Gregory Robbins
BMW Agents -- A Framework For Task Automation Through Multi-agent Collaboration
Jun 28, 2024Abstract:Autonomous agents driven by Large Language Models (LLMs) offer enormous potential for automation. Early proof of this technology can be found in various demonstrations of agents solving complex tasks, interacting with external systems to augment their knowledge, and triggering actions. In particular, workflows involving multiple agents solving complex tasks in a collaborative fashion exemplify their capacity to operate in less strict and less well-defined environments. Thus, a multi-agent approach has great potential for serving as a backbone in many industrial applications, ranging from complex knowledge retrieval systems to next generation robotic process automation. Given the reasoning abilities within the current generation of LLMs, complex processes require a multi-step approach that includes a plan of well-defined and modular tasks. Depending on the level of complexity, these tasks can be executed either by a single agent or a group of agents. In this work, we focus on designing a flexible agent engineering framework with careful attention to planning and execution, capable of handling complex use case applications across various domains. The proposed framework provides reliability in industrial applications and presents techniques to ensure a scalable, flexible, and collaborative workflow for multiple autonomous agents working together towards solving tasks.
Natural Language Processing to Detect Cognitive Concerns in Electronic Health Records Using Deep Learning
Nov 12, 2020
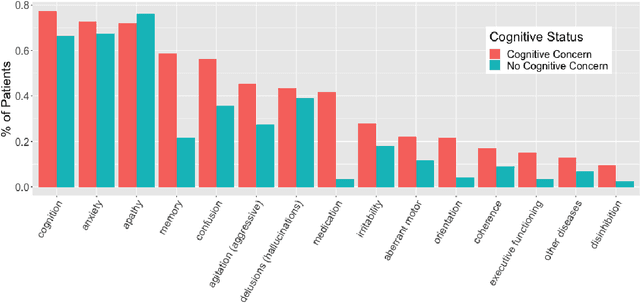
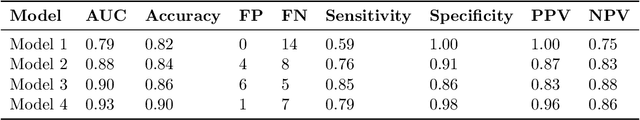
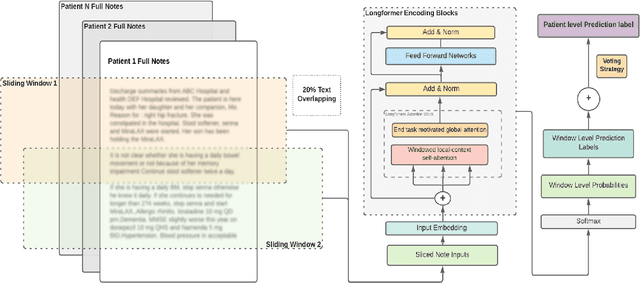
Abstract:Dementia is under-recognized in the community, under-diagnosed by healthcare professionals, and under-coded in claims data. Information on cognitive dysfunction, however, is often found in unstructured clinician notes within medical records but manual review by experts is time consuming and often prone to errors. Automated mining of these notes presents a potential opportunity to label patients with cognitive concerns who could benefit from an evaluation or be referred to specialist care. In order to identify patients with cognitive concerns in electronic medical records, we applied natural language processing (NLP) algorithms and compared model performance to a baseline model that used structured diagnosis codes and medication data only. An attention-based deep learning model outperformed the baseline model and other simpler models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge