Fujio Toriumi
QANA: LLM-based Question Generation and Network Analysis for Zero-shot Key Point Analysis and Beyond
Apr 29, 2024Abstract:The proliferation of social media has led to information overload and increased interest in opinion mining. We propose "Question-Answering Network Analysis" (QANA), a novel opinion mining framework that utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate questions from users' comments, constructs a bipartite graph based on the comments' answerability to the questions, and applies centrality measures to examine the importance of opinions. We investigate the impact of question generation styles, LLM selections, and the choice of embedding model on the quality of the constructed QA networks by comparing them with annotated Key Point Analysis datasets. QANA achieves comparable performance to previous state-of-the-art supervised models in a zero-shot manner for Key Point Matching task, also reducing the computational cost from quadratic to linear. For Key Point Generation, questions with high PageRank or degree centrality align well with manually annotated key points. Notably, QANA enables analysts to assess the importance of key points from various aspects according to their selection of centrality measure. QANA's primary contribution lies in its flexibility to extract key points from a wide range of perspectives, which enhances the quality and impartiality of opinion mining.
HyperS2V: A Framework for Structural Representation of Nodes in Hyper Networks
Nov 07, 2023Abstract:In contrast to regular (simple) networks, hyper networks possess the ability to depict more complex relationships among nodes and store extensive information. Such networks are commonly found in real-world applications, such as in social interactions. Learning embedded representations for nodes involves a process that translates network structures into more simplified spaces, thereby enabling the application of machine learning approaches designed for vector data to be extended to network data. Nevertheless, there remains a need to delve into methods for learning embedded representations that prioritize structural aspects. This research introduces HyperS2V, a node embedding approach that centers on the structural similarity within hyper networks. Initially, we establish the concept of hyper-degrees to capture the structural properties of nodes within hyper networks. Subsequently, a novel function is formulated to measure the structural similarity between different hyper-degree values. Lastly, we generate structural embeddings utilizing a multi-scale random walk framework. Moreover, a series of experiments, both intrinsic and extrinsic, are performed on both toy and real networks. The results underscore the superior performance of HyperS2V in terms of both interpretability and applicability to downstream tasks.
User's Position-Dependent Strategies in Consumer-Generated Media with Monetary Rewards
Oct 07, 2023Abstract:Numerous forms of consumer-generated media (CGM), such as social networking services (SNS), are widely used. Their success relies on users' voluntary participation, often driven by psychological rewards like recognition and connection from reactions by other users. Furthermore, a few CGM platforms offer monetary rewards to users, serving as incentives for sharing items such as articles, images, and videos. However, users have varying preferences for monetary and psychological rewards, and the impact of monetary rewards on user behaviors and the quality of the content they post remains unclear. Hence, we propose a model that integrates some monetary reward schemes into the SNS-norms game, which is an abstraction of CGM. Subsequently, we investigate the effect of each monetary reward scheme on individual agents (users), particularly in terms of their proactivity in posting items and their quality, depending on agents' positions in a CGM network. Our experimental results suggest that these factors distinctly affect the number of postings and their quality. We believe that our findings will help CGM platformers in designing better monetary reward schemes.
Effect of Monetary Reward on Users' Individual Strategies Using Co-Evolutionary Learning
Jun 01, 2023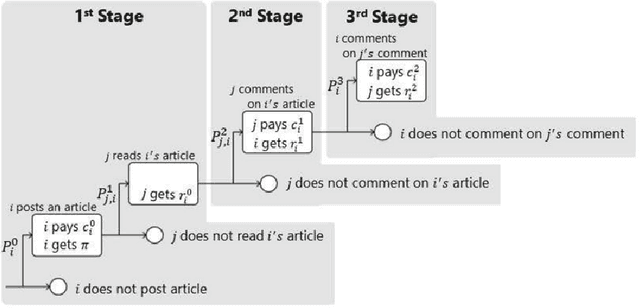

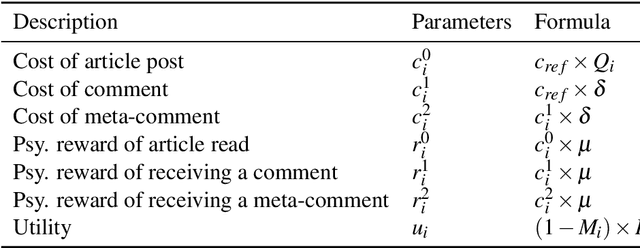
Abstract:Consumer generated media (CGM), such as social networking services rely on the voluntary activity of users to prosper, garnering the psychological rewards of feeling connected with other people through comments and reviews received online. To attract more users, some CGM have introduced monetary rewards (MR) for posting activity and quality articles and comments. However, the impact of MR on the article posting strategies of users, especially frequency and quality, has not been fully analyzed by previous studies, because they ignored the difference in the standpoint in the CGM networks, such as how many friends/followers they have, although we think that their strategies vary with their standpoints. The purpose of this study is to investigate the impact of MR on individual users by considering the differences in dominant strategies regarding user standpoints. Using the game-theoretic model for CGM, we experimentally show that a variety of realistic dominant strategies are evolved depending on user standpoints in the CGM network, using multiple-world genetic algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge