Guido van Wingen
Benchmarking Graph Neural Networks for FMRI analysis
Nov 16, 2022Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have emerged as a powerful tool to learn from graph-structured data. A paramount example of such data is the brain, which operates as a network, from the micro-scale of neurons, to the macro-scale of regions. This organization deemed GNNs a natural tool of choice to model brain activity, and have consequently attracted a lot of attention in the neuroimaging community. Yet, the advantage of adopting these models over conventional methods has not yet been assessed in a systematic way to gauge if GNNs are capable of leveraging the underlying structure of the data to improve learning. In this work, we study and evaluate the performance of five popular GNN architectures in diagnosing major depression disorder and autism spectrum disorder in two multi-site clinical datasets, and sex classification on the UKBioBank, from functional brain scans under a general uniform framework. Our results show that GNNs fail to outperform kernel-based and structure-agnostic deep learning models, in which 1D CNNs outperform the other methods in all scenarios. We highlight that creating optimal graph structures for functional brain data is a major bottleneck hindering the performance of GNNs, where existing works use arbitrary measures to define the edges resulting in noisy graphs. We therefore propose to integrate graph diffusion into existing architectures and show that it can alleviate this problem and improve their performance. Our results call for increased moderation and rigorous validation when evaluating graph methods and advocate for more data-centeric approaches in developing GNNs for functional neuroimaging applications.
Dynamic Adaptive Spatio-temporal Graph Convolution for fMRI Modelling
Sep 26, 2021



Abstract:The characterisation of the brain as a functional network in which the connections between brain regions are represented by correlation values across time series has been very popular in the last years. Although this representation has advanced our understanding of brain function, it represents a simplified model of brain connectivity that has a complex dynamic spatio-temporal nature. Oversimplification of the data may hinder the merits of applying advanced non-linear feature extraction algorithms. To this end, we propose a dynamic adaptive spatio-temporal graph convolution (DAST-GCN) model to overcome the shortcomings of pre-defined static correlation-based graph structures. The proposed approach allows end-to-end inference of dynamic connections between brain regions via layer-wise graph structure learning module while mapping brain connectivity to a phenotype in a supervised learning framework. This leverages the computational power of the model, data and targets to represent brain connectivity, and could enable the identification of potential biomarkers for the supervised target in question. We evaluate our pipeline on the UKBiobank dataset for age and gender classification tasks from resting-state functional scans and show that it outperforms currently adapted linear and non-linear methods in neuroimaging. Further, we assess the generalizability of the inferred graph structure by transferring the pre-trained graph to an independent dataset for the same task. Our results demonstrate the task-robustness of the graph against different scanning parameters and demographics.
* Accepted at International Workshop on Machine Learning in Clinical Neuroimaging (MLCN2021)
A Hybrid 3DCNN and 3DC-LSTM based model for 4D Spatio-temporal fMRI data: An ABIDE Autism Classification study
Feb 14, 2020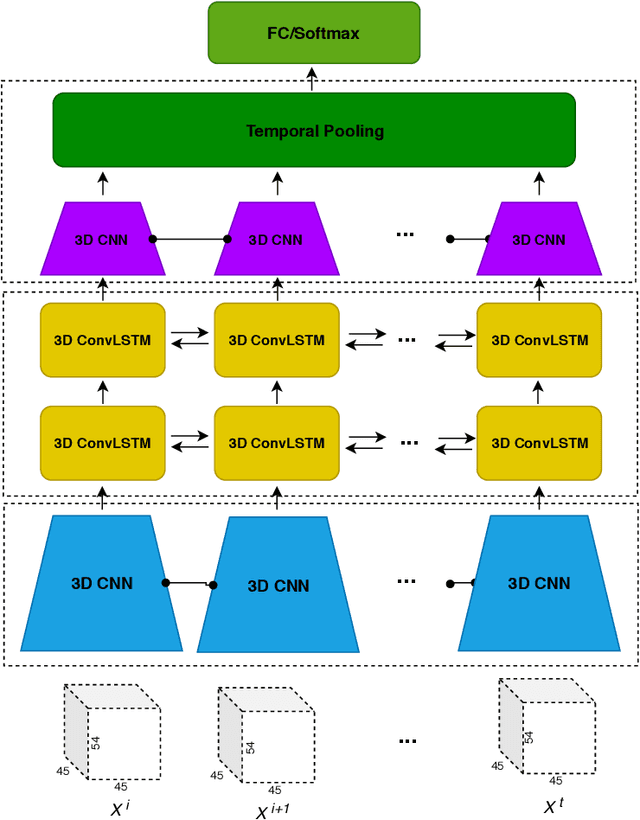
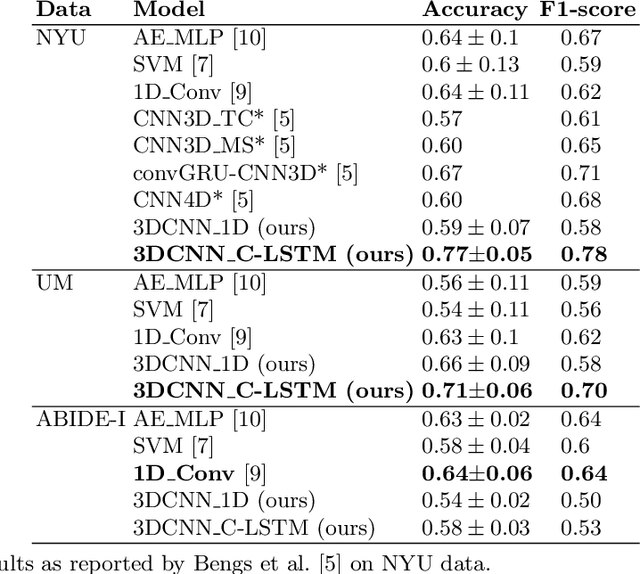
Abstract:Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) captures the temporal dynamics of neural activity as a function of spatial location in the brain. Thus, fMRI scans are represented as 4-Dimensional (3-space + 1-time) tensors. And it is widely believed that the spatio-temporal patterns in fMRI manifests as behaviour and clinical symptoms. Because of the high dimensionality ($\sim$ 1 Million) of fMRI, and the added constraints of limited cardinality of data sets, extracting such patterns are challenging. A standard approach to overcome these hurdles is to reduce the dimensionality of the data by either summarizing activation over time or space at the expense of possible loss of useful information. Here, we introduce an end-to-end algorithm capable of extracting spatiotemporal features from the full 4-D data using 3-D CNNs and 3-D Convolutional LSTMs. We evaluate our proposed model on the publicly available ABIDE dataset to demonstrate the capability of our model to classify Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) from resting-state fMRI data. Our results show that the proposed model achieves state of the art results on single sites with F1-scores of 0.78 and 0.7 on NYU and UM sites, respectively.
* 8pages
Simple 1-D Convolutional Networks for Resting-State fMRI Based Classification in Autism
Jul 02, 2019
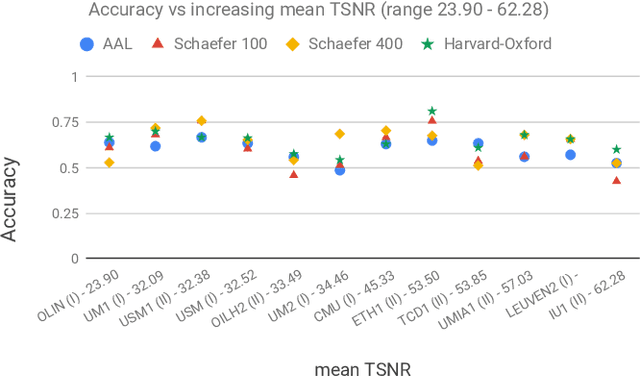
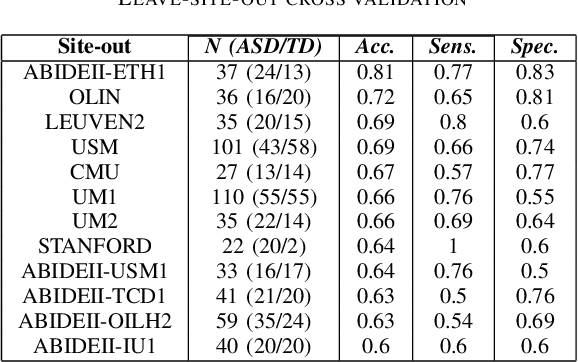
Abstract:Deep learning methods are increasingly being used with neuroimaging data like structural and function magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to predict the diagnosis of neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders. For psychiatric disorders in particular, it is believed that one of the most promising modality is the resting-state functional MRI (rsfMRI), which captures the intrinsic connectivity between regions in the brain. Because rsfMRI data points are inherently high-dimensional (~1M), it is impossible to process the entire input in its raw form. In this paper, we propose a very simple transformation of the rsfMRI images that captures all of the temporal dynamics of the signal but sub-samples its spatial extent. As a result, we use a very simple 1-D convolutional network which is fast to train, requires minimal preprocessing and performs at par with the state-of-the-art on the classification of Autism spectrum disorders.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge