Guillaume Raille
Darts: User-Friendly Modern Machine Learning for Time Series
Oct 08, 2021Abstract:We present Darts, a Python machine learning library for time series, with a focus on forecasting. Darts offers a variety of models, from classics such as ARIMA to state-of-the-art deep neural networks. The emphasis of the library is on offering modern machine learning functionalities, such as supporting multidimensional series, meta-learning on multiple series, training on large datasets, incorporating external data, ensembling models, and providing a rich support for probabilistic forecasting. At the same time, great care goes into the API design to make it user-friendly and easy to use. For instance, all models can be used using fit()/predict(), similar to scikit-learn.
Fast Cross-domain Data Augmentation through Neural Sentence Editing
Mar 23, 2020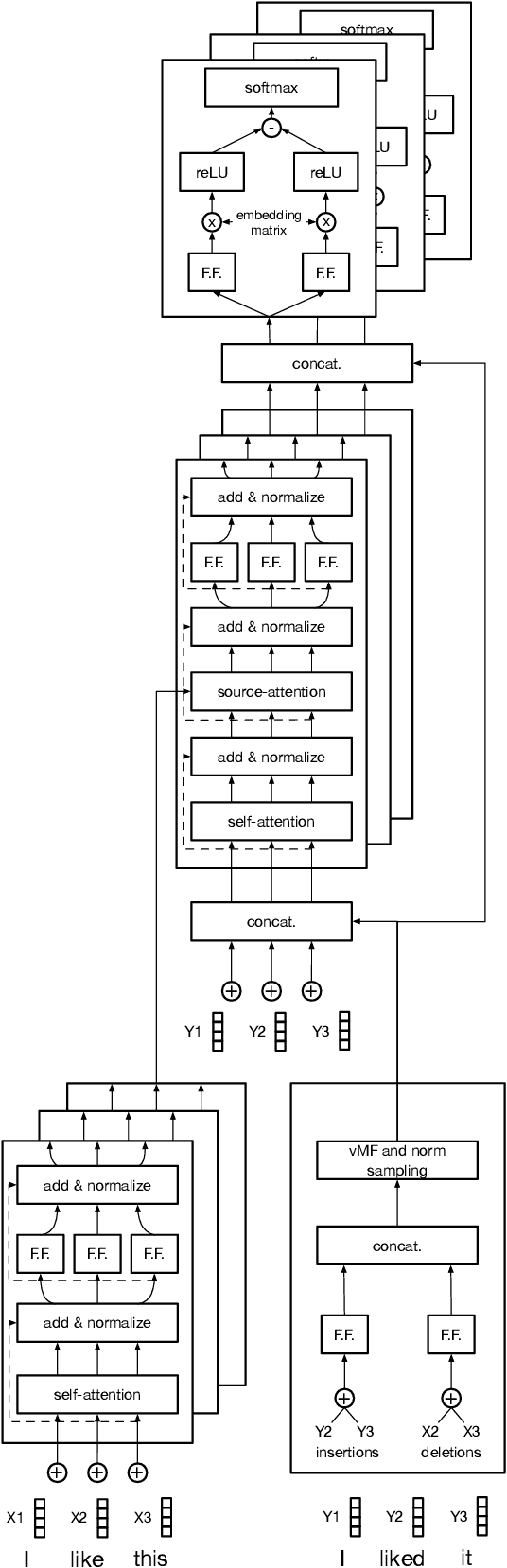

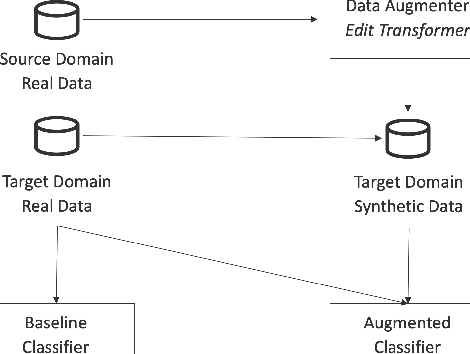
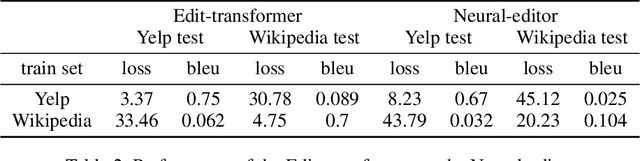
Abstract:Data augmentation promises to alleviate data scarcity. This is most important in cases where the initial data is in short supply. This is, for existing methods, also where augmenting is the most difficult, as learning the full data distribution is impossible. For natural language, sentence editing offers a solution - relying on small but meaningful changes to the original ones. Learning which changes are meaningful also requires large amounts of training data. We thus aim to learn this in a source domain where data is abundant and apply it in a different, target domain, where data is scarce - cross-domain augmentation. We create the Edit-transformer, a Transformer-based sentence editor that is significantly faster than the state of the art and also works cross-domain. We argue that, due to its structure, the Edit-transformer is better suited for cross-domain environments than its edit-based predecessors. We show this performance gap on the Yelp-Wikipedia domain pairs. Finally, we show that due to this cross-domain performance advantage, the Edit-transformer leads to meaningful performance gains in several downstream tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge