Francesca Randone
Model Learning with Personalized Interpretability Estimation (ML-PIE)
Apr 27, 2021
Abstract:High-stakes applications require AI-generated models to be interpretable. Current algorithms for the synthesis of potentially interpretable models rely on objectives or regularization terms that represent interpretability only coarsely (e.g., model size) and are not designed for a specific user. Yet, interpretability is intrinsically subjective. In this paper, we propose an approach for the synthesis of models that are tailored to the user by enabling the user to steer the model synthesis process according to her or his preferences. We use a bi-objective evolutionary algorithm to synthesize models with trade-offs between accuracy and a user-specific notion of interpretability. The latter is estimated by a neural network that is trained concurrently to the evolution using the feedback of the user, which is collected using uncertainty-based active learning. To maximize usability, the user is only asked to tell, given two models at the time, which one is less complex. With experiments on two real-world datasets involving 61 participants, we find that our approach is capable of learning estimations of interpretability that can be very different for different users. Moreover, the users tend to prefer models found using the proposed approach over models found using non-personalized interpretability indices.
Learning a Formula of Interpretability to Learn Interpretable Formulas
May 28, 2020
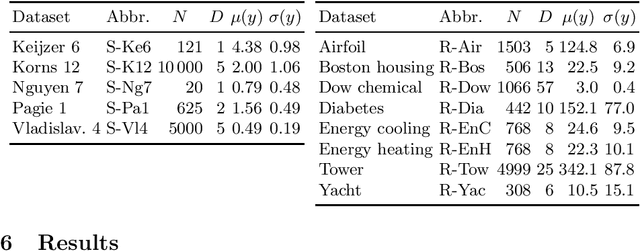

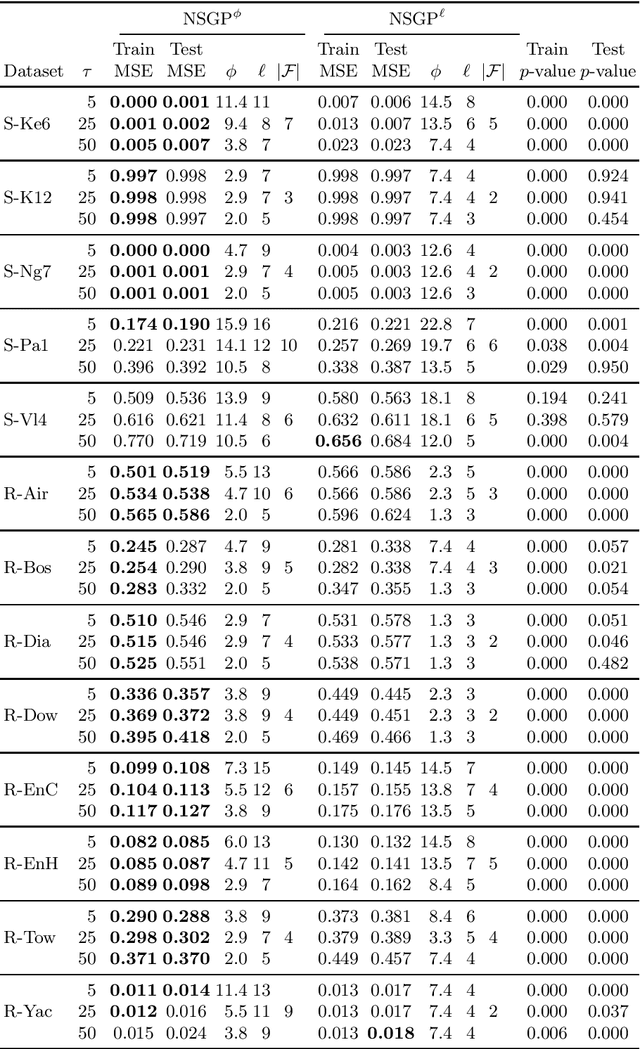
Abstract:Many risk-sensitive applications require Machine Learning (ML) models to be interpretable. Attempts to obtain interpretable models typically rely on tuning, by trial-and-error, hyper-parameters of model complexity that are only loosely related to interpretability. We show that it is instead possible to take a meta-learning approach: an ML model of non-trivial Proxies of Human Interpretability (PHIs) can be learned from human feedback, then this model can be incorporated within an ML training process to directly optimize for interpretability. We show this for evolutionary symbolic regression. We first design and distribute a survey finalized at finding a link between features of mathematical formulas and two established PHIs, simulatability and decomposability. Next, we use the resulting dataset to learn an ML model of interpretability. Lastly, we query this model to estimate the interpretability of evolving solutions within bi-objective genetic programming. We perform experiments on five synthetic and eight real-world symbolic regression problems, comparing to the traditional use of solution size minimization. The results show that the use of our model leads to formulas that are, for a same level of accuracy-interpretability trade-off, either significantly more or equally accurate. Moreover, the formulas are also arguably more interpretable. Given the very positive results, we believe that our approach represents an important stepping stone for the design of next-generation interpretable (evolutionary) ML algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge