Gal Patel
MuLER: Detailed and Scalable Reference-based Evaluation
May 24, 2023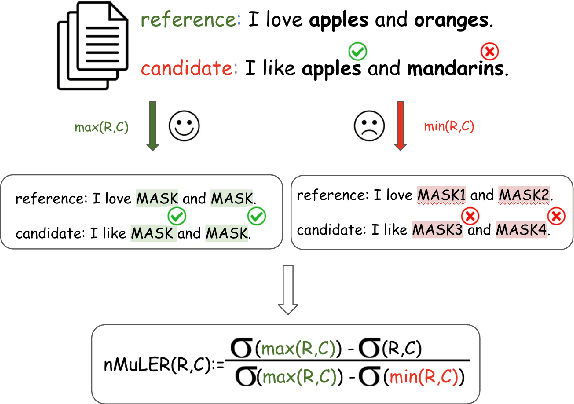
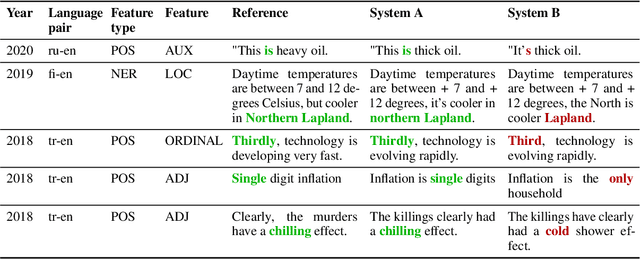
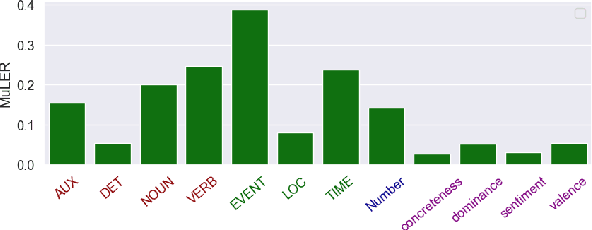
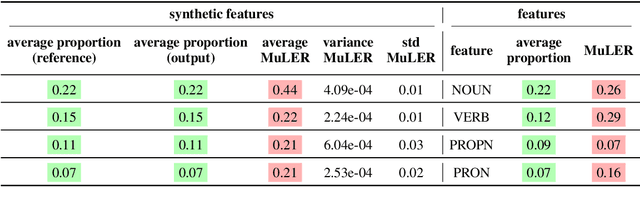
Abstract:We propose a novel methodology (namely, MuLER) that transforms any reference-based evaluation metric for text generation, such as machine translation (MT) into a fine-grained analysis tool. Given a system and a metric, MuLER quantifies how much the chosen metric penalizes specific error types (e.g., errors in translating names of locations). MuLER thus enables a detailed error analysis which can lead to targeted improvement efforts for specific phenomena. We perform experiments in both synthetic and naturalistic settings to support MuLER's validity and showcase its usability in MT evaluation, and other tasks, such as summarization. Analyzing all submissions to WMT in 2014-2020, we find consistent trends. For example, nouns and verbs are among the most frequent POS tags. However, they are among the hardest to translate. Performance on most POS tags improves with overall system performance, but a few are not thus correlated (their identity changes from language to language). Preliminary experiments with summarization reveal similar trends.
On Neurons Invariant to Sentence Structural Changes in Neural Machine Translation
Oct 06, 2021
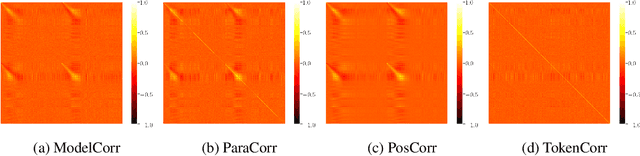

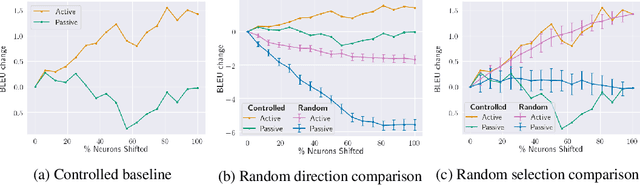
Abstract:To gain insight into the role neurons play, we study the activation patterns corresponding to meaning-preserving paraphrases (e.g., active-passive). We compile a dataset of controlled syntactic paraphrases in English with their reference German translations and demonstrate our model-agnostic approach with the Transformer translation model. First, we identify neurons that correlate across paraphrases and dissect the observed correlation into possible confounds. Although lower-level components are found as the cause of similar activations, no sentence-level semantics or syntax are detected locally. Later, we manipulate neuron activations to influence translation towards a particular syntactic form. We find that a simple value shift is effective, and more so when many neurons are modified. These suggest that complex syntactic constructions are indeed encoded in the model. We conclude by discussing how to better manipulate it using the correlations we first obtained.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge