Fredrik Gunnarsson
Vehicular Wireless Positioning -- A Survey
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:The rapid advancement of connected and autonomous vehicles has driven a growing demand for precise and reliable positioning systems capable of operating in complex environments. Meeting these demands requires an integrated approach that combines multiple positioning technologies, including wireless-based systems, perception-based technologies, and motion-based sensors. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of wireless-based positioning for vehicular applications, with a focus on satellite-based positioning (such as global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) and low-Earth-orbit (LEO) satellites), cellular-based positioning (5G and beyond), and IEEE-based technologies (including Wi-Fi, ultrawideband (UWB), Bluetooth, and vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communications). First, the survey reviews a wide range of vehicular positioning use cases, outlining their specific performance requirements. Next, it explores the historical development, standardization, and evolution of each wireless positioning technology, providing an in-depth categorization of existing positioning solutions and algorithms, and identifying open challenges and contemporary trends. Finally, the paper examines sensor fusion techniques that integrate these wireless systems with onboard perception and motion sensors to enhance positioning accuracy and resilience in real-world conditions. This survey thus offers a holistic perspective on the historical foundations, current advancements, and future directions of wireless-based positioning for vehicular applications, addressing a critical gap in the literature.
5G Deployment Strategies for High Positioning Accuracy in Indoor Environments
May 20, 2021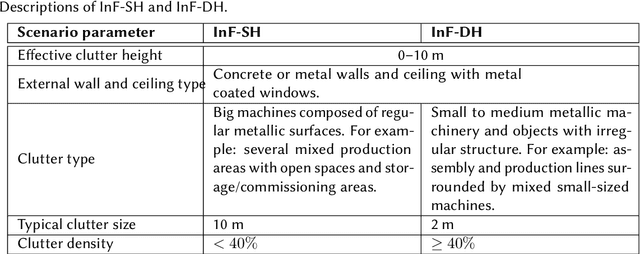
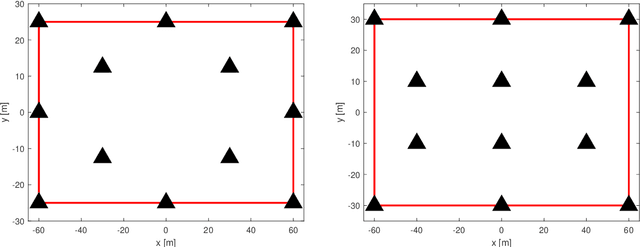

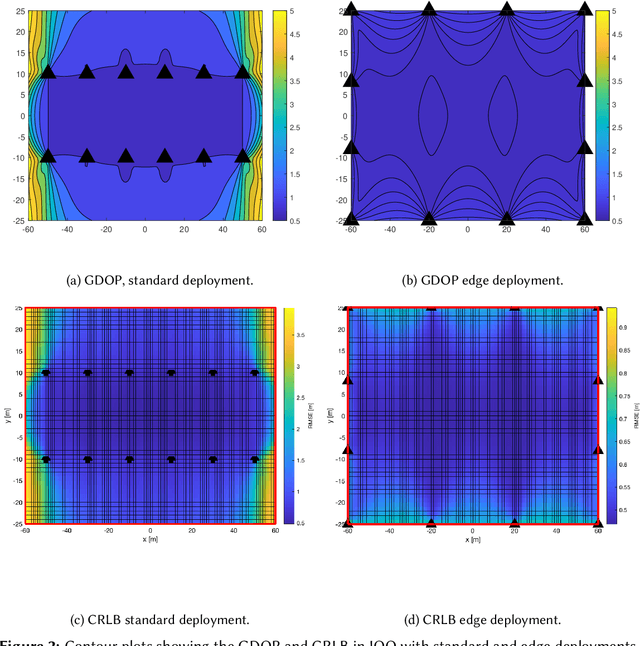
Abstract:Indoor positioning is currently recognized as one of the important features in emergency, commercial and industrial applications. The 5G network enhances mobility, flexibility, reliability, and security to new higher levels which greatly benefit the IoT and industrial applications. Industrial IoT (IIoT) use-cases are characterized by ambitious system requirements for positioning accuracy in many verticals. For example, on the factory floor, it is important to locate assets and moving objects such as forklifts. The deployment design for different IIoT environments has a significant impact on the positioning per-performance in terms of both accuracy and availability of the service. Indoor factory (InF) and indoor open office (IOO) are two available and standardized Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) scenarios for evaluation of indoor channel models and positioning performance in IIoT use cases. This paper aims to evaluate the positioning performance in terms of accuracy and availability while considering different deployment strategies. Our simulation-based evaluation shows that deployment plays a vital role when it comes to achieving high accuracy positioning performance. It is for example favorable to deploy the 5G Transmission and Reception Points (TRPs) on the walls of the factory halls than deploying them attached to the ceiling.
Gaussian Processes for Analyzing Positioned Trajectories in Sports
Jul 05, 2019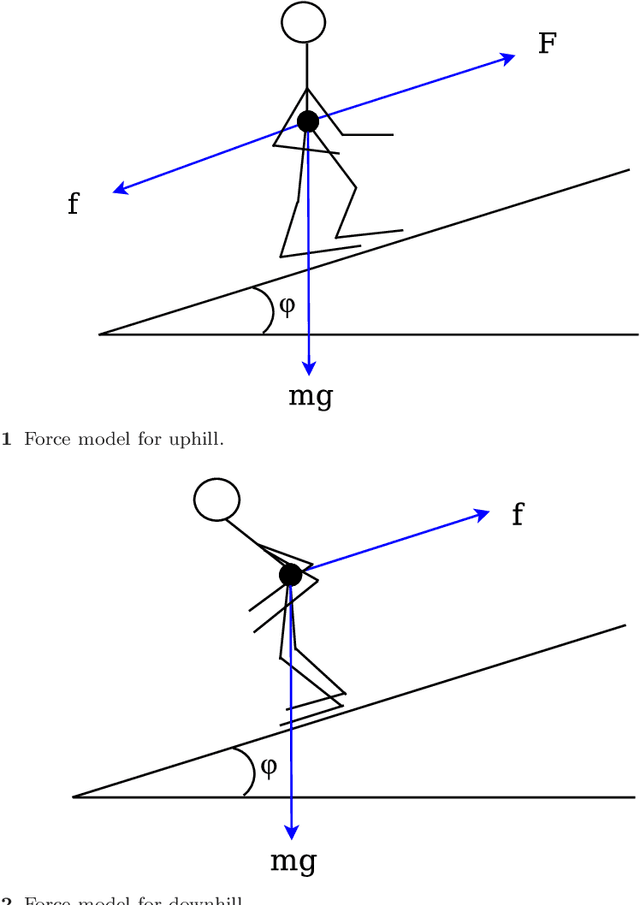
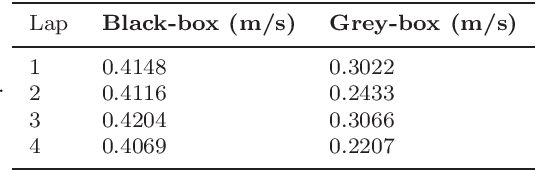
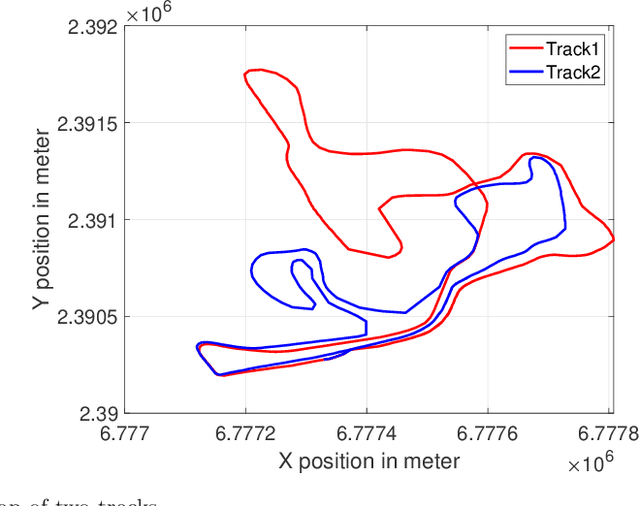
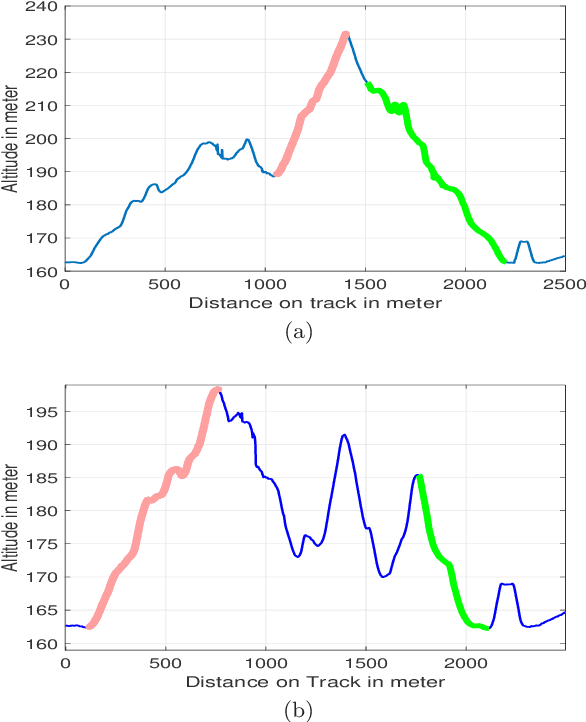
Abstract:Kernel-based machine learning approaches are gaining increasing interest for exploring and modeling large dataset in recent years. Gaussian process (GP) is one example of such kernel-based approaches, which can provide very good performance for nonlinear modeling problems. In this work, we first propose a grey-box modeling approach to analyze the forces in cross country skiing races. To be more precise, a disciplined set of kinetic motion model formulae is combined with data-driven Gaussian process regression model, which accounts for everything unknown in the system. Then, a modeling approach is proposed to analyze the kinetic flow of both individual and clusters of skiers. The proposed approaches can be generally applied to use cases where positioned trajectories and kinetic measurements are available. The proposed approaches are evaluated using data collected from the Falun Nordic World Ski Championships 2015, in particular the Men's cross country $4\times10$ km relay. Forces during the cross country skiing races are analyzed and compared. Velocity models for skiers at different competition stages are also evaluated. Finally, the comparisons between the grey-box and black-box approach are carried out, where the grey-box approach can reduce the predictive uncertainty by $30\%$ to $40\%$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge