Genevieve Fried
About Face: A Survey of Facial Recognition Evaluation
Feb 01, 2021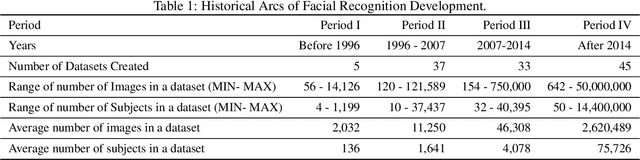
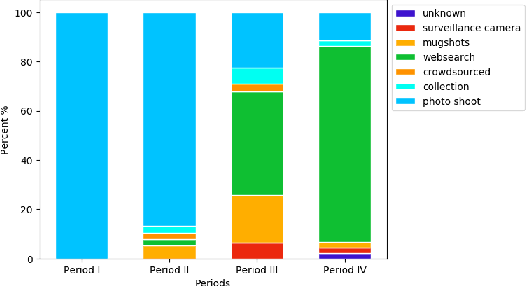
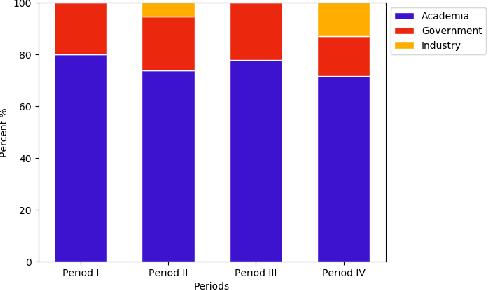
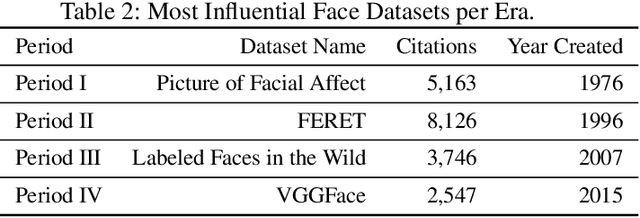
Abstract:We survey over 100 face datasets constructed between 1976 to 2019 of 145 million images of over 17 million subjects from a range of sources, demographics and conditions. Our historical survey reveals that these datasets are contextually informed, shaped by changes in political motivations, technological capability and current norms. We discuss how such influences mask specific practices (some of which may actually be harmful or otherwise problematic) and make a case for the explicit communication of such details in order to establish a more grounded understanding of the technology's function in the real world.
Ethical Challenges in Data-Driven Dialogue Systems
Nov 24, 2017



Abstract:The use of dialogue systems as a medium for human-machine interaction is an increasingly prevalent paradigm. A growing number of dialogue systems use conversation strategies that are learned from large datasets. There are well documented instances where interactions with these system have resulted in biased or even offensive conversations due to the data-driven training process. Here, we highlight potential ethical issues that arise in dialogue systems research, including: implicit biases in data-driven systems, the rise of adversarial examples, potential sources of privacy violations, safety concerns, special considerations for reinforcement learning systems, and reproducibility concerns. We also suggest areas stemming from these issues that deserve further investigation. Through this initial survey, we hope to spur research leading to robust, safe, and ethically sound dialogue systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge