Ghassan Harmarneh
AViT: Adapting Vision Transformers for Small Skin Lesion Segmentation Datasets
Jul 26, 2023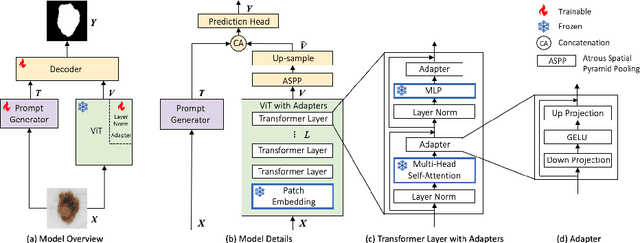
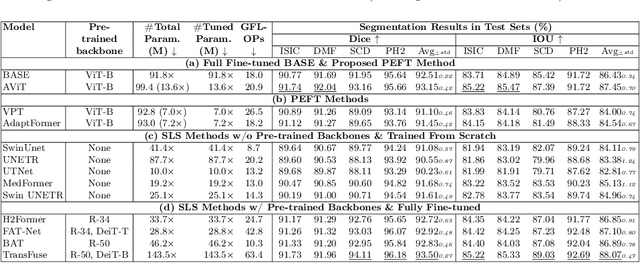
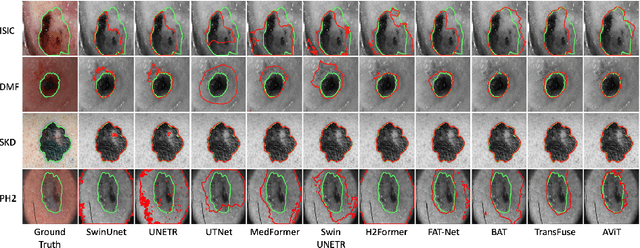
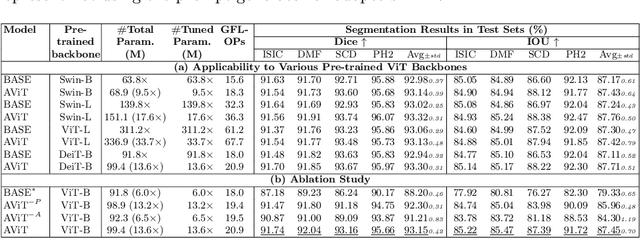
Abstract:Skin lesion segmentation (SLS) plays an important role in skin lesion analysis. Vision transformers (ViTs) are considered an auspicious solution for SLS, but they require more training data compared to convolutional neural networks (CNNs) due to their inherent parameter-heavy structure and lack of some inductive biases. To alleviate this issue, current approaches fine-tune pre-trained ViT backbones on SLS datasets, aiming to leverage the knowledge learned from a larger set of natural images to lower the amount of skin training data needed. However, fully fine-tuning all parameters of large backbones is computationally expensive and memory intensive. In this paper, we propose AViT, a novel efficient strategy to mitigate ViTs' data-hunger by transferring any pre-trained ViTs to the SLS task. Specifically, we integrate lightweight modules (adapters) within the transformer layers, which modulate the feature representation of a ViT without updating its pre-trained weights. In addition, we employ a shallow CNN as a prompt generator to create a prompt embedding from the input image, which grasps fine-grained information and CNN's inductive biases to guide the segmentation task on small datasets. Our quantitative experiments on 4 skin lesion datasets demonstrate that AViT achieves competitive, and at times superior, performance to SOTA but with significantly fewer trainable parameters. Our code is available at https://github.com/siyi-wind/AViT.
MDViT: Multi-domain Vision Transformer for Small Medical Image Segmentation Datasets
Jul 26, 2023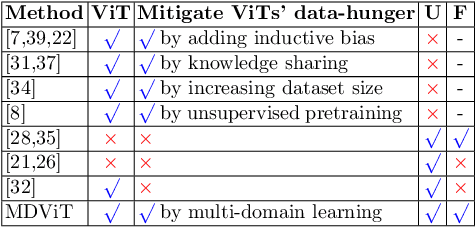
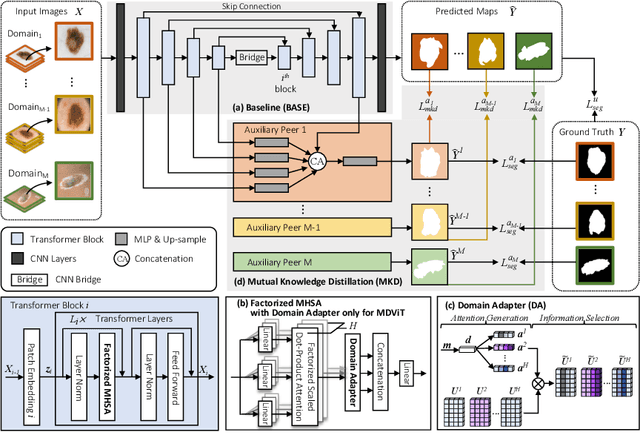
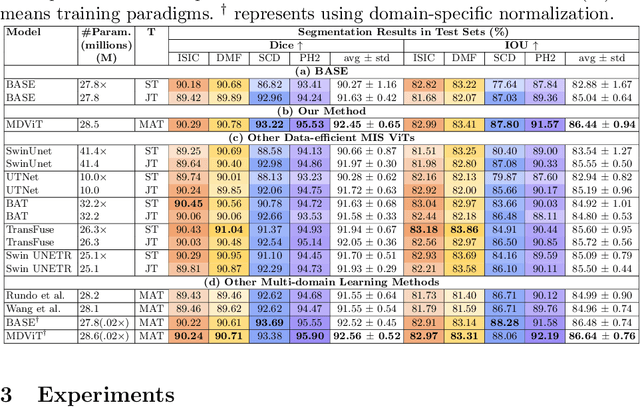
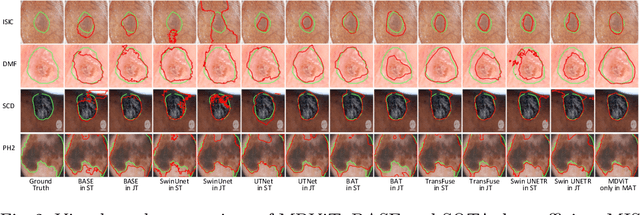
Abstract:Despite its clinical utility, medical image segmentation (MIS) remains a daunting task due to images' inherent complexity and variability. Vision transformers (ViTs) have recently emerged as a promising solution to improve MIS; however, they require larger training datasets than convolutional neural networks. To overcome this obstacle, data-efficient ViTs were proposed, but they are typically trained using a single source of data, which overlooks the valuable knowledge that could be leveraged from other available datasets. Naivly combining datasets from different domains can result in negative knowledge transfer (NKT), i.e., a decrease in model performance on some domains with non-negligible inter-domain heterogeneity. In this paper, we propose MDViT, the first multi-domain ViT that includes domain adapters to mitigate data-hunger and combat NKT by adaptively exploiting knowledge in multiple small data resources (domains). Further, to enhance representation learning across domains, we integrate a mutual knowledge distillation paradigm that transfers knowledge between a universal network (spanning all the domains) and auxiliary domain-specific branches. Experiments on 4 skin lesion segmentation datasets show that MDViT outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms, with superior segmentation performance and a fixed model size, at inference time, even as more domains are added. Our code is available at https://github.com/siyi-wind/MDViT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge