G. S. Yogesh
Integration of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data for Earth surface classification using Machine Learning algorithms implemented on Google Earth Engine
Aug 22, 2023



Abstract:In this study, Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and optical data are both considered for Earth surface classification. Specifically, the integration of Sentinel-1 (S-1) and Sentinel-2 (S-2) data is carried out through supervised Machine Learning (ML) algorithms implemented on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform for the classification of a particular region of interest. Achieved results demonstrate how in this case radar and optical remote detection provide complementary information, benefiting surface cover classification and generally leading to increased mapping accuracy. In addition, this paper works in the direction of proving the emerging role of GEE as an effective cloud-based tool for handling large amounts of satellite data.
Multitemporal analysis in Google Earth Engine for detecting urban changes using optical data and machine learning algorithms
Aug 22, 2023
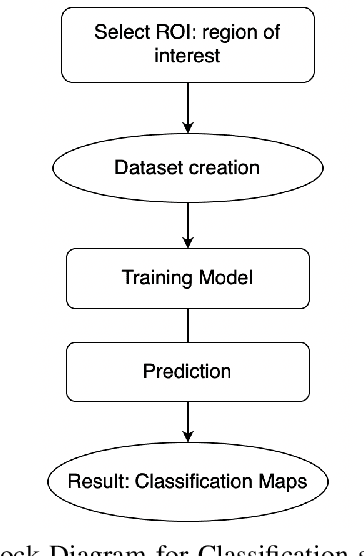


Abstract:The aim of this work is to perform a multitemporal analysis using the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform for the detection of changes in urban areas using optical data and specific machine learning (ML) algorithms. As a case study, Cairo City has been identified, in Egypt country, as one of the five most populous megacities of the last decade in the world. Classification and change detection analysis of the region of interest (ROI) have been carried out from July 2013 to July 2021. Results demonstrate the validity of the proposed method in identifying changed and unchanged urban areas over the selected period. Furthermore, this work aims to evidence the growing significance of GEE as an efficient cloud-based solution for managing large quantities of satellite data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge