Gonzalo Rubio
Aerodynamic and structural airfoil shape optimisation via Transfer Learning-enhanced Deep Reinforcement Learning
May 05, 2025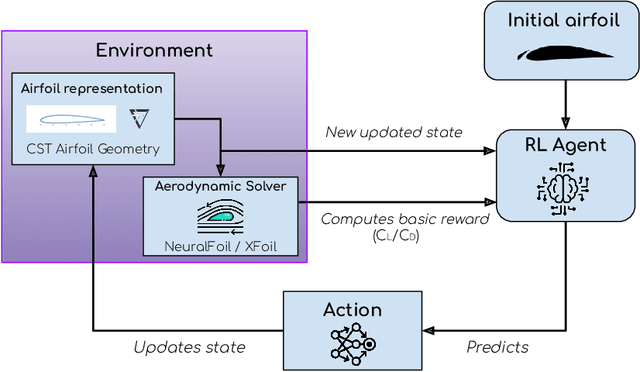
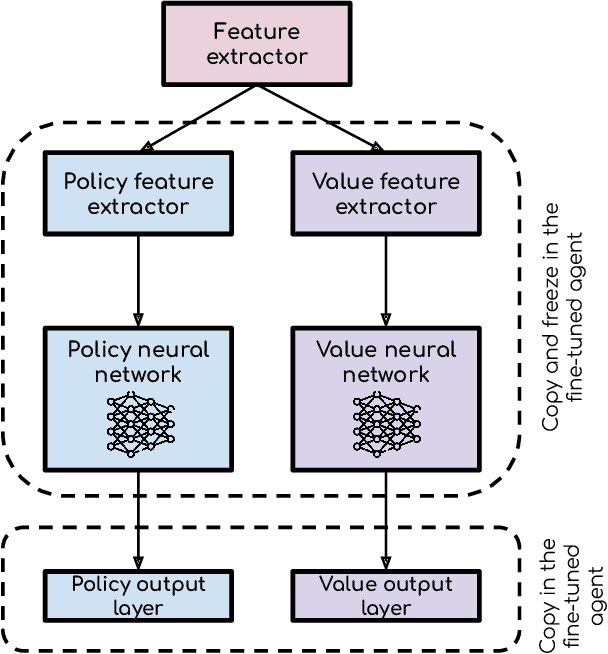

Abstract:The main objective of this paper is to introduce a transfer learning-enhanced, multi-objective, deep reinforcement learning (DRL) methodology that is able to optimise the geometry of any airfoil based on concomitant aerodynamic and structural criteria. To showcase the method, we aim to maximise the lift-to-drag ratio $C_L/C_D$ while preserving the structural integrity of the airfoil -- as modelled by its maximum thickness -- and train the DRL agent using a list of different transfer learning (TL) strategies. The performance of the DRL agent is compared with Particle Swarm Optimisation (PSO), a traditional gradient-free optimisation method. Results indicate that DRL agents are able to perform multi-objective shape optimisation, that the DRL approach outperforms PSO in terms of computational efficiency and shape optimisation performance, and that the TL-enhanced DRL agent achieves performance comparable to the DRL one, while further saving substantial computational resources.
Towards certification: A complete statistical validation pipeline for supervised learning in industry
Nov 04, 2024



Abstract:Methods of Machine and Deep Learning are gradually being integrated into industrial operations, albeit at different speeds for different types of industries. The aerospace and aeronautical industries have recently developed a roadmap for concepts of design assurance and integration of neural network-related technologies in the aeronautical sector. This paper aims to contribute to this paradigm of AI-based certification in the context of supervised learning, by outlining a complete validation pipeline that integrates deep learning, optimization and statistical methods. This pipeline is composed by a directed graphical model of ten steps. Each of these steps is addressed by a merging key concepts from different contributing disciplines (from machine learning or optimization to statistics) and adapting them to an industrial scenario, as well as by developing computationally efficient algorithmic solutions. We illustrate the application of this pipeline in a realistic supervised problem arising in aerostructural design: predicting the likelikood of different stress-related failure modes during different airflight maneuvers based on a (large) set of features characterising the aircraft internal loads and geometric parameters.
Reinforcement learning for anisotropic p-adaptation and error estimation in high-order solvers
Jul 26, 2024Abstract:We present a novel approach to automate and optimize anisotropic p-adaptation in high-order h/p solvers using Reinforcement Learning (RL). The dynamic RL adaptation uses the evolving solution to adjust the high-order polynomials. We develop an offline training approach, decoupled from the main solver, which shows minimal overcost when performing simulations. In addition, we derive a RL-based error estimation approach that enables the quantification of local discretization errors. The proposed methodology is agnostic to both the computational mesh and the partial differential equation being solved. The application of RL to mesh adaptation offers several benefits. It enables automated, adaptive mesh refinement, reducing the need for manual intervention. It optimizes computational resources by dynamically allocating high-order polynomials where necessary and minimizing refinement in stable regions. This leads to computational cost savings while maintaining solution accuracy. Furthermore, RL allows for the exploration of unconventional mesh adaptations, potentially enhancing the accuracy and robustness of simulations. This work extends our original research, offering a more robust, reproducible, and generalizable approach applicable to complex three-dimensional problems. We provide validation for laminar and turbulent cases: circular cylinders, Taylor Green Vortex and a 10MW wind turbine to illustrate the flexibility of the proposed approach.
A reinforcement learning strategy to automate and accelerate h/p-multigrid solvers
Jul 18, 2024Abstract:We explore a reinforcement learning strategy to automate and accelerate h/p-multigrid methods in high-order solvers. Multigrid methods are very efficient but require fine-tuning of numerical parameters, such as the number of smoothing sweeps per level and the correction fraction (i.e., proportion of the corrected solution that is transferred from a coarser grid to a finer grid). The objective of this paper is to use a proximal policy optimization algorithm to automatically tune the multigrid parameters and, by doing so, improve stability and efficiency of the h/p-multigrid strategy. Our findings reveal that the proposed reinforcement learning h/p-multigrid approach significantly accelerates and improves the robustness of steady-state simulations for one dimensional advection-diffusion and nonlinear Burgers' equations, when discretized using high-order h/p methods, on uniform and nonuniform grids.
Unsupervised machine-learning shock-capturing technique for high-order solvers
Aug 07, 2023Abstract:We present a novel unsupervised machine learning shock capturing algorithm based on Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs). The proposed GMM sensor demonstrates remarkable accuracy in detecting shocks and is robust across diverse test cases without the need for parameter tuning. We compare the GMM-based sensor with state-of-the-art alternatives. All methods are integrated into a high-order compressible discontinuous Galerkin solver where artificial viscosity can be modulated to capture shocks. Supersonic test cases, including high Reynolds numbers, showcase the sensor's performance, demonstrating the same effectiveness as fine-tuned state-of-the-art sensors. %The nodal DG aproach allows for potential applications in sub-cell flux-differencing formulations, supersonic feature detection, and mesh refinement. The adaptive nature and ability to function without extensive training datasets make this GMM-based sensor suitable for complex geometries and varied flow configurations. Our study reveals the potential of unsupervised machine learning methods, exemplified by the GMM sensor, to improve the robustness and efficiency of advanced CFD codes.
A reinforcement learning strategy for p-adaptation in high order solvers
Jun 14, 2023Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a promising approach to automating decision processes. This paper explores the application of RL techniques to optimise the polynomial order in the computational mesh when using high-order solvers. Mesh adaptation plays a crucial role in improving the efficiency of numerical simulations by improving accuracy while reducing the cost. Here, actor-critic RL models based on Proximal Policy Optimization offer a data-driven approach for agents to learn optimal mesh modifications based on evolving conditions. The paper provides a strategy for p-adaptation in high-order solvers and includes insights into the main aspects of RL-based mesh adaptation, including the formulation of appropriate reward structures and the interaction between the RL agent and the simulation environment. We discuss the impact of RL-based mesh p-adaptation on computational efficiency and accuracy. We test the RL p-adaptation strategy on a 1D inviscid Burgers' equation to demonstrate the effectiveness of the strategy. The RL strategy reduces the computational cost and improves accuracy over uniform adaptation, while minimising human intervention.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge