Flávio Rainho Ávila
Bayesian Restoration of Audio Degraded by Low-Frequency Pulses Modeled via Gaussian Process
May 28, 2020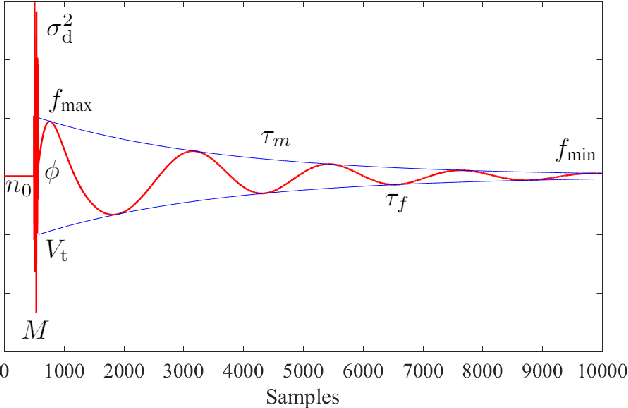
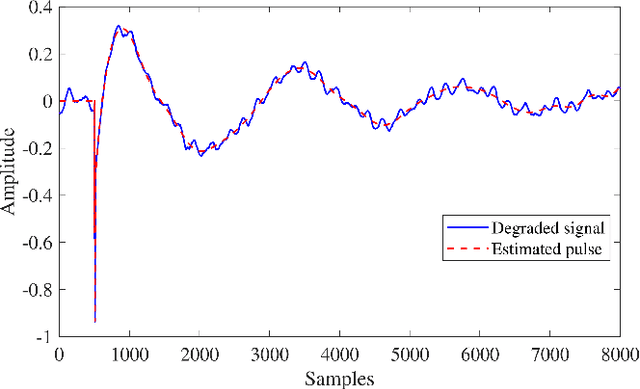
Abstract:A common defect found when reproducing old vinyl and gramophone recordings with mechanical devices are the long pulses with significant low-frequency content caused by the interaction of the arm-needle system with deep scratches or even breakages on the media surface. Previous approaches to their suppression on digital counterparts of the recordings depend on a prior estimation of the pulse location, usually performed via heuristic methods. This paper proposes a novel Bayesian approach capable of jointly estimating the pulse location; interpolating the almost annihilated signal underlying the strong discontinuity that initiates the pulse; and also estimating the long pulse tail by a simple Gaussian Process, allowing its suppression from the corrupted signal. The posterior distribution for the model parameters as well for the pulse is explored via Markov-Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithms. Controlled experiments indicate that the proposed method, while requiring significantly less user intervention, achieves perceptual results similar to those of previous approaches and performs well when dealing with naturally degraded signals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge