Gunther Schauberger
Hybrid Machine Learning Forecasts for the UEFA EURO 2020
Jun 07, 2021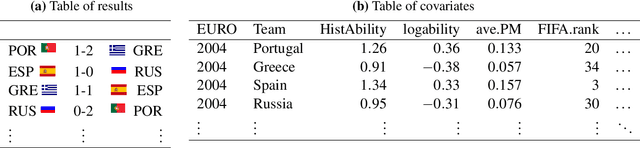
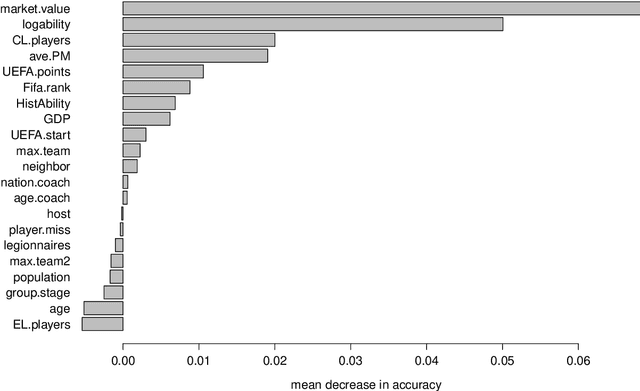
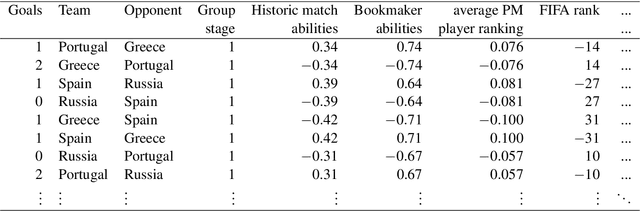
Abstract:Three state-of-the-art statistical ranking methods for forecasting football matches are combined with several other predictors in a hybrid machine learning model. Namely an ability estimate for every team based on historic matches; an ability estimate for every team based on bookmaker consensus; average plus-minus player ratings based on their individual performances in their home clubs and national teams; and further team covariates (e.g., market value, team structure) and country-specific socio-economic factors (population, GDP). The proposed combined approach is used for learning the number of goals scored in the matches from the four previous UEFA EUROs 2004-2016 and then applied to current information to forecast the upcoming UEFA EURO 2020. Based on the resulting estimates, the tournament is simulated repeatedly and winning probabilities are obtained for all teams. A random forest model favors the current World Champion France with a winning probability of 14.8% before England (13.5%) and Spain (12.3%). Additionally, we provide survival probabilities for all teams and at all tournament stages.
Deducing neighborhoods of classes from a fitted model
Sep 17, 2020



Abstract:In todays world the request for very complex models for huge data sets is rising steadily. The problem with these models is that by raising the complexity of the models, it gets much harder to interpret them. The growing field of \emph{interpretable machine learning} tries to make up for the lack of interpretability in these complex (or even blackbox-)models by using specific techniques that can help to understand those models better. In this article a new kind of interpretable machine learning method is presented, which can help to understand the partitioning of the feature space into predicted classes in a classification model using quantile shifts. To illustrate in which situations this quantile shift method (QSM) could become beneficial, it is applied to a theoretical medical example and a real data example. Basically, real data points (or specific points of interest) are used and the changes of the prediction after slightly raising or decreasing specific features are observed. By comparing the predictions before and after the manipulations, under certain conditions the observed changes in the predictions can be interpreted as neighborhoods of the classes with regard to the manipulated features. Chordgraphs are used to visualize the observed changes.
Hybrid Machine Learning Forecasts for the FIFA Women's World Cup 2019
Jun 03, 2019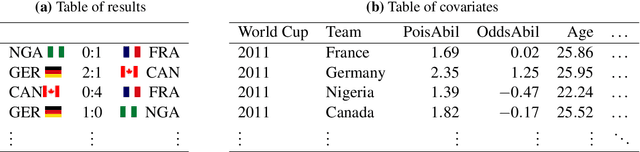
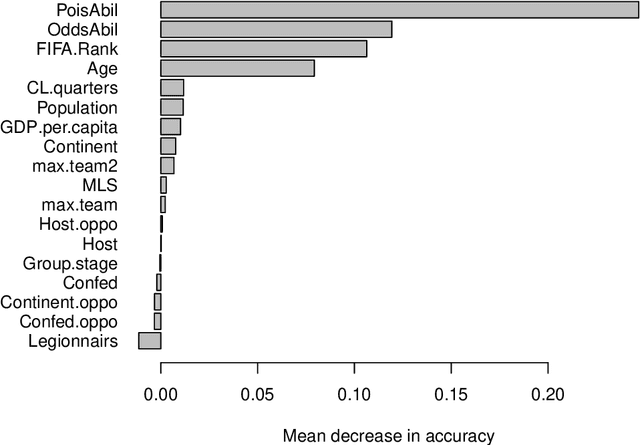
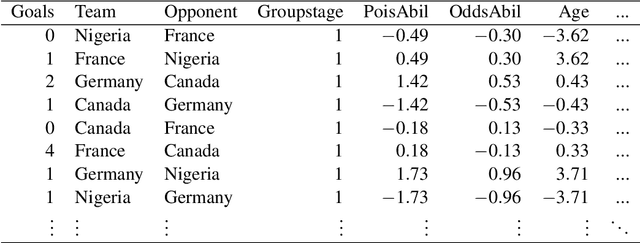
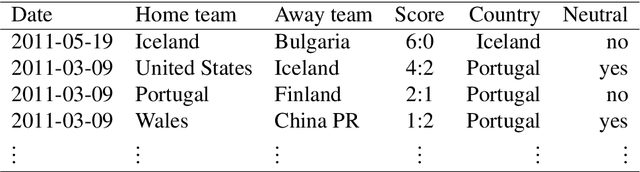
Abstract:In this work, we combine two different ranking methods together with several other predictors in a joint random forest approach for the scores of soccer matches. The first ranking method is based on the bookmaker consensus, the second ranking method estimates adequate ability parameters that reflect the current strength of the teams best. The proposed combined approach is then applied to the data from the two previous FIFA Women's World Cups 2011 and 2015. Finally, based on the resulting estimates, the FIFA Women's World Cup 2019 is simulated repeatedly and winning probabilities are obtained for all teams. The model clearly favors the defending champion USA before the host France.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge