George Mastorakos
The 2024 Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) Challenge: Glioma Segmentation on Post-treatment MRI
May 28, 2024
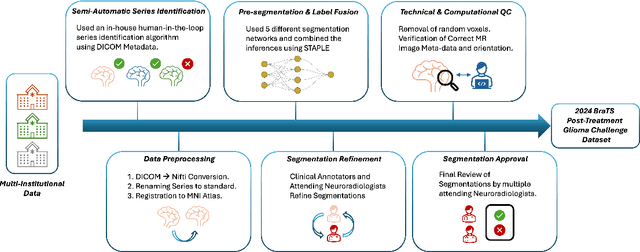
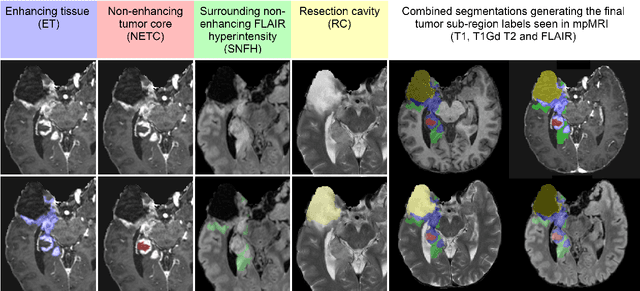
Abstract:Gliomas are the most common malignant primary brain tumors in adults and one of the deadliest types of cancer. There are many challenges in treatment and monitoring due to the genetic diversity and high intrinsic heterogeneity in appearance, shape, histology, and treatment response. Treatments include surgery, radiation, and systemic therapies, with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) playing a key role in treatment planning and post-treatment longitudinal assessment. The 2024 Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) challenge on post-treatment glioma MRI will provide a community standard and benchmark for state-of-the-art automated segmentation models based on the largest expert-annotated post-treatment glioma MRI dataset. Challenge competitors will develop automated segmentation models to predict four distinct tumor sub-regions consisting of enhancing tissue (ET), surrounding non-enhancing T2/fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) hyperintensity (SNFH), non-enhancing tumor core (NETC), and resection cavity (RC). Models will be evaluated on separate validation and test datasets using standardized performance metrics utilized across the BraTS 2024 cluster of challenges, including lesion-wise Dice Similarity Coefficient and Hausdorff Distance. Models developed during this challenge will advance the field of automated MRI segmentation and contribute to their integration into clinical practice, ultimately enhancing patient care.
Learning Unbiased Image Segmentation: A Case Study with Plain Knee Radiographs
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:Automatic segmentation of knee bony anatomy is essential in orthopedics, and it has been around for several years in both pre-operative and post-operative settings. While deep learning algorithms have demonstrated exceptional performance in medical image analysis, the assessment of fairness and potential biases within these models remains limited. This study aims to revisit deep learning-powered knee-bony anatomy segmentation using plain radiographs to uncover visible gender and racial biases. The current contribution offers the potential to advance our understanding of biases, and it provides practical insights for researchers and practitioners in medical imaging. The proposed mitigation strategies mitigate gender and racial biases, ensuring fair and unbiased segmentation results. Furthermore, this work promotes equal access to accurate diagnoses and treatment outcomes for diverse patient populations, fostering equitable and inclusive healthcare provision.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge