Govert Verkes
BYOC: Personalized Few-Shot Classification with Co-Authored Class Descriptions
Oct 09, 2023Abstract:Text classification is a well-studied and versatile building block for many NLP applications. Yet, existing approaches require either large annotated corpora to train a model with or, when using large language models as a base, require carefully crafting the prompt as well as using a long context that can fit many examples. As a result, it is not possible for end-users to build classifiers for themselves. To address this issue, we propose a novel approach to few-shot text classification using an LLM. Rather than few-shot examples, the LLM is prompted with descriptions of the salient features of each class. These descriptions are coauthored by the user and the LLM interactively: while the user annotates each few-shot example, the LLM asks relevant questions that the user answers. Examples, questions, and answers are summarized to form the classification prompt. Our experiments show that our approach yields high accuracy classifiers, within 82% of the performance of models trained with significantly larger datasets while using only 1% of their training sets. Additionally, in a study with 30 participants, we show that end-users are able to build classifiers to suit their specific needs. The personalized classifiers show an average accuracy of 90%, which is 15% higher than the state-of-the-art approach.
High-bandwidth Close-Range Information Transport through Light Pipes
Jan 19, 2023
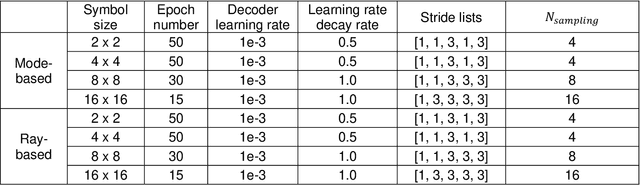

Abstract:Image retrieval after propagation through multi-mode fibers is gaining attention due to their capacity to confine light and efficiently transport it over distances in a compact system. Here, we propose a generally applicable information-theoretic framework to transmit maximal-entropy (data) images and maximize the information transmission over sub-meter distances, a crucial capability that allows optical storage applications to scale and address different parts of storage media. To this end, we use millimeter-sized square optical waveguides to image a megapixel 8-bit spatial-light modulator. Data is thus represented as a 2D array of 8-bit values (symbols). Transmitting 100000s of symbols requires innovation beyond transmission matrix approaches. Deep neural networks have been recently utilized to retrieve images, but have been limited to small (thousands of symbols) and natural looking (low entropy) images. We maximize information transmission by combining a bandwidth-optimized homodyne detector with a differentiable hybrid neural-network consisting of a digital twin of the experiment setup and a U-Net. For the digital twin, we implement and compare a differentiable mode-based twin with a differentiable ray-based twin. Importantly, the latter can adapt to manufacturing-related setup imperfections during training which we show to be crucial. Our pipeline is trained end-to-end to recover digital input images while maximizing the achievable information page size based on a differentiable mutual-information estimator. We demonstrate retrieval of 66 kB at maximum with 1.7 bit per symbol on average with a range of 0.3 - 3.4 bit.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge