Gonçalo Raposo
Document-Level Abstractive Summarization
Dec 06, 2022Abstract:The task of automatic text summarization produces a concise and fluent text summary while preserving key information and overall meaning. Recent approaches to document-level summarization have seen significant improvements in recent years by using models based on the Transformer architecture. However, the quadratic memory and time complexities with respect to the sequence length make them very expensive to use, especially with long sequences, as required by document-level summarization. Our work addresses the problem of document-level summarization by studying how efficient Transformer techniques can be used to improve the automatic summarization of very long texts. In particular, we will use the arXiv dataset, consisting of several scientific papers and the corresponding abstracts, as baselines for this work. Then, we propose a novel retrieval-enhanced approach based on the architecture which reduces the cost of generating a summary of the entire document by processing smaller chunks. The results were below the baselines but suggest a more efficient memory a consumption and truthfulness.
Question rewriting? Assessing its importance for conversational question answering
Jan 22, 2022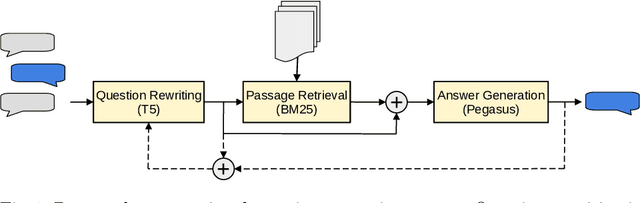
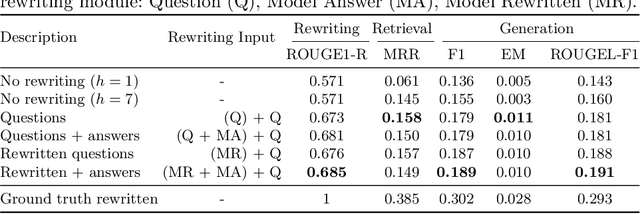
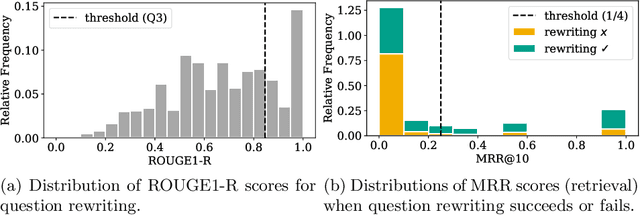
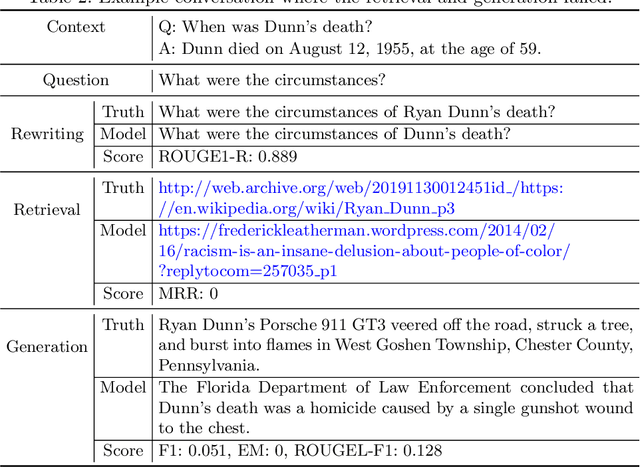
Abstract:In conversational question answering, systems must correctly interpret the interconnected interactions and generate knowledgeable answers, which may require the retrieval of relevant information from a background repository. Recent approaches to this problem leverage neural language models, although different alternatives can be considered in terms of modules for (a) representing user questions in context, (b) retrieving the relevant background information, and (c) generating the answer. This work presents a conversational question answering system designed specifically for the Search-Oriented Conversational AI (SCAI) shared task, and reports on a detailed analysis of its question rewriting module. In particular, we considered different variations of the question rewriting module to evaluate the influence on the subsequent components, and performed a careful analysis of the results obtained with the best system configuration. Our system achieved the best performance in the shared task and our analysis emphasizes the importance of the conversation context representation for the overall system performance.
PositNN: Training Deep Neural Networks with Mixed Low-Precision Posit
May 14, 2021



Abstract:Low-precision formats have proven to be an efficient way to reduce not only the memory footprint but also the hardware resources and power consumption of deep learning computations. Under this premise, the posit numerical format appears to be a highly viable substitute for the IEEE floating-point, but its application to neural networks training still requires further research. Some preliminary results have shown that 8-bit (and even smaller) posits may be used for inference and 16-bit for training, while maintaining the model accuracy. The presented research aims to evaluate the feasibility to train deep convolutional neural networks using posits. For such purpose, a software framework was developed to use simulated posits and quires in end-to-end training and inference. This implementation allows using any bit size, configuration, and even mixed precision, suitable for different precision requirements in various stages. The obtained results suggest that 8-bit posits can substitute 32-bit floats during training with no negative impact on the resulting loss and accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge