Gaël Guibon
LIPN, LORIA
Towards Ontology-Based Descriptions of Conversations with Qualitatively-Defined Concepts
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:The controllability of Large Language Models (LLMs) when used as conversational agents is a key challenge, particularly to ensure predictable and user-personalized responses. This work proposes an ontology-based approach to formally define conversational features that are typically qualitative in nature. By leveraging a set of linguistic descriptors, we derive quantitative definitions for qualitatively-defined concepts, enabling their integration into an ontology for reasoning and consistency checking. We apply this framework to the task of proficiency-level control in conversations, using CEFR language proficiency levels as a case study. These definitions are then formalized in description logic and incorporated into an ontology, which guides controlled text generation of an LLM through fine-tuning. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach provides consistent and explainable proficiency-level definitions, improving transparency in conversational AI.
Context-Aware Siamese Networks for Efficient Emotion Recognition in Conversation
Apr 17, 2024Abstract:The advent of deep learning models has made a considerable contribution to the achievement of Emotion Recognition in Conversation (ERC). However, this task still remains an important challenge due to the plurality and subjectivity of human emotions. Previous work on ERC provides predictive models using mostly graph-based conversation representations. In this work, we propose a way to model the conversational context that we incorporate into a metric learning training strategy, with a two-step process. This allows us to perform ERC in a flexible classification scenario and to end up with a lightweight yet efficient model. Using metric learning through a Siamese Network architecture, we achieve 57.71 in macro F1 score for emotion classification in conversation on DailyDialog dataset, which outperforms the related work. This state-of-the-art result is promising regarding the use of metric learning for emotion recognition, yet perfectible compared to the microF1 score obtained.
Few-Shot Emotion Recognition in Conversation with Sequential Prototypical Networks
Sep 20, 2021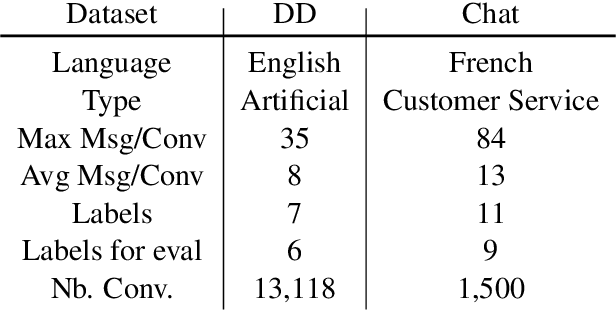
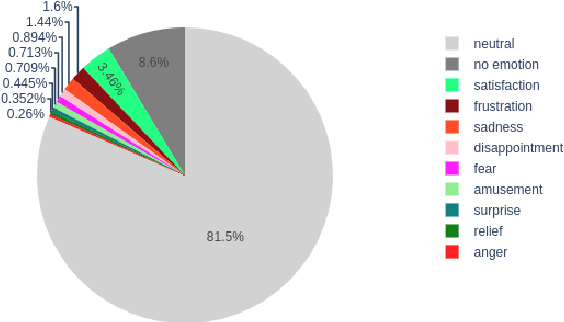
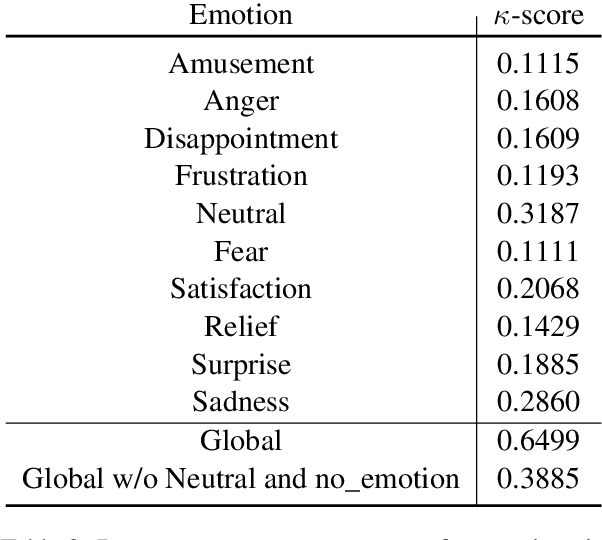
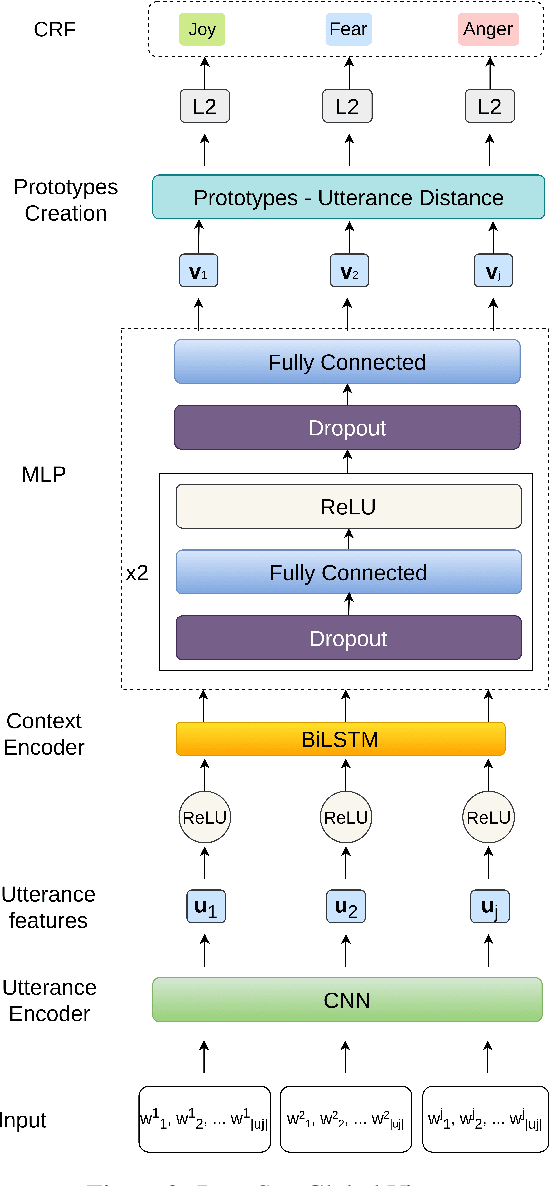
Abstract:Several recent studies on dyadic human-human interactions have been done on conversations without specific business objectives. However, many companies might benefit from studies dedicated to more precise environments such as after sales services or customer satisfaction surveys. In this work, we place ourselves in the scope of a live chat customer service in which we want to detect emotions and their evolution in the conversation flow. This context leads to multiple challenges that range from exploiting restricted, small and mostly unlabeled datasets to finding and adapting methods for such context.We tackle these challenges by using Few-Shot Learning while making the hypothesis it can serve conversational emotion classification for different languages and sparse labels. We contribute by proposing a variation of Prototypical Networks for sequence labeling in conversation that we name ProtoSeq. We test this method on two datasets with different languages: daily conversations in English and customer service chat conversations in French. When applied to emotion classification in conversations, our method proved to be competitive even when compared to other ones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge