifiers, wherein the training dataset is poisoned with a small number of samples that each possess the backdoor pattern (usually a pattern that is either imperceptible or innocuous) and which are mislabeled to the attacker's target class. When trained on a backdoor-poisoned dataset, a DNN behaves normally on most benign test samples but makes incorrect predictions to the target class when the test sample has the backdoor pattern incorporated (i.e., contains a backdoor trigger). Here we focus on image classification tasks and show that supervised training may build stronger association between the backdoor pattern and the associated target class than that between normal features and the true class of origin. By contrast, self-supervised representation learning ignores the labels of samples and learns a feature embedding based on images' semantic content. %We thus propose to use unsupervised representation learning to avoid emphasising backdoor-poisoned training samples and learn a similar feature embedding for samples of the same class. Using a feature embedding found by self-supervised representation learning, a data cleansing method, which combines sample filtering and re-labeling, is developed. Experiments on CIFAR-10 benchmark datasets show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in mitigating backdoor attacks.
The Cyborg Astrobiologist: Testing a Novelty-Detection Algorithm on Two Mobile Exploration Systems at Rivas Vaciamadrid in Spain and at the Mars Desert Research Station in Utah
Oct 28, 2009



Abstract:(ABRIDGED) In previous work, two platforms have been developed for testing computer-vision algorithms for robotic planetary exploration (McGuire et al. 2004b,2005; Bartolo et al. 2007). The wearable-computer platform has been tested at geological and astrobiological field sites in Spain (Rivas Vaciamadrid and Riba de Santiuste), and the phone-camera has been tested at a geological field site in Malta. In this work, we (i) apply a Hopfield neural-network algorithm for novelty detection based upon color, (ii) integrate a field-capable digital microscope on the wearable computer platform, (iii) test this novelty detection with the digital microscope at Rivas Vaciamadrid, (iv) develop a Bluetooth communication mode for the phone-camera platform, in order to allow access to a mobile processing computer at the field sites, and (v) test the novelty detection on the Bluetooth-enabled phone-camera connected to a netbook computer at the Mars Desert Research Station in Utah. This systems engineering and field testing have together allowed us to develop a real-time computer-vision system that is capable, for example, of identifying lichens as novel within a series of images acquired in semi-arid desert environments. We acquired sequences of images of geologic outcrops in Utah and Spain consisting of various rock types and colors to test this algorithm. The algorithm robustly recognized previously-observed units by their color, while requiring only a single image or a few images to learn colors as familiar, demonstrating its fast learning capability.
* 28 pages, 12 figures, accepted for publication in the International Journal of Astrobiology
Multi-Modal Human-Machine Communication for Instructing Robot Grasping Tasks
May 24, 2005



Abstract:A major challenge for the realization of intelligent robots is to supply them with cognitive abilities in order to allow ordinary users to program them easily and intuitively. One way of such programming is teaching work tasks by interactive demonstration. To make this effective and convenient for the user, the machine must be capable to establish a common focus of attention and be able to use and integrate spoken instructions, visual perceptions, and non-verbal clues like gestural commands. We report progress in building a hybrid architecture that combines statistical methods, neural networks, and finite state machines into an integrated system for instructing grasping tasks by man-machine interaction. The system combines the GRAVIS-robot for visual attention and gestural instruction with an intelligent interface for speech recognition and linguistic interpretation, and an modality fusion module to allow multi-modal task-oriented man-machine communication with respect to dextrous robot manipulation of objects.
* 7 pages, 8 figures
Neural Architectures for Robot Intelligence
Oct 18, 2004
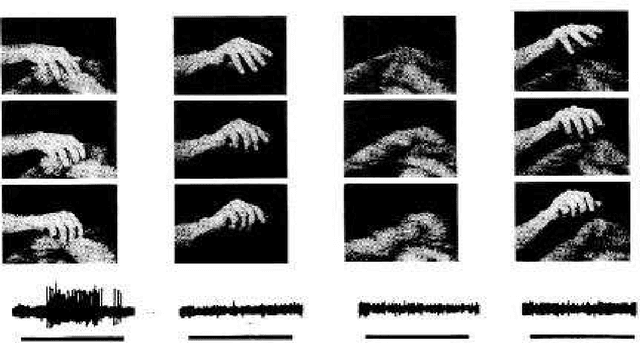
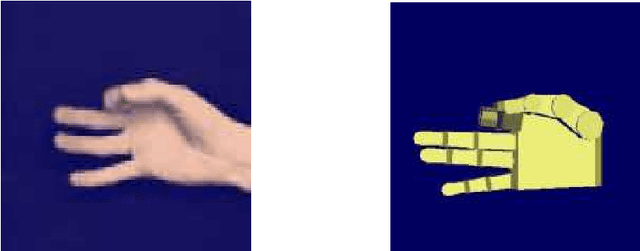
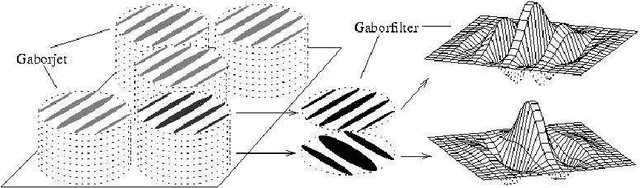
Abstract:We argue that the direct experimental approaches to elucidate the architecture of higher brains may benefit from insights gained from exploring the possibilities and limits of artificial control architectures for robot systems. We present some of our recent work that has been motivated by that view and that is centered around the study of various aspects of hand actions since these are intimately linked with many higher cognitive abilities. As examples, we report on the development of a modular system for the recognition of continuous hand postures based on neural nets, the use of vision and tactile sensing for guiding prehensile movements of a multifingered hand, and the recognition and use of hand gestures for robot teaching. Regarding the issue of learning, we propose to view real-world learning from the perspective of data mining and to focus more strongly on the imitation of observed actions instead of purely reinforcement-based exploration. As a concrete example of such an effort we report on the status of an ongoing project in our lab in which a robot equipped with an attention system with a neurally inspired architecture is taught actions by using hand gestures in conjunction with speech commands. We point out some of the lessons learnt from this system, and discuss how systems of this kind can contribute to the study of issues at the junction between natural and artificial cognitive systems.
* 37 pages, 17 figures
Cyborg Systems as Platforms for Computer-Vision Algorithm-Development for Astrobiology
May 09, 2004



Abstract:Employing the allegorical imagery from the film "The Matrix", we motivate and discuss our `Cyborg Astrobiologist' research program. In this research program, we are using a wearable computer and video camcorder in order to test and train a computer-vision system to be a field-geologist and field-astrobiologist.
* Updated biblio info
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge