Gordon Lim
Label Errors in the Tobacco3482 Dataset
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Tobacco3482 is a widely used document classification benchmark dataset. However, our manual inspection of the entire dataset uncovers widespread ontological issues, especially large amounts of annotation label problems in the dataset. We establish data label guidelines and find that 11.7% of the dataset is improperly annotated and should either have an unknown label or a corrected label, and 16.7% of samples in the dataset have multiple valid labels. We then analyze the mistakes of a top-performing model and find that 35% of the model's mistakes can be directly attributed to these label issues, highlighting the inherent problems with using a noisily labeled dataset as a benchmark. Supplementary material, including dataset annotations and code, is available at https://github.com/gordon-lim/tobacco3482-mistakes/.
Robust Testing for Deep Learning using Human Label Noise
Nov 29, 2024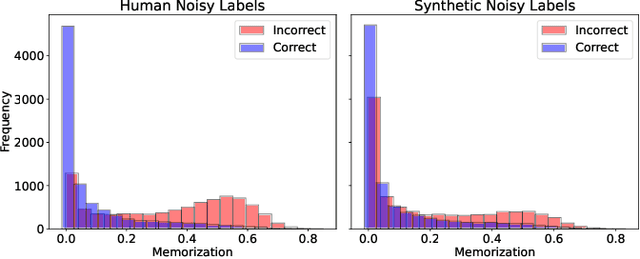
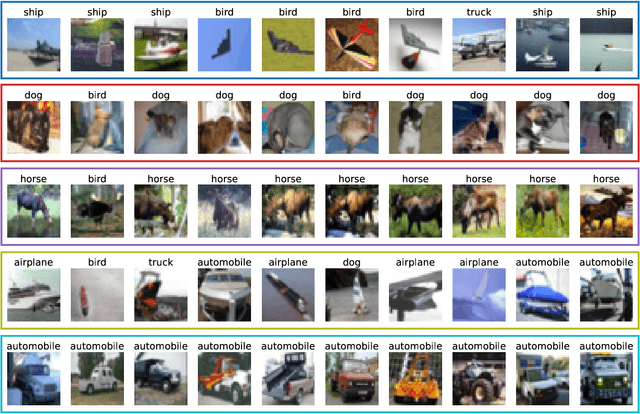
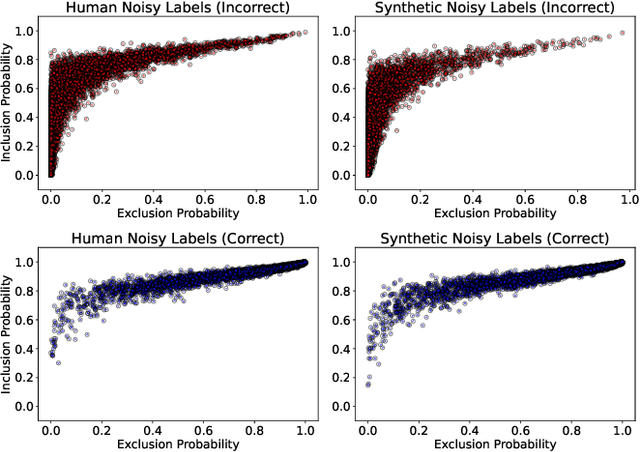
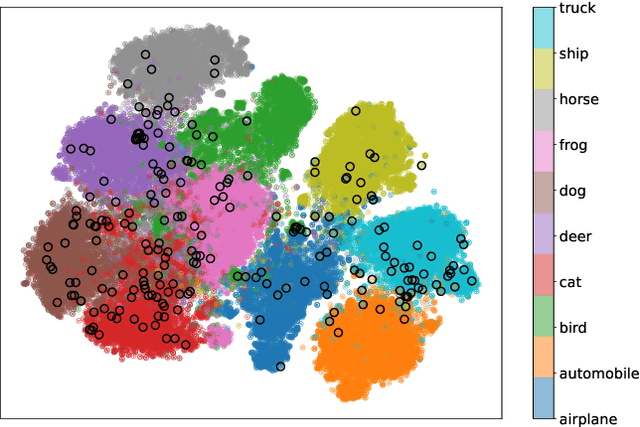

Abstract:In deep learning (DL) systems, label noise in training datasets often degrades model performance, as models may learn incorrect patterns from mislabeled data. The area of Learning with Noisy Labels (LNL) has introduced methods to effectively train DL models in the presence of noisily-labeled datasets. Traditionally, these methods are tested using synthetic label noise, where ground truth labels are randomly (and automatically) flipped. However, recent findings highlight that models perform substantially worse under human label noise than synthetic label noise, indicating a need for more realistic test scenarios that reflect noise introduced due to imperfect human labeling. This underscores the need for generating realistic noisy labels that simulate human label noise, enabling rigorous testing of deep neural networks without the need to collect new human-labeled datasets. To address this gap, we present Cluster-Based Noise (CBN), a method for generating feature-dependent noise that simulates human-like label noise. Using insights from our case study of label memorization in the CIFAR-10N dataset, we design CBN to create more realistic tests for evaluating LNL methods. Our experiments demonstrate that current LNL methods perform worse when tested using CBN, highlighting its use as a rigorous approach to testing neural networks. Next, we propose Soft Neighbor Label Sampling (SNLS), a method designed to handle CBN, demonstrating its improvement over existing techniques in tackling this more challenging type of noise.
On Evaluation of Document Classification using RVL-CDIP
Jun 21, 2023



Abstract:The RVL-CDIP benchmark is widely used for measuring performance on the task of document classification. Despite its widespread use, we reveal several undesirable characteristics of the RVL-CDIP benchmark. These include (1) substantial amounts of label noise, which we estimate to be 8.1% (ranging between 1.6% to 16.9% per document category); (2) presence of many ambiguous or multi-label documents; (3) a large overlap between test and train splits, which can inflate model performance metrics; and (4) presence of sensitive personally-identifiable information like US Social Security numbers (SSNs). We argue that there is a risk in using RVL-CDIP for benchmarking document classifiers, as its limited scope, presence of errors (state-of-the-art models now achieve accuracy error rates that are within our estimated label error rate), and lack of diversity make it less than ideal for benchmarking. We further advocate for the creation of a new document classification benchmark, and provide recommendations for what characteristics such a resource should include.
Evaluating Out-of-Distribution Performance on Document Image Classifiers
Oct 14, 2022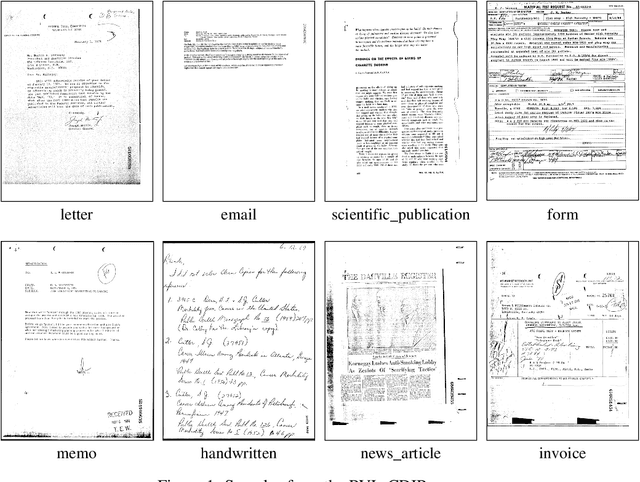
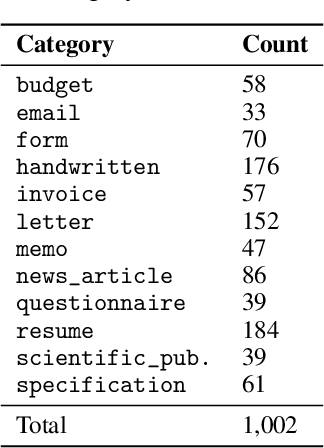

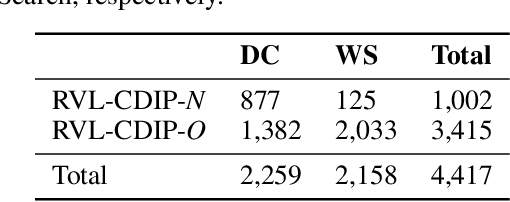
Abstract:The ability of a document classifier to handle inputs that are drawn from a distribution different from the training distribution is crucial for robust deployment and generalizability. The RVL-CDIP corpus is the de facto standard benchmark for document classification, yet to our knowledge all studies that use this corpus do not include evaluation on out-of-distribution documents. In this paper, we curate and release a new out-of-distribution benchmark for evaluating out-of-distribution performance for document classifiers. Our new out-of-distribution benchmark consists of two types of documents: those that are not part of any of the 16 in-domain RVL-CDIP categories (RVL-CDIP-O), and those that are one of the 16 in-domain categories yet are drawn from a distribution different from that of the original RVL-CDIP dataset (RVL-CDIP-N). While prior work on document classification for in-domain RVL-CDIP documents reports high accuracy scores, we find that these models exhibit accuracy drops of between roughly 15-30% on our new out-of-domain RVL-CDIP-N benchmark, and further struggle to distinguish between in-domain RVL-CDIP-N and out-of-domain RVL-CDIP-O inputs. Our new benchmark provides researchers with a valuable new resource for analyzing out-of-distribution performance on document classifiers. Our new out-of-distribution data can be found at https://tinyurl.com/4he6my23.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge