Fabio Baruffa
A hybrid classical-quantum workflow for natural language processing
Apr 12, 2020
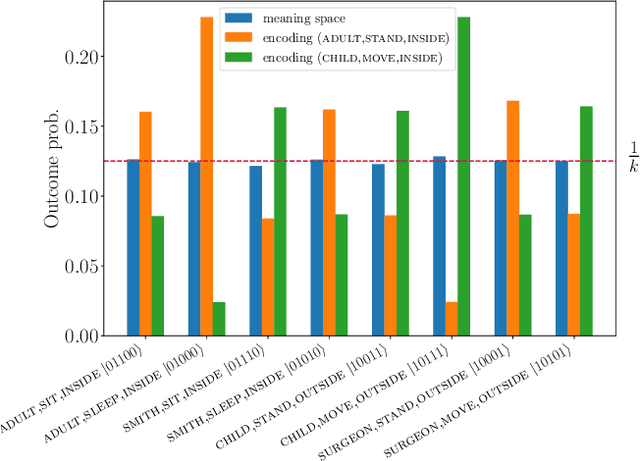
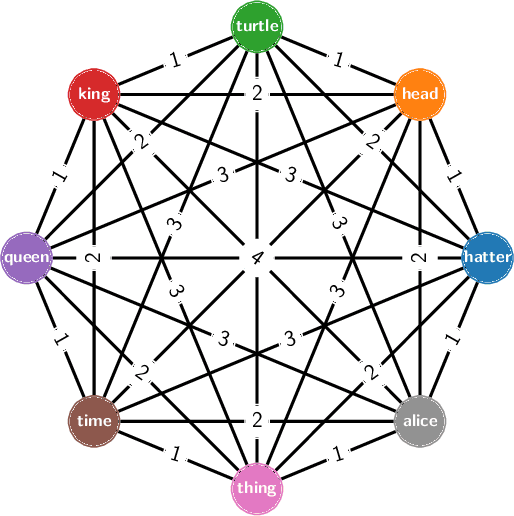
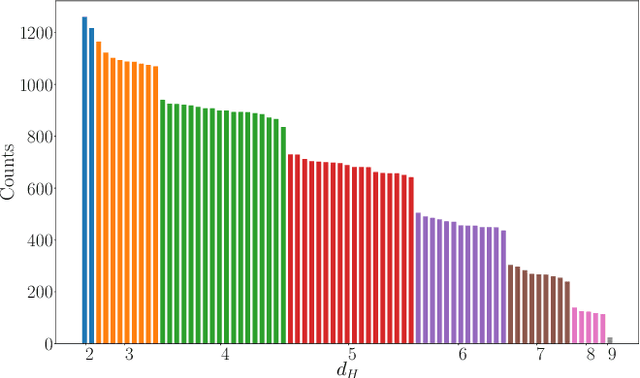
Abstract:Natural language processing (NLP) problems are ubiquitous in classical computing, where they often require significant computational resources to infer sentence meanings. With the appearance of quantum computing hardware and simulators, it is worth developing methods to examine such problems on these platforms. In this manuscript we demonstrate the use of quantum computing models to perform NLP tasks, where we represent corpus meanings, and perform comparisons between sentences of a given structure. We develop a hybrid workflow for representing small and large scale corpus data sets to be encoded, processed, and decoded using a quantum circuit model. In addition, we provide our results showing the efficacy of the method, and release our developed toolkit as an open software suite.
Deploying AI Frameworks on Secure HPC Systems with Containers
May 24, 2019

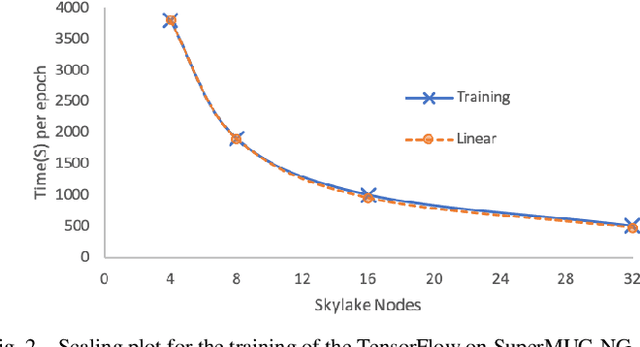
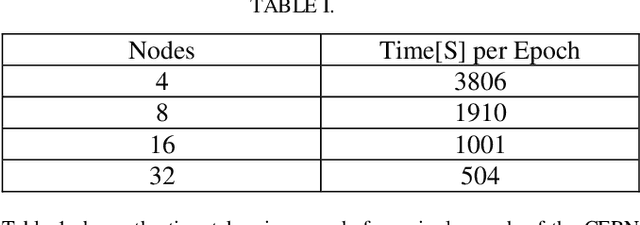
Abstract:The increasing interest in the usage of Artificial Intelligence techniques (AI) from the research community and industry to tackle "real world" problems, requires High Performance Computing (HPC) resources to efficiently compute and scale complex algorithms across thousands of nodes. Unfortunately, typical data scientists are not familiar with the unique requirements and characteristics of HPC environments. They usually develop their applications with high-level scripting languages or frameworks such as TensorFlow and the installation process often requires connection to external systems to download open source software during the build. HPC environments, on the other hand, are often based on closed source applications that incorporate parallel and distributed computing API's such as MPI and OpenMP, while users have restricted administrator privileges, and face security restrictions such as not allowing access to external systems. In this paper we discuss the issues associated with the deployment of AI frameworks in a secure HPC environment and how we successfully deploy AI frameworks on SuperMUC-NG with Charliecloud.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge