Gerhard Klimeck
Probabilistic Diagnostic Tests for Degradation Problems in Supervised Learning
Apr 15, 2020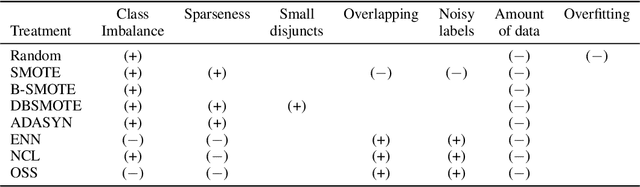
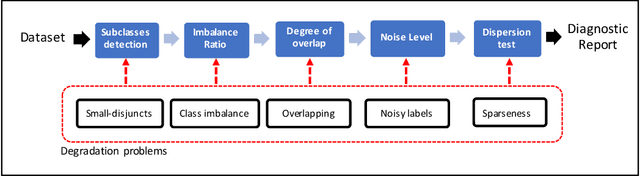
Abstract:Several studies point out different causes of performance degradation in supervised machine learning. Problems such as class imbalance, overlapping, small-disjuncts, noisy labels, and sparseness limit accuracy in classification algorithms. Even though a number of approaches either in the form of a methodology or an algorithm try to minimize performance degradation, they have been isolated efforts with limited scope. Most of these approaches focus on remediation of one among many problems, with experimental results coming from few datasets and classification algorithms, insufficient measures of prediction power, and lack of statistical validation for testing the real benefit of the proposed approach. This paper consists of two main parts: In the first part, a novel probabilistic diagnostic model based on identifying signs and symptoms of each problem is presented. Thereby, early and correct diagnosis of these problems is to be achieved in order to select not only the most convenient remediation treatment but also unbiased performance metrics. Secondly, the behavior and performance of several supervised algorithms are studied when training sets have such problems. Therefore, prediction of success for treatments can be estimated across classifiers.
A Statistical Approach to Increase Classification Accuracy in Supervised Learning Algorithms
Sep 05, 2017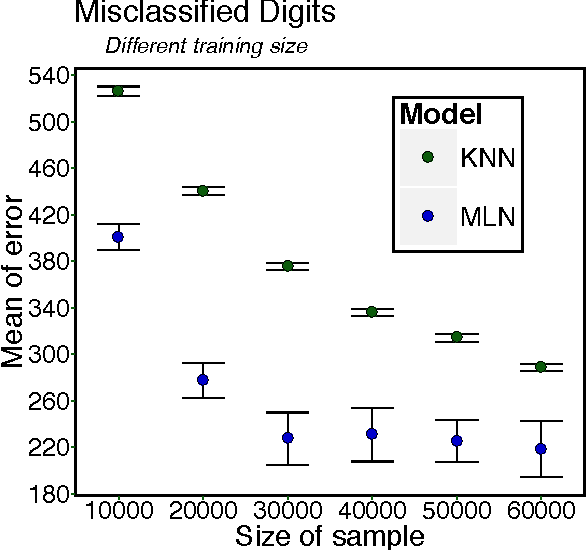
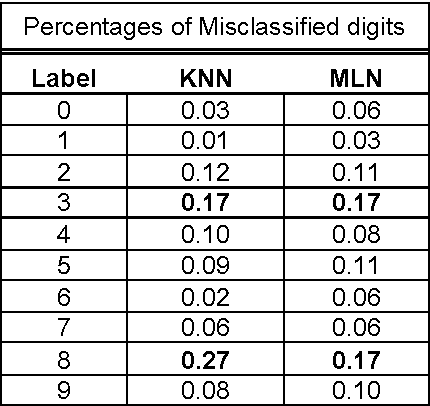
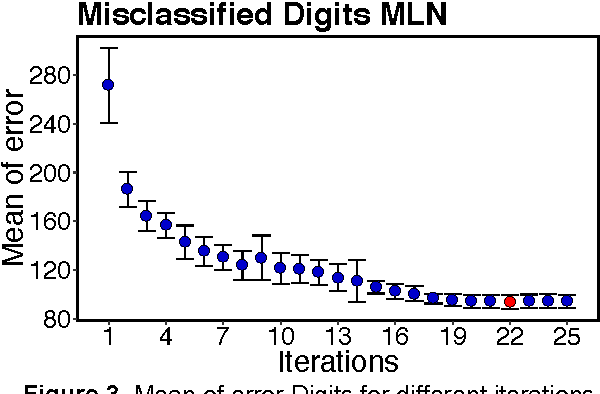
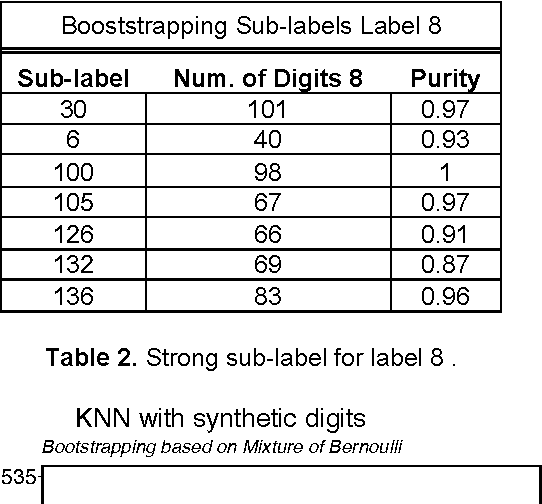
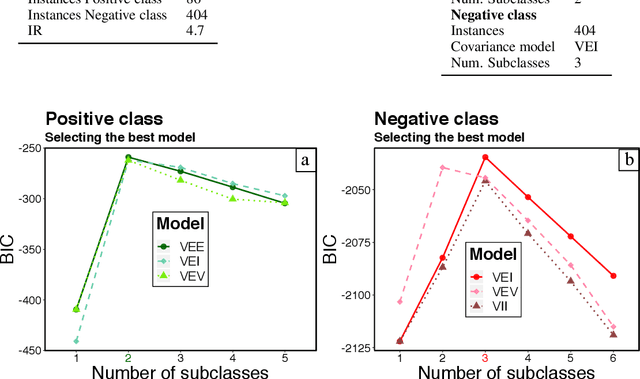
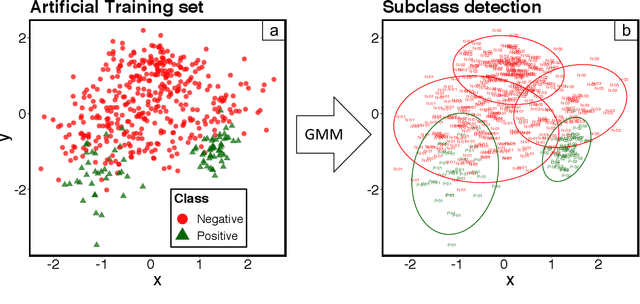
Abstract:Probabilistic mixture models have been widely used for different machine learning and pattern recognition tasks such as clustering, dimensionality reduction, and classification. In this paper, we focus on trying to solve the most common challenges related to supervised learning algorithms by using mixture probability distribution functions. With this modeling strategy, we identify sub-labels and generate synthetic data in order to reach better classification accuracy. It means we focus on increasing the training data synthetically to increase the classification accuracy.
* 7 pages, 9 figures, IPSI BgD Transactions
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge