Fatima J. Rolland
NODE-SELECT: A Graph Neural Network Based On A Selective Propagation Technique
Feb 17, 2021
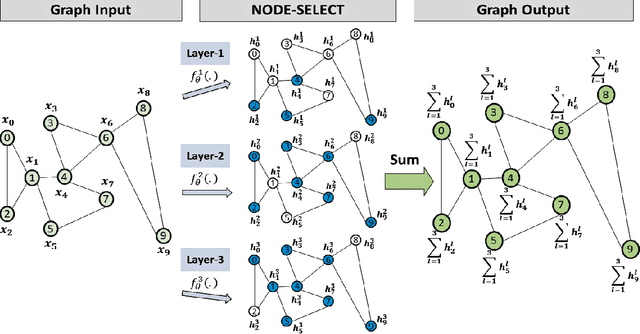
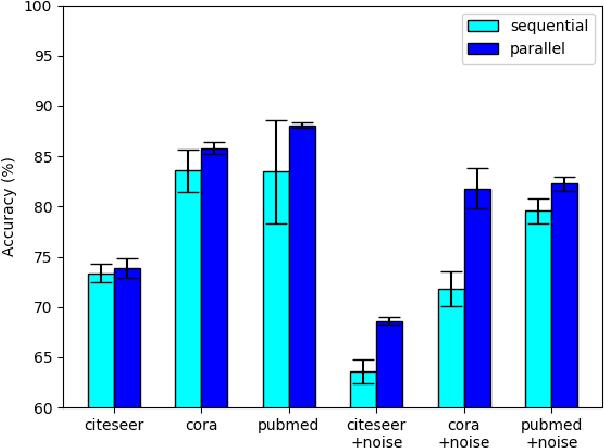
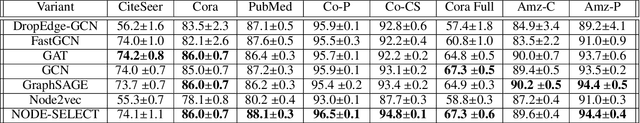
Abstract:While there exists a wide variety of graph neural networks (GNN) for node classification, only a minority of them adopt mechanisms that effectively target noise propagation during the message-passing procedure. Additionally, a very important challenge that significantly affects graph neural networks is the issue of scalability which limits their application to larger graphs. In this paper we propose our method named NODE-SELECT: an efficient graph neural network that uses subsetting layers which only allow the best sharing-fitting nodes to propagate their information. By having a selection mechanism within each layer which we stack in parallel, our proposed method NODE-SELECT is able to both reduce the amount noise propagated and adapt the restrictive sharing concept observed in real world graphs. Our NODE-SELECT significantly outperformed existing GNN frameworks in noise experiments and matched state-of-the art results in experiments without noise over different benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge